Orchestrate OpenAI operations with Apache Airflow
OpenAI is an AI research and deployment company that provides an API for accessing state of the art models like GPT-4 and DALL·E 3. The OpenAI Airflow provider offers modules to easily integrate OpenAI with Airflow.
In this tutorial you’ll use Airflow and the OpenAI Airflow provider to ask a question to Star Trek captains, create embeddings of the answers from each captain, and plot them in two dimensions.
Why use Airflow with OpenAI?
OpenAI offers a variety of powerful model endpoints for different tasks like text generation, vector embedding, and translation tasks. These models are used in both user-facing applications, such as chatbots, and internal applications, such as a smart search for internal knowledge base content.
Integrating OpenAI with Airflow into an end-to-end machine learning pipeline allows you to:
- Use Airflow’s data-driven scheduling to run operations using OpenAI model endpoints based on upstream events in your data ecosystem, such as when new user input is ingested or a new dataset is available.
- Send several requests to a model endpoint in parallel based on upstream events in your data ecosystem or user input via Airflow params.
- Monitor the OpenAI service using Airflow alerts and protect against API rate limits and outages with Airflow retries.
- Use Airflow to orchestrate the creation of vector embeddings using OpenAI models, which is especially useful for large datasets that can’t be processed automatically by vector databases.
Time to complete
This tutorial takes approximately 15 minutes to complete.
Assumed knowledge
To get the most out of this tutorial, make sure you have an understanding of:
- The basics of the OpenAI API. See OpenAI Introduction.
- The basics of vector embeddings. See the OpenAI Embeddings guide.
- Airflow fundamentals, such as writing DAGs and defining tasks. See Get started with Apache Airflow.
- Airflow operators. See Operators 101.
- Airflow hooks. See Hooks 101.
Prerequisites
- The Astro CLI.
- An OpenAI API key with at least tier 1 usage limits.
Step 1: Configure your Astro project
-
Create a new Astro project:
-
Add the following lines to your
requirements.txtfile to install the OpenAI Airflow provider and other supporting packages: -
To create an Airflow connection to OpenAI, add the following environment variables to your
.envfile. Make sure to replace<your-openai-api-key>with your own OpenAI API key.
Step 2: Create your DAG
-
In your
dagsfolder, create a file calledcaptains_dag.py. -
Copy the following code into the file.
This DAG consists of four tasks to make a simple MLOps pipeline.
- The
get_captains_listtask fetches the list of Star Trek captains you want to ask your question to. You’ll provide the list of captains when you run the DAG with Airflow params. - The
ask_a_captaintask uses the OpenAIHook to connect to the OpenAI API. It then uses the chat completion endpoint to generate answers to the question you provide. This task is dynamically mapped over the list of captains to generate one dynamically mapped task instance per captain. - The
get_embeddingstask is defined using the OpenAIEmbeddingOperator to generate vector embeddings of the answers generated by the upstreamask_a_captaintask. This task is dynamically mapped over the list of answers to retrieve one set of embeddings per answer. This pattern allows for efficient parallelization of the vector embedding generation. - The
plot_embeddingstask takes the embeddings created by the upstream task and performs dimensionality reduction using PCA to plot the embeddings in two dimensions.
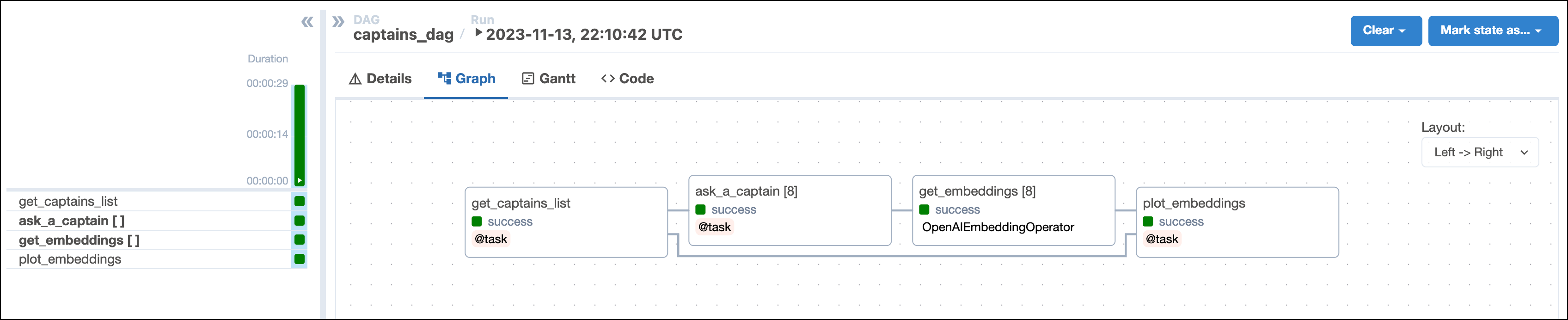
- The
Step 3: Run your DAG
-
Run
astro dev startin your Astro project to start Airflow, then open the Airflow UI atlocalhost:8080. -
In the Airflow UI, run the
captains_dagDAG by clicking the play button. Then, provide Airflow params for:Question to ask the captain: The question you want to ask the captains.captains_to_ask: A list of Star Trek captains you want to ask the question to. Make sure to create one line per captain and to provide at least two names.max_tokens_answer: The maximum number of tokens available for the answer.randomness_of_answer: The randomness of the answer. The value provided is divided by 10 and given to thetemperatureparameter of the chat completion endpoint. The scale for the param ranges from 0 to 20, with 0 being the most deterministic and 20 being the most random.
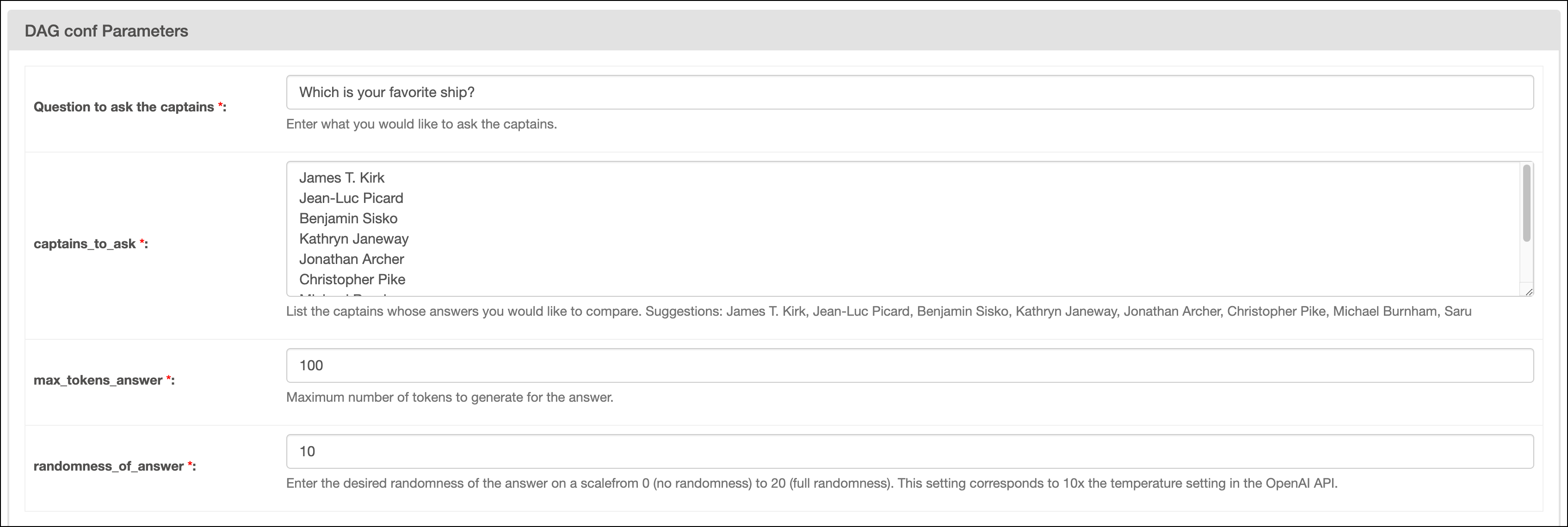
-
After the DAG run completed, go to the
includefolder to view the image file created by theplot_embeddingstask. The image should look similar to the one below.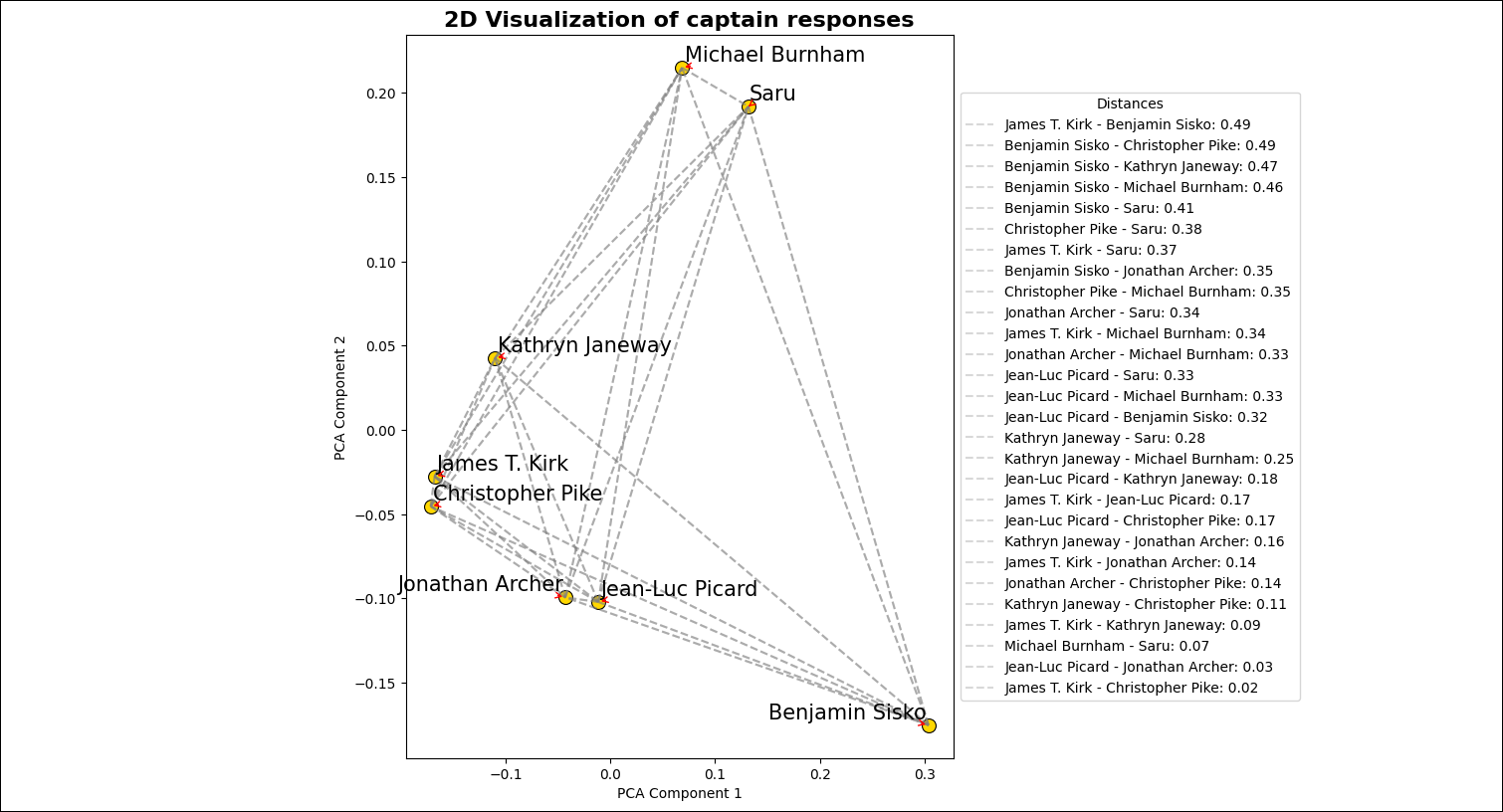
Conclusion
Congratulations! You used Airflow and OpenAI to get answers from your favorite Star Trek captains and compare them visually. You can now use Airflow to orchestrate OpenAI operations in your own machine learning pipelines. 🖖