Manage your ML models with Weights and Biases and Airflow
Info
This page has not yet been updated for Airflow 3. The concepts shown are relevant, but some code may need to be updated. If you run any examples, take care to update import statements and watch for any other breaking changes.
Weights and Biases (W&B) is a machine learning platform for model management that includes features like experiment tracking, dataset versioning, and model performance evaluation and visualization. Using W&B with Airflow gives you a powerful ML orchestration stack with first-class features for building, training, and managing your models.
In this tutorial, you’ll learn how to create an Airflow DAG that completes feature engineering, model training, and predictions with the Astro Python SDK and scikit-learn, and registers the model with W&B for evaluation and visualization.
Info
This tutorial was developed in partnership with Weights and Biases. For resources on implementing other use cases with W&B, see Tutorials.
Time to complete
This tutorial takes approximately one hour to complete.
Assumed knowledge
To get the most out of this tutorial, you should be familiar with:
- Airflow operators. See Operators 101.
- Weights and Biases. See What is Weights and Biases?.
Prerequisites
- The Astro CLI.
- A Weights and Biases account. Personal accounts are available for free.
Quickstart
If you have a Github account, you can get started quickly by cloning the demo repository. For more detailed instructions for setting up the project, start with Step 1.
-
Clone the demo repository:
-
Update the .env file with your WANDB_API_KEY.
-
Start Airflow by running:
-
Continue with Step 7 below.
Step 1: Configure your Astro project
Use the Astro CLI to create and run an Airflow project locally.
-
Create a new Astro project:
-
Add the following line to the
requirements.txtfile of your Astro project:This installs the packages needed to transform the data and run feature engineering, model training, and predictions.
Step 2: Prepare the data
This tutorial will create a model that classifies churn risk based on customer data.
- Create a subfolder called
datain your Astro projectincludefolder. - Download the demo CSV files from this GitHub directory.
- Save the downloaded CSV files in the
include/datafolder. You should have 5 files in total.
Step 3: Create your SQL transformation scripts
Before feature engineering and training, the data needs to be transformed. This tutorial uses the Astro Python SDK transform_file function to complete several transformations using SQL.
-
Create a file in your
includefolder calledcustomer_churn_month.sqland copy the following code into the file. -
Create another file in your
includefolder calledcustomers.sqland copy the following code into the file.
Step 4: Create a W&B API Key
In your W&B account, create an API key that you will use to connect Airflow to W&B. You can create a key by going to the Authorize page or your user settings.
Step 5: Set up your connections and environment variables
You’ll use environment variables to create Airflow connections to Snowflake and W&B, as well as to configure the Astro Python SDK.
-
Open the
.envfile in your Astro project and paste the following code. -
Replace
<your-wandb-api-key>with the API key you created in Step 4. No changes are needed for the AIRFLOW_CONN_POSTGRES_DEFAULT environment variable.
Step 6: Create your DAG
-
Create a file in your Astro project
dagsfolder calledcustomer_analytics.pyand copy the following code into the file:This DAG completes the following steps:
- The
extract_and_loadtask group contains one task for each CSV in yourinclude/datafolder that uses the Astro Python SDKload_filefunction to load the data to Postgres. - The
transformtask group contains two tasks that transform the data using the Astro Python SDKtransform_filefunction and the SQL scripts in yourincludefolder. - The
featurestask is a Python function implemented with the Astro Python SDK@dataframedecorator that uses Pandas to create the features needed for the model. - The
traintask is a Python function implemented with the Astro Python SDK@dataframedecorator that uses scikit-learn to train a Random Forest classifier model and push the results to W&B. - The
predicttask pulls the model from W&B in order to make predictions and stores them in postgres.
- The
-
Run the following command to start your project in a local environment:
Step 7: Run your DAG and view results
-
Open the (Airflow UI)[http://localhost:8080], unpause the
customer_analyticsDAG, and trigger the DAG. -
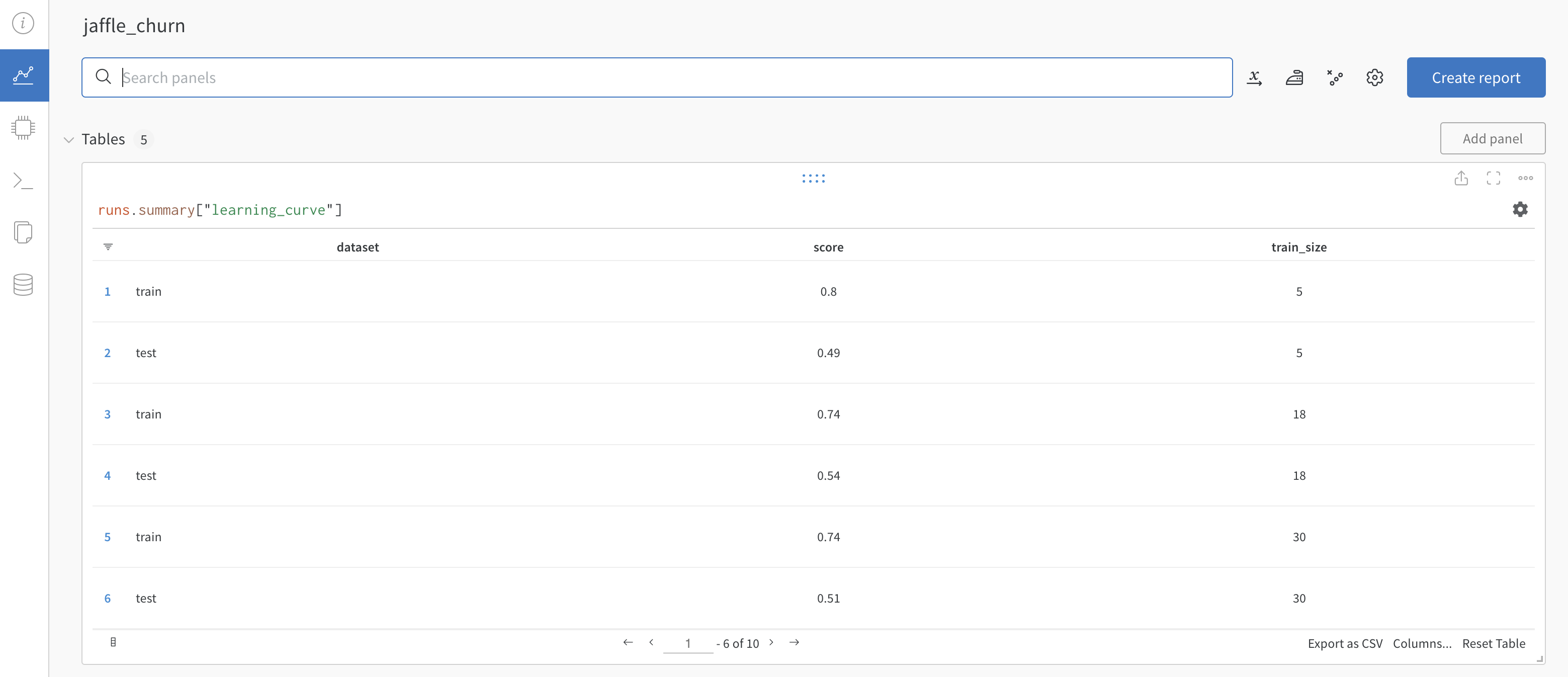
The logs in the
trainandpredicttasks will contain a link to your W&B project which shows plotted results from the training and prediction.
Go to one of the links to view the results in W&B.