Big Data Architecture: Core Components, Use Cases, and Limitations

Lately, there has been a lot of buzz on how businesses are carrying out their strategies based on striking big data analytics findings. They make it seem easy - just look into the data and leverage it! However, not so many people discuss the need to develop a powerful strategy for data analysis - the Big Data Architecture.
The vast majority of articles on Big Data Architecture begin with “big data is everywhere around us.” That’s a fact; however, what truly matters is how this big data is managed. It can be ubiquitous yet still essentially worthless if there is no proper architecture to handle the dataflow.
The architecture used to be a technical decision, but times have changed since then. Today, data architecture is increasingly bridging the gap between technical prowess and business strategy. Moreover, a specific type of data architecture can successfully improve agility, allowing companies to adapt swiftly and fulfill their business objectives. Simply put, when a company has a data-driven business strategy, data architecture is at its foundation. Let’s get to know it better.
What Is Big Data Architecture?
According to the English dictionary, architecture is the art or science of building, as well as a unifying, coherent structure. And big data is, quite intuitively, a concept of datasets so large that they cannot be handled by traditional processing technologies. Together, they create the Big Data Architecture - the physical and logical structure dictating how high volumes of data are ingested, processed, stored, and, ultimately, accessed.
Big Data Architecture is the silent “how” of implementing a big data strategy.
In other words, Data Architecture is a collection of policies that offers a solid basis for the business model. Many processes have guidelines in Data Architecture, such as data collection, consumption, processing, storage, and integration with other systems. Big data architectural framework can act as a design for infrastructures and solutions, logically outlining how big data solutions will operate, the components that will be used, how the information will flow, and security aspects. Nowadays, any organization’s strategy is dependent on the efficient utilization of data.
Big Data Processing
Big data solutions generally incorporate one or more of the workloads listed below:
- Batch Processing of big data sources at rest
Because the data is so large, the architecture requires using a batch processing system to filter, aggregate, and analyze data for analytics. These are batch tasks that run for a long time.
- Real-time processing of big data in motion
Real-time data processing is the trendiest trend in the big data industry. It describes feeding real-time data into data storage for processing. To achieve this, the architecture must incorporate a robust and reliable system for capturing and storing real-time data.
- Big data exploration
- Machine learning and predictive analytics
Big Data Architecture Components
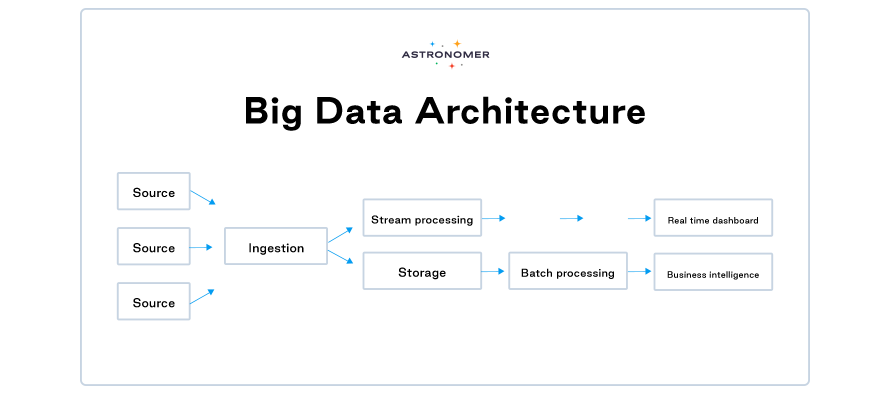
- Sources Layer
Sources are places from which the data is ingested, and a big data environment can usually manage batch processing and real-time processing from sources such as SaaS applications, IoT devices, machines, database management systems, third-party providers, or, simply, data warehouses, and so on. In a way, the sources are in charge of the Big Data Architecture. The design of the architecture is heavily reliant on the sources, as they quickly accumulate massive amounts of data. The Big Data Architecture is built in order to handle this inflow efficiently. 2. Data Ingestion Layer
This is the initial layer in the journey of big data entering from many sources. This layer is in charge of classifying data to make it flow smoothly into the other levels of the architecture. The major objective of this layer is to provide trouble-free data transit into the subsequent levels of data architecture. 3. Storage Layer
The receiving end of the big data journey. Saves the data in the most appropriate way, often modifying the format of the data based on the system’s needs. For example, batch processing data is typically kept in distributed file storage systems such as HDFS, which are capable of storing large amounts of data in a variety of formats. Structured data, on the other hand, can only be saved using RDBMS. It all depends on the data format and the reason for which we want it. 4. Analysis & BI Layer
As we mentioned before, the main goal of implementing Big Data Architecture is to get insights from it and make data-driven decisions. The analysis layer is the essential layer in the Big Data Architecture for enabling users to evaluate big data. To acquire important insights, this analysis layer interacts with the storage layer. Structured data is simple to manage, but unstructured data requires the use of specialized technologies to analyze. The final analysis output is received by the BI tools, which allow for creating a report or a dashboard based on the insights. 5. Bonus Layer – Orchestration
Most big data solutions are made up of repetitive data processing activities wrapped in workflows that convert source data, transfer data across various sources, load processed data into an analytical data store, or send the findings directly to a report or dashboard. Automating these operations is a must. There is no better tool for data orchestration than Apache Airflow®.
Big Data Architecture Use Cases (and Who Exactly Is It For?)
Who is Big Data Architecture for? Who can benefit most from implementing it? The answer is quite obvious - it’s companies who collect big amounts of data, including companies who suffer from siloed data. However, what can be counterintuitive, is that these aren’t necessarily only big companies and enterprises. We could imagine a small internet-based company having a lot of data as well as a traditional big business generating data because they have so much activity going on. It’s not based on the size of the company at all, moreover, an interesting artifact is that it was really rather small companies that started the big data revolution. So everyone who has a reason to collect data potentially is a big data company! It’s only a matter of time when they realize it.
For some organizations, facing hundreds of gigabytes of data for the first time may trigger a need to reconsider data management options. For others, it may take tens or hundreds of terabytes before data size becomes a significant consideration.
Roger Magoulas, Senior Director Data Strategy at Astronomer
It also cannot be distinguished by industries, as virtually every industry can benefit from big data solutions. There are hundreds of ways that big data can give businesses a competitive advantage.
In manufacturing, Big Data Architecture helps with predictive maintenance, operational efficiency, and production optimization. Spotting manufacturing issues before they actually occur is an incredibly valuable benefit for manufacturing companies.
When it comes to retail - it can be the key to better product development, customer experiences, pricing analytics. Take a look at how data orchestration can drive sales processes in e-commerce.
In FinTech or banking, big data’s popularity is growing exponentially, helping with anti-money laundering processes, financial regulations, compliance analytics, and fraud avoidance. We did a similar thing for Societe Generale recently. If you’d like to find out more on Airflow benefits in banking, make sure to read our interview. Healthcare, telecommunications, automotive, and other industries can benefit from proper data architecture just as well.
Challenges and Limitations
The biggest challenges include having the rigor and discipline to explore the data and understand its limitations, including what’s missing. Yes, it may seem counterintuitive, but there’s a tendency when people are working with a dataset, they think that it explains their entire universe - and it often doesn’t. And if they don’t acknowledge what’s missing, then they are going to think the answer is more complete than it actually is. Of course - the more data sources, the more accurate the insights will be, especially when it comes to machine learning. But all the data in the world won’t give you better decisions without proper critical thinking and awareness that correlation does not equal causation.
I think that there’s a way that people think of big data as an answer to their problems. And it’s never the whole story. Big data is one LEGO piece in a bigger puzzle for insights. It can provide you with more accurate or more useful information, but you still need to think about it qualitatively. In a lot of ways, what people should be doing with big data is figuring out what questions their data doesn’t answer, rather than what it does.
Roger Magoulas, Senior Director Data Strategy at Astronomer
The second challenge is time. Building a strong Big Data Architecture is time-consuming, or it requires spending a lot of money to make it fast enough. Luckily, there are some great scaling solutions that can help the entire process go smoother, and data orchestration platforms like Astronomer can automate the ETL process.
Summary
Companies can access more data than ever before. However, these new possibilities are useless unless they know how to put their data to real work. And implementing big data analytics in any organization is not as simple as it may appear. To get the most out of big data and analytics, a solid Big Data Architecture is required, as the pillar around which analytics can be built. However, it’s vital to treat big data as only one piece of the puzzle, not the entire answer to business problems. It is the foundation of business strategy, delivering agility and insights, but data needs to be treated with scientific care and respect.
Having all this in mind, data architecture can assist your company in charting its course over the next few years. This aspect of business also allows you to select the best technology for the highest chance of success. Most likely, you could benefit from a partner that will help you manage your big data flows and enhance the efficiency and accuracy of your architecture. And there is no better partner than Astronomer.
How Astronomer Can Help With Big Data Architecture
Data orchestration isn’t always mentioned as an architectural layer, but it is indubitably a vital piece of the whole big data puzzle. Companies realize that they need their processes to be repeatable, and to run almost all the time - and it can only be achieved through proper automation and formalization. Apache Airflow® is a tool that can orchestrate your data pipelinesthrough a variety of systems, tools, and coding languages. Airflow has the edge over other platforms, as it is scalable, code-based, and has a fantastic open-source community to help with any issues. And Astronomer makes Airflow even better due to rapid customer service and lots of available operators, guides, and valuable content. That’s why numerous companies have trusted us with their Big Data, and we’d be delighted to help you gain more agility, too.
Feel free to get in touch with Astronomer’s experts and learn more about our tool.
