Why Airflow?

Apache Airflow® continues to win vs. other workflow orchestration tools due to two main factors:
- An active and expanding community
- Deep, proven functionality
Community
As a result, thousands of companies — including Fortune 500s, tech giants, and early-stage startups — are adopting Airflow as their preferred tool to programmatically author, schedule, and monitor workflows.
The Airflow community is strong, healthy, and vibrant, with over 1700 code contributors — and growing at a healthy pace.

The velocity of Github stars for Airflow continues to accelerate - currently exceeding 23k.
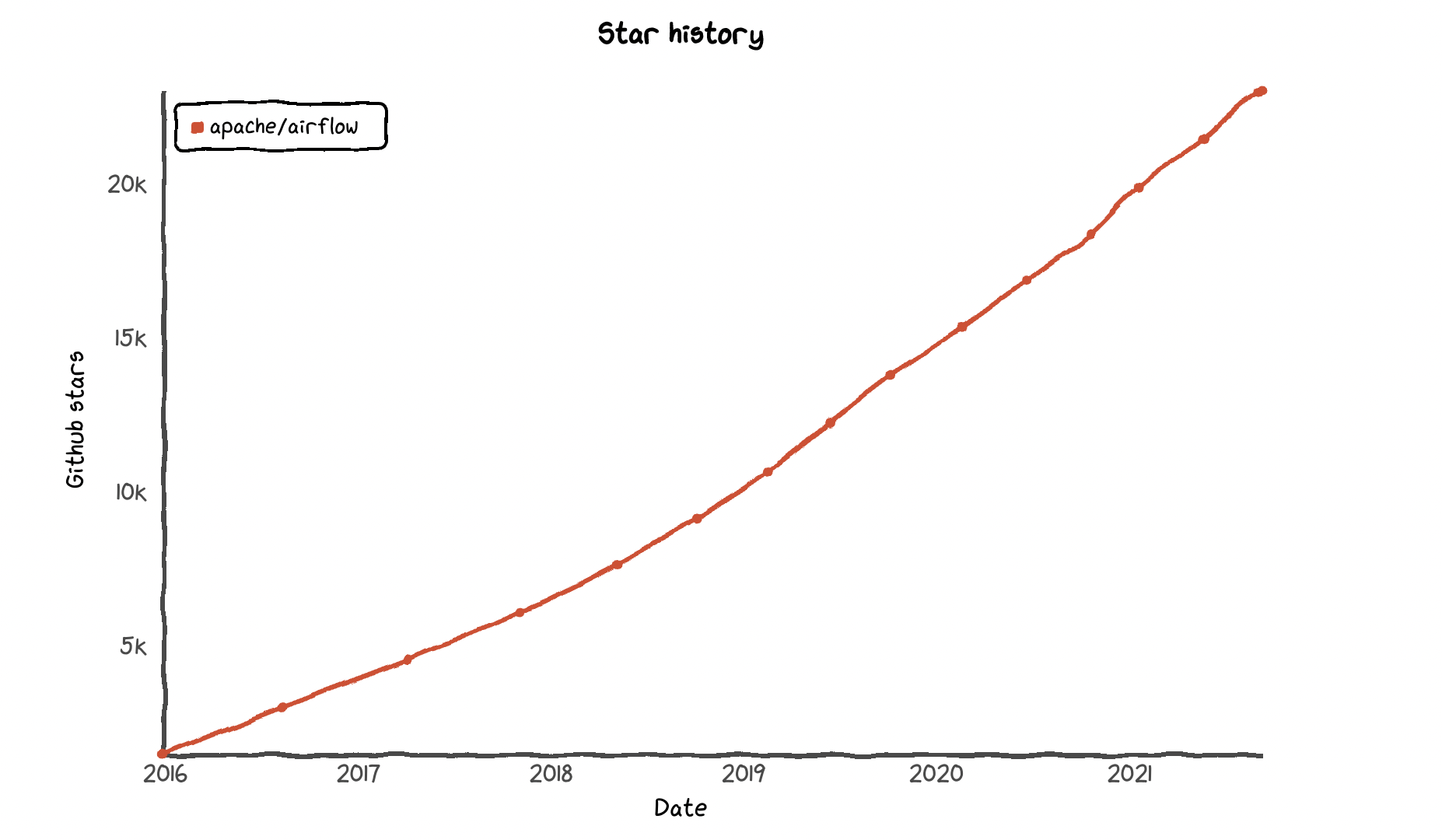
As the project accelerated towards the major 2.0 release, it entered a second "golden age" eclipsing the rate of commits from the early days when the first generation of project developers Maxime Beauchemin, Bolke de Bruin, Jeremiah Lowin, Chris Riccomini, Sid Anand, and Arthur Wiedmer were originally working on it.
The Airflow project was already gaining momentum in 2018 thanks to open-source activities in companies like Airbnb, Lyft, Twitter, Glassdoor, and many, many others.
In 2019, an elevated level of activity has been driven by companies like Astronomer, Google, Polidea, and GoDataDriven, who dedicated significant resources to the project, including an expanded group of people working on the project full-time.
In 2020, project activity was taken to a new level as the team pushed to 2.0.
Functionality
Airflow has accumulated an impressive amount of functionality that solves many data engineering challenges both on-prem and on any cloud provider. Being built on the backs of numerous data engineers working to solve countless edge cases, it’s a complete solution.
Along with Airflow. 2.0 came the following improvements:
A New Scheduler
With the new Scheduler, you can expect faster performance with near-zero task latency. By launching Scheduler replicas you increase task throughput and ensure high availability.
Full REST API
Full REST API allows you to build programmatic services around your Airflow environment with Airflow's new API, now featuring a robust permissions framework.
Smart Sensors
You can now fit Airflow to event-driven paradigms with resource-saving sensors that operate as single, long-running tasks and don't take up a worker slot.
TaskFlow API
Use TaskFlow API to pass information between tasks with clean, efficient code that's abstracted from the task dependency layer. The feature includes support for custom XCom backends.
Task Groups
Task Groups replace SubDAGs as a new way to group tasks in the Airflow UI. They don't affect task execution behavior and do not limit parallelism.
Independent Providers
In Airflow 2.0 you can pull the latest version of any Provider at any time, or follow an easy contribution process to build your own and install it as a Python package.
Simplified Kubernetes Executor
Now users can make the most of the `pod_override` parameter for easy 1:1 overrides and the new yaml `pod_template_file`, which replaces configs set in `airflow.cfg`.
UI/UX Improvements
A new look for the Airflow UI, now boasting a clean, modern color palette and an auto-refresh toggle in the Graph view.
Additionally, the community also implemented new features in Airflow 2.1. Some of the most noteworthy ones are:
- DAG Calendar View
- Cross-DAG dependencies view
- Auto-refresh on Tree View
With an accelerating number of committers and companies implementing Apache Airflow® as part of their Modern Data Stack, the future is bright.
If you'd like to learn more even more about Apache Airflow® and its functionality, contact our experts.
