Orchestrate semantic querying in Qdrant with Airflow
Info
This page has not yet been updated for Airflow 3. The concepts shown are relevant, but some code may need to be updated. If you run any examples, take care to update import statements and watch for any other breaking changes.
Qdrant is an open-source vector database and similarity search engine designed for AI applications.
In this tutorial, you’ll use the Qdrant Airflow provider to write a DAG that generates embeddings in parallel and performs semantic retrieval based on user input.
Airflow provides useful operational and orchestration when running operations in Qdrant based on data events or building parallel tasks for generating vector embeddings. By using Airflow, you can set up monitoring and alerts for your pipelines for full observability.
Time to complete
This tutorial takes approximately 30 minutes to complete.
Prerequisites
- A running Qdrant instance. A free instance is available.
- The Astro CLI. See Install the Astro CLI.
- A HuggingFace token to generate embeddings.
Step 1: Set up the project
-
Create a new Astro project:
-
To use Qdrant in Airflow, install the Qdrant Airflow provider by adding the following to your
requirements.txtfile:
Step 2: Configure credentials
Add the following code to your .env file to create Airflow connections between Airflow and HuggingFace and Qdrant. Make sure to update the sample code with your HuggingFace access token and Qdrant instance details.
Step 3: Add your data
Paste the following sample data into a file called books.txt in your include directory.
Step 4: Create your DAG
-
In your
dagsfolder, create a file calledbooks_recommend.py. -
Copy the code from the recommend_books_dag.py file into your
books_recommend.pyfile.
This QDrant Demo DAG consists of six tasks that generate embeddings in parallel for the data corpus and perform semantic retrieval based on user input.
-
import_books: This task reads a text file containing information about the books (such as title, genre, and description) and then returns the data as a list of dictionaries. -
init_collection: This task initializes a collection in the Qdrant database, where you store the vector representations of the book descriptions. Therecreate_collection()function deletes a collection first if it already exists. Trying to create a collection that already exists throws an error. -
embed_description: This is a dynamic task that creates one mapped task instance for each book in the list. The task uses theembedfunction to generate vector embeddings for each description. To use a different embedding model, you can adjust theEMBEDDING_MODEL_IDandEMBEDDING_DIMENSIONvalues. -
embed_user_preference: This task takes a user’s input and converts it into a vector using the same pre-trained model used for the book descriptions. -
qdrant_vector_ingest: This task ingests the book data into the Qdrant collection using theQdrantIngestOperator, associating each book description with its corresponding vector embeddings. -
search_qdrant: Finally, this task performs a search in the Qdrant database using the vectorized user preference. It finds the most relevant book in the collection based on vector similarity.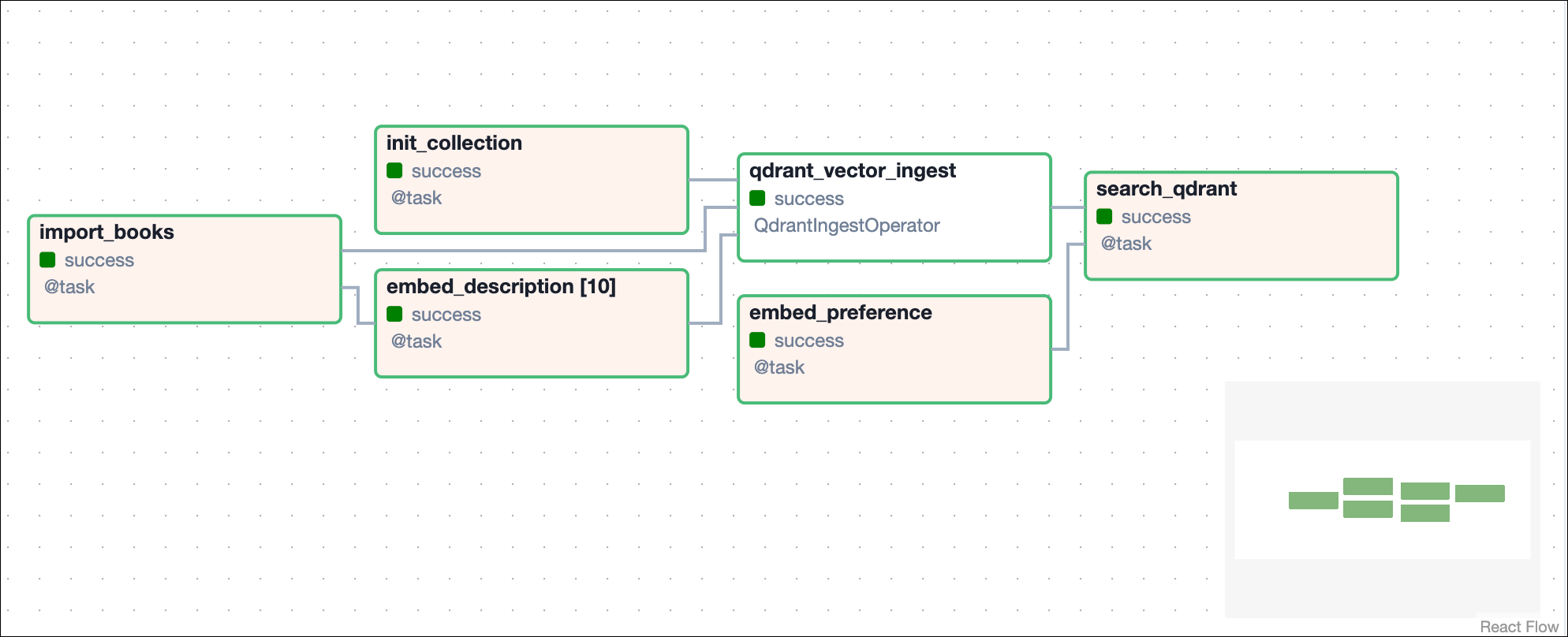
Step 5: Run your DAG
-
Run
astro dev startin your Astro project to start Airflow and open the Airflow UI atlocalhost:8080. -
In the Airflow UI, run the
books_recommendDAG by clicking the play button. You’ll be asked for input about your book preference.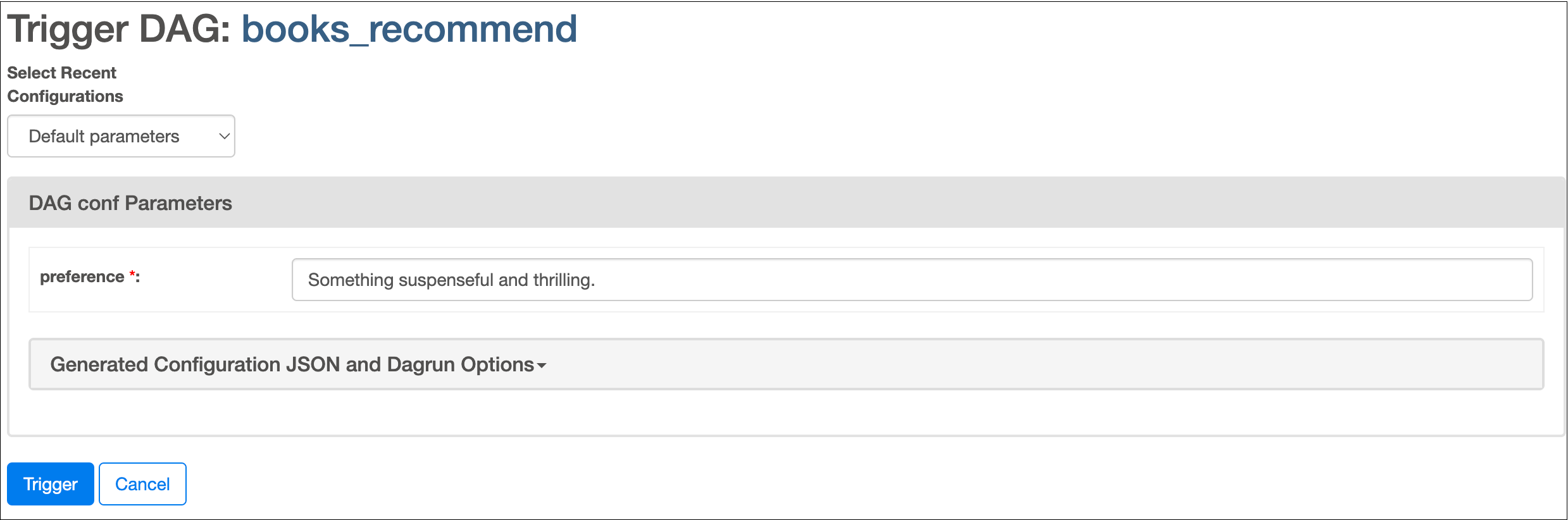
-
View the output of your search in the logs of the
search_qdranttask.