Integrate OpenLineage and Airflow
Data lineage is the concept of tracking and visualizing data from its origin to wherever it flows and is consumed downstream. Lineage is growing in importance as companies must rely on increasingly complex data ecosystems to make business-critical decisions. Data lineage can help with everything from understanding your data sources, to troubleshooting job failures, to managing PII, to ensuring compliance with data regulations.
As a one-stop-shop orchestrator for an organization’s data pipelines, Apache Airflow is an ideal platform for integrating data lineage to understand the movement of and interactions within your data.
In this guide, you’ll learn about core data lineage concepts and understand how lineage works with Airflow.
Astro Observe offers robust support for extracting and visualizing data lineage. To learn more, see Astro Observe overview.
Other ways to learn
There are multiple resources for learning about this topic. See also:
Assumed knowledge
To get the most out of this guide, make sure you have an understanding of:
- Airflow fundamentals, such as writing DAGs and defining tasks. See Get started with Apache Airflow.
- Airflow operators. See Operators 101.
What is data lineage?
Data lineage represents the complex set of relationships that exist among datasets within an ecosystem. Typically, a lineage solution has three basic elements:
- Lineage metadata, which describes your datasets (tables in Snowflake or S3 buckets, for example) and jobs (tasks in your DAG, for example).
- A lineage backend, which stores and processes lineage metadata.
- A lineage frontend, which allows you to view and interact with your lineage metadata – e.g., a visual graph of jobs, datasets and columns that shows how they are connected.
If you want to read more about the concept of data lineage and its value, see: What is data lineage and why does it matter?.
Visually, your data lineage graph might look like this lineage graph in Astro Observe:
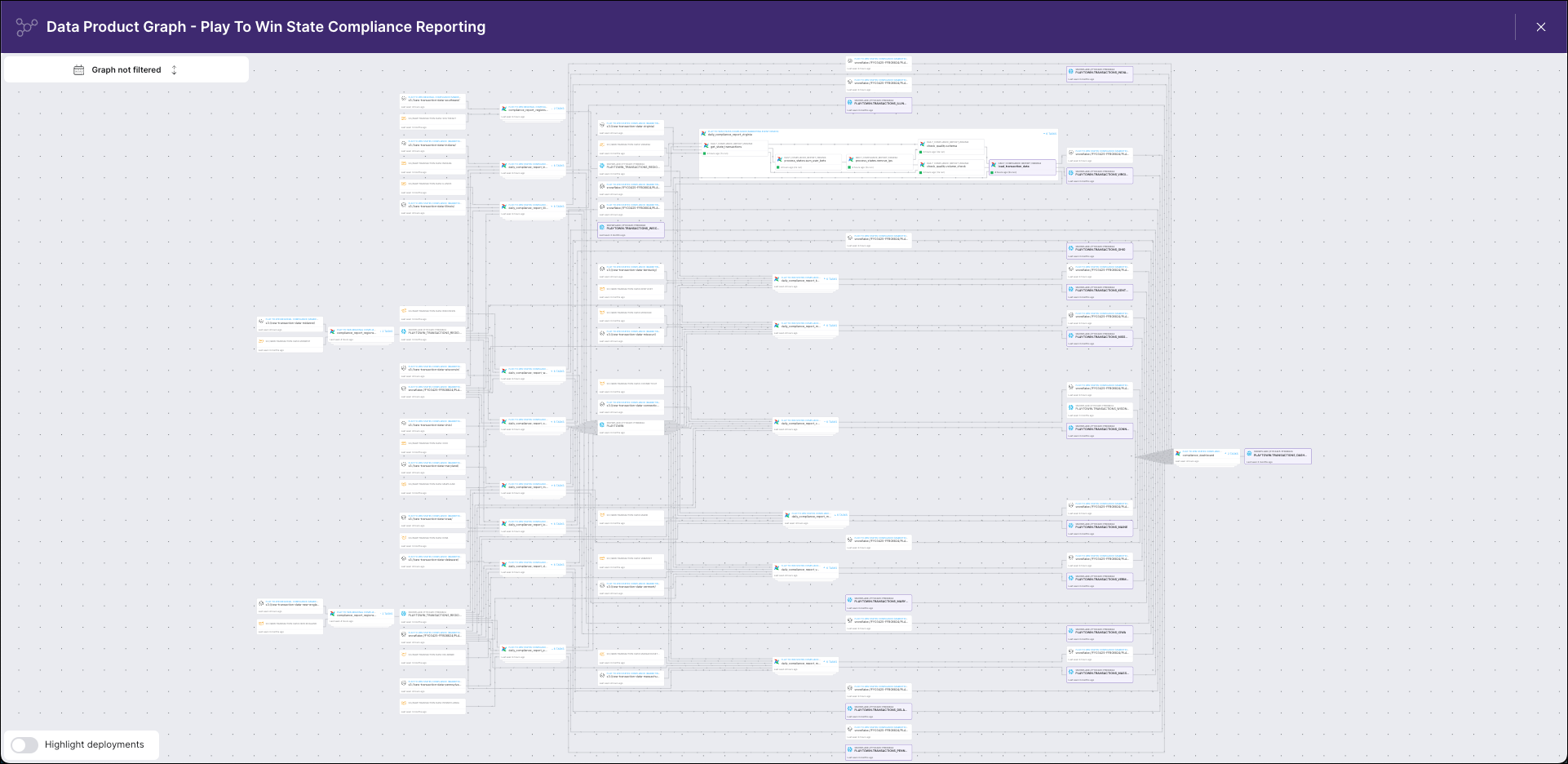
If you are using data lineage, your solution most likely has a lineage backend that collects and stores lineage metadata and a frontend that visualizes the metadata. There are proprietary tools, including Astro Observe, that provide these services, and there are open-source options that can be integrated with Airflow: namely OpenLineage, a lineage specification and collection API for getting lineage from tools in your pipelines, and Marquez, a tool for storing and visualizing lineage that includes a metadata repository, query API, and graphical UI.
OpenLineage
OpenLineage is the open-source industry standard framework for data lineage. It standardizes the definition of data lineage, the metadata that makes up lineage metadata, and the approach to collecting lineage metadata from external systems. In other words, it defines a formalized specification for all the core concepts related to data lineage.
The purpose of an open standard for lineage is to create a more cohesive governance and monitoring experience across the industry and reduce duplicated work for stakeholders. It allows for a simpler, more consistent experience when integrating lineage from many different tools, similarly to how Airflow providers reduce the work of dag authoring by providing standardized modules for integrating Airflow with other tools.
In Airflow, OpenLineage implementations use two main components, each serving a distinct function:
-
OpenLineage Airflow Provider (
apache-airflow-providers-openlineage) This library functions as an adapter, integrating OpenLineage with Airflow. It hooks into Airflow’s internal mechanisms to capture metadata about dag and task execution. As a plugin, it is version-coupled with Airflow. -
OpenLineage Client (
openlineage-python) This is the core library responsible for building and sending OpenLineage events to backends such as Astro Observe. The client is updated and configured independently of Airflow, allowing users on all Airflow versions to upgrade this package at any time and take advantage of the latest improvements, fixes, or features.
Getting started on Astro
Astro Observe offers the easiest path to reliable lineage from Airflow using OpenLineage. You can use Astro Observe whether you use open-source Airflow, Astro, or another managed service for Airflow.
Core lineage concepts
The following terms are used frequently when discussing data lineage in general and OpenLineage in particular:
- Integration: a means of gathering lineage metadata from a source system such as a scheduler or data platform. For example, the OpenLineage Airflow Provider allows lineage metadata to be collected from Airflow DAGs. Airflow operators automatically gather lineage metadata from the source system every time a DAG runs, preparing and transmitting OpenLineage events to a lineage backend.
- Job: a process that consumes or produces datasets. Jobs can be viewed on your lineage graph. In Airflow, an OpenLineage job corresponds to a task in your DAG or the DAG itself. Note that only supported operators will have input/output metadata; other tasks in your DAG may show up as orphans on the lineage graph if those dataset metadata is missing. On Astro, jobs appear as nodes on your lineage graphs in the lineage UI.
- Dataset: a representation of a set of data in your lineage metadata and graph. For example, it might correspond to a table in your database or a set of data on which you run a Great Expectations check. Typically, a dataset is registered as part of your lineage metadata when a job writing to the dataset is completed (e.g., data is inserted into a table).
- Run: an instance of a job in which lineage metadata is generated. An OpenLineage run is generated with each DAG and task run, for example.
- Facet: a piece of lineage metadata about a job, dataset, or run (e.g., you might hear “job facet” in reference to a piece of metadata attached to a job).
Why OpenLineage with Airflow?
Using OpenLineage with Airflow allows you to have more insight into the operation and structure of complex data ecosystems and supports better data governance. Airflow is a natural place to integrate data lineage because it is often used as a one-stop-shop orchestrator that touches data across many parts of an organization.
OpenLineage with Airflow provides the following capabilities:
- Quickly find the root cause of task failures by identifying issues in upstream datasets (e.g., if an upstream job outside Airflow failed to populate a key dataset).
- Easily see the blast radius of any job failures or changes to data by visualizing the relationship between jobs and datasets, including column-level lineage for some operators.
- Identify where sensitive data is used in jobs across an organization.
These capabilities translate into real-world benefits by:
- Making recovery from complex failures faster. The faster you can identify the problem and the blast radius, the easier it is to find a solution and prevent erroneous decisions based on bad data.
- Making it easier for teams to work together across an organization. Visualizing the full scope of where an asset is used reduces “sleuthing” time.
- Helping ensure compliance with data regulations by fully understanding where data is used in an organization.
Lineage on Astro
For Airflow users leveraging Astro Observe, data lineage is built-in. Viewing the graph in Astro Observe helps you troubleshoot issues with your data pipelines and understand the movement of data within a Data Product. For help getting started with Astro Observe, see: Astro Observe overview.
Lineage with open-source tools
If you want to build your own lineage stack using open-source tools, Astronomer recommends the official OpenLineage Airflow Provider for producing lineage. The provider supports many operators, and more are added regularly. You can find a list of currently supported operators in the Provider documentation. You won’t have to modify your DAGs to start emitting lineage information, but some basic configuration is necessary, including installing a package and setting up a transport. For more details about configuring the Provider, see: Using OpenLineage integration.
Starting with Apache Airflow version 2.10, the OpenLineage Airflow Provider automatically collects lineage from supported hooks. Hook-based lineage enables lineage collection from custom operators, PythonOperator, and DAGs using the TaskFlow API.
To consume and visualize data lineage from Airflow using open-source tools, Astronomer recommends running OpenLineage with Marquez as your lineage metadata repository, query API (backend), and UI (frontend). See the Integrate OpenLineage and Airflow locally with Marquez tutorial to get started. For a configuration-free option for demo purposes, you can explore Marquez on GitPod.