ML for Customer Analytics with Airflow, Snowpark, and Weaviate
Snowpark ML, a Snowflake Public Preview feature, is a Python framework for creating Machine Learning workloads with Snowpark. Currently Snowpark ML provides a model registry that
- Stores ML tracking data and models in Snowflake tables and stages
- Feature engineering primitives similar to scikit-learn, such as LabelEncoder, OneHotEncoder, and support for training and deploying certain model types
- Deployments as user-defined functions (UDFs)
In this use case example we demonstrate how to use Apache Airflow® to orchestrate a machine learning pipeline with the Snowpark provider and Snowpark ML for feature engineering and model tracking. While Snowpark ML has its own support for models similar to Scikit-Learn, this code demonstrates a "bring-your-own" model approach. Instead of working with a Snowpark user-defined function (UDF), this code shows how to use open-source Scikit-Learn along with both the Snowpark ML model registry and model serving in an Airflow task.
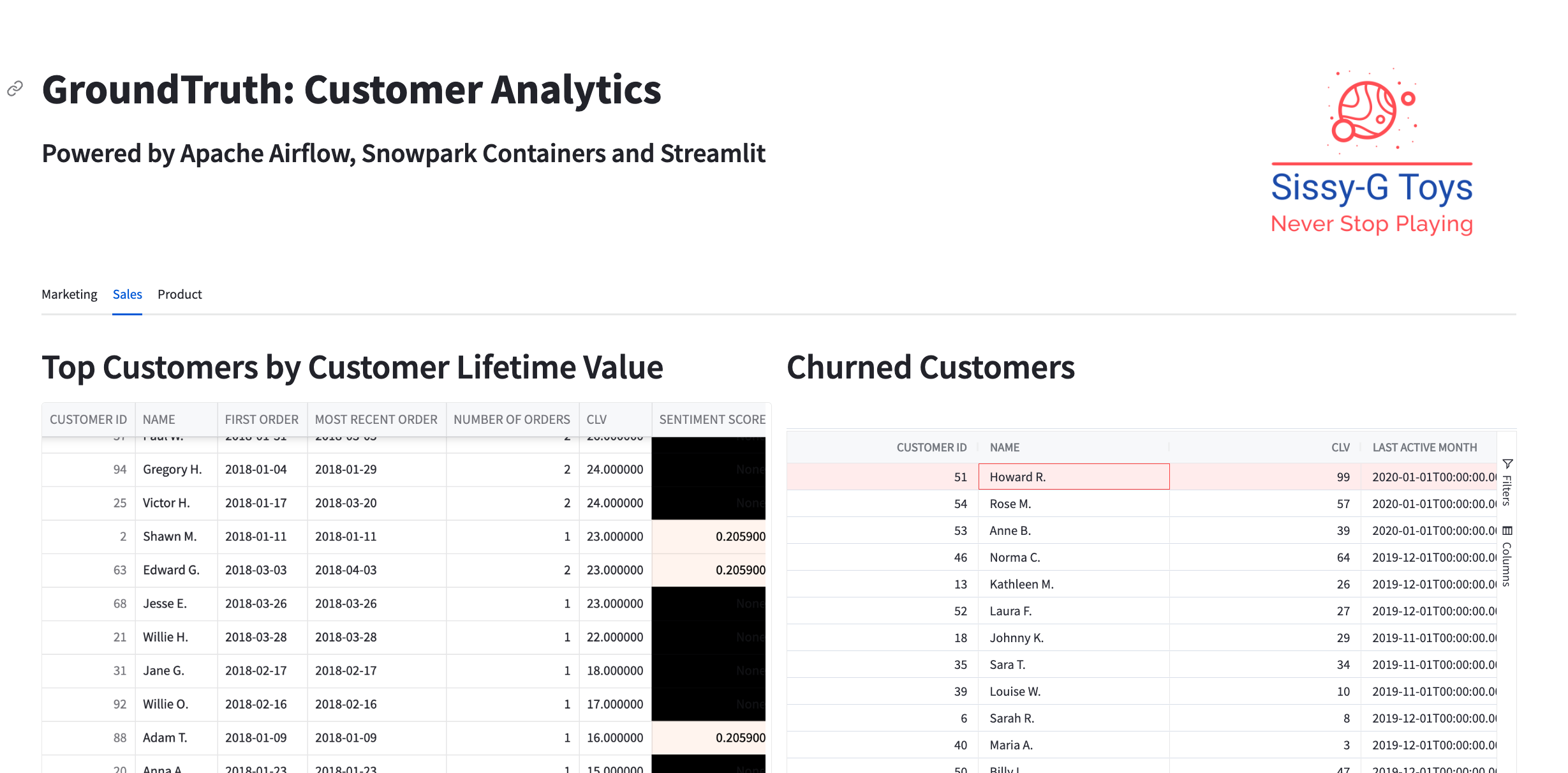
This demonstration shows how to build a customer analytics dashboard for a fictitious online retailer for toys and games. The application uses machine learning models for audio transcription, natural language embeddings, and sentiment analysis on structured, semi-structured, and unstructured data.
This demo also shows how to use the Snowflake XCom backend, which supports security and governance by serializing all task input and output to Snowflake tables and stages, while also storing a URI pointer to the data in the Airflow XCom table.
This workflow includes the following processes and presents them in a Streamlit application:
- Sourcing structured, unstructured, and semistructured data from different systems.
- Extract, transform, and load with Snowpark Python provider for Airflow
- Ingest with Astronomer's python SDK for Airflow
- Audio file transcription with OpenAI Whisper
- Natural language embeddings with OpenAI Embeddings and the Weaviate provider for Airflow
- Vector search with Weaviate
- Sentiment classification with LightGBM
- ML model management with Snowflake ML
Before you start
To try this example yourself, make sure you have:
- The Astro CLI.
- Docker Desktop.
- A Snowflake Account with AccountAdmin permissions.
- (Optional) OpenAI account or Trial Account.
Clone the project
- Clone the example project from the Astronomer GitHub.
git clone https://github.com/astronomer/airflow-snowparkml-demo
cd airflow-snowparkml-demo
- Open the
.envfile in an editor and update the following variables with you account information. You only need to update the Snowflake Connection details to be able to run the Customer Analytics DAG. However, if you'd like to enable chat capabilities in the final Streamlit application, add an OpenAI API key where designated in the.envfile as well.
Note: This demo assumes the use of a new Snowflake trial account with admin privileges. A database named 'DEMO' and schema named 'DEMO' will be created in the DAG. Running this demo without admin privileges or with existing database/schema requires additional updates to the .env file.
AIRFLOW_CONN_SNOWFLAKE_DEFAULT='{"conn_type": "snowflake", "login": "<USER_NAME>", "password": "<PASSWORD>", "schema": "DEMO", "extra": {"account": "<ORG_NAME>-<ACCOUNT_NAME>", "warehouse": "COMPUTE_WH", "database": "DEMO", "region": "", "role": "ACCOUNTADMIN", "authenticator": "snowflake", "session_parameters": null, "application": "AIRFLOW"}}'
OPENAI_APIKEY='sk-xxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxx'
Use the the new ORG_NAME-ACCOUNT_NAME format for the Snowflake account field of the connection as explained in the Snowflake Account Identifier policies. You can find the ORG and ACCOUNT names in your Snowflake trial confirmation email or in the Snowflake login link, for example, https://xxxxxxx-yyy11111.snowflakecomputing.com/console/login.
Do not specify a region when using this format for accounts. Capitalize database and schema names due to a bug in Snowpark ML.
Run the project
-
To run the example project, first make sure Docker Desktop is running.
-
Then, open your project directory in terminal and run:
astro dev start
This command builds your project and spins up 5 Docker containers on your machine to run it. In addition to the 4 standard Airflow containers, a Weaviate container is spun up. This allows you to run a fully local Weaviate environment for local development, giving every developer their own dedicated testing environment.
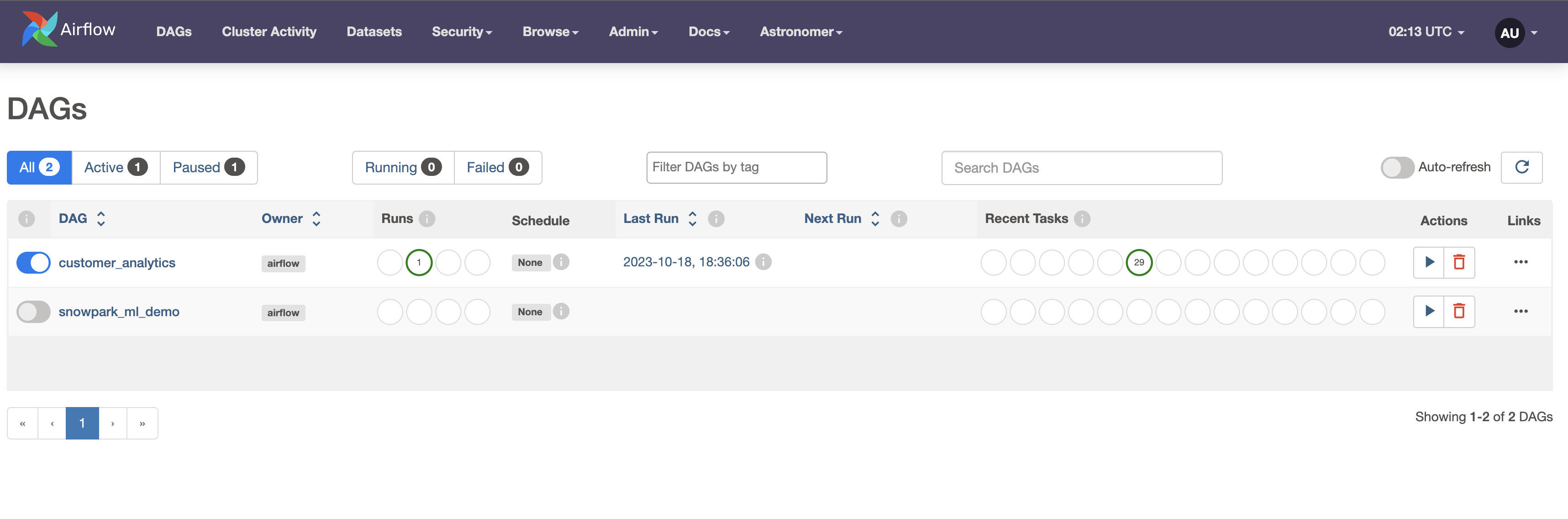
- After the command finishes, open the the Airflow UI
http://localhost:8080/and trigger thecustomer_analyticsDAG by clicking the play button. Then, monitor its status as it completes via the graph view.
View Results in Streamlit
After the DAG completes, you can view the results in a Streamlit customer analytics dashboard.
Streamlit is installed alongside the Airflow UI in the webserver container, and there's a script in the include directory called streamlit_app.py that you use to create the dashboard.
- Go to your project's root directory and connect to the webserver container with the Astro CLI by running the following command.
astro dev bash -w
- Run the following command to start Streamlit.
cd include/streamlit/src
python -m streamlit run ./streamlit_app.py
- Open the streamlit application
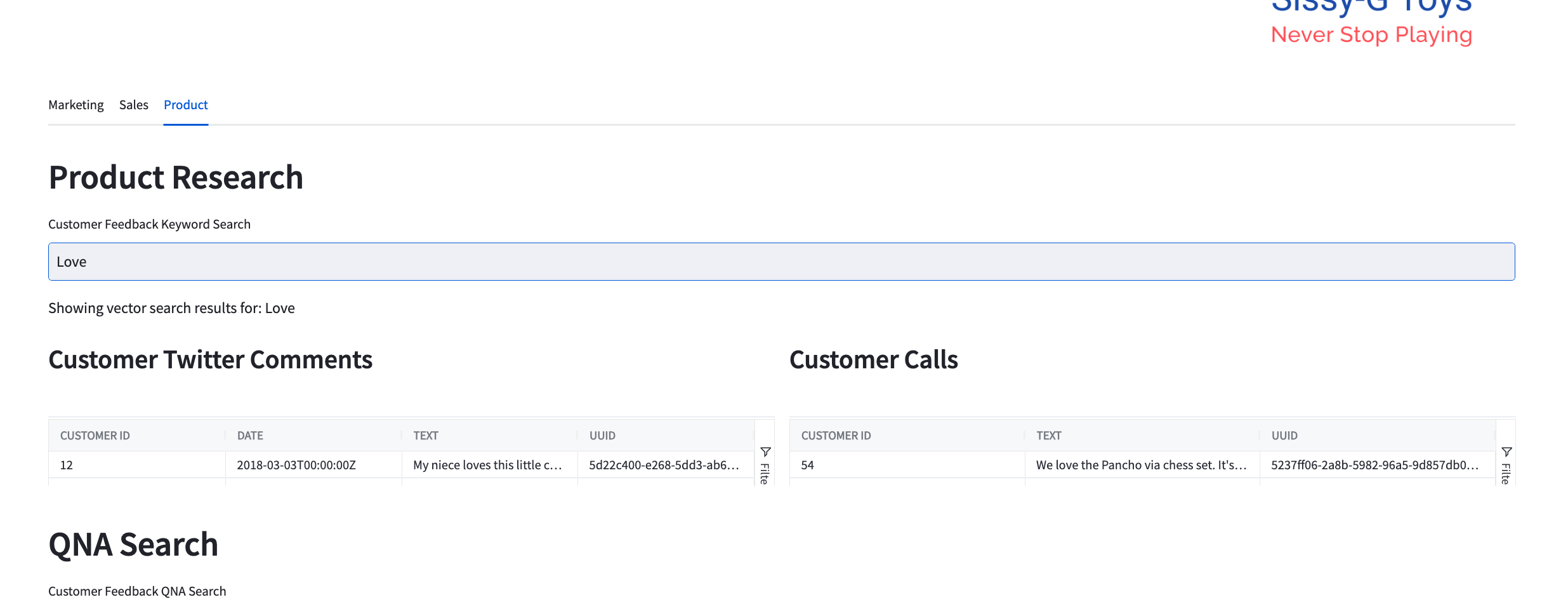
http://localhost:8501in a browser to see a visualization of all the customer analytics that your DAG produces. If you added an Open-AI key to your.envfile, you can use the chatbot functionality to search for customer reviews by keyword.
Project Code
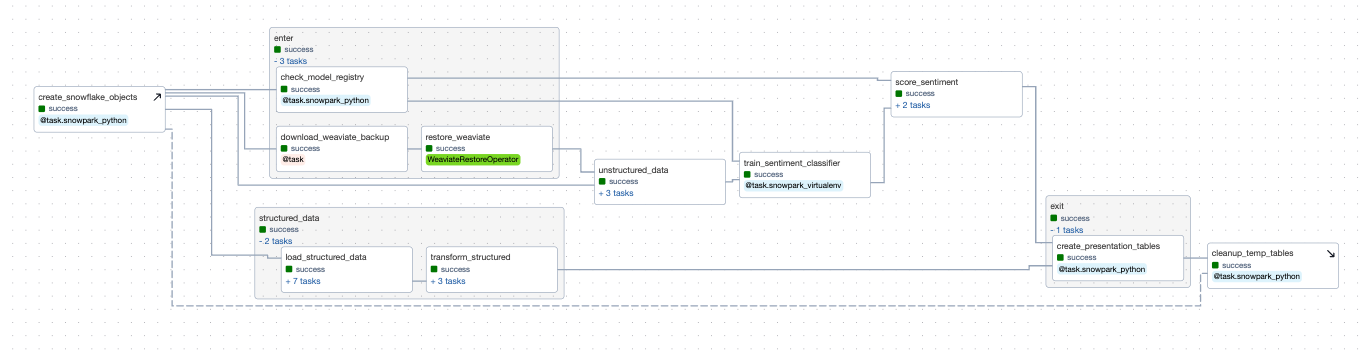
This project consists of two DAGs, a basic example snowpark_ml_dag DAG, and a much more complex customer_analytics DAG.. This guide focuses on the customer_analytics DAG, which demonstrates an end-to-end ML application workflow using OpenAI embeddings with a Weaviate vector database. The customer_analytics DAG also includes examples of Snowpark decorators, the Snowflake XCom backend, and the Snowpark ML model registry.
The Astro CLI commands include additional Docker-based services for Weaviate and Streamlit.
Setup Tasks
The first tasks in the the set-up task group create all the resources necessary to run the pipeline, including creating the necessary Snowflake tables, restoring Weaviate data from prior runs, and creating a Snowpark model registry if none exists already. Using an enter() task group allows you to group together tasks that should be run to setup state for the rest of the DAG. Functionally this is very similar to setup tasks but allows some additional flexibility in dependency mapping.
@task.snowpark_python() def create_snowflake_objects(snowflake_objects:dict, calls_directory_stage:str): snowpark_session.sql(f"""CREATE DATABASE IF NOT EXISTS \ {snowflake_objects['demo_database']};""").collect() snowpark_session.sql(f"""CREATE SCHEMA IF NOT EXISTS \ {snowflake_objects['demo_database']}.\ {snowflake_objects['demo_schema']};""").collect() snowpark_session.sql(f"""CREATE STAGE IF NOT EXISTS \ {snowflake_objects['demo_database']}.\ {snowflake_objects['demo_schema']}.\ {snowflake_objects['demo_xcom_stage']} DIRECTORY = (ENABLE = TRUE) ENCRYPTION = (TYPE = 'SNOWFLAKE_SSE'); """).collect() snowpark_session.sql(f"""CREATE TABLE IF NOT EXISTS \ {snowflake_objects['demo_database']}.\ {snowflake_objects['demo_schema']}.\ {snowflake_objects['demo_xcom_table']} ( dag_id varchar NOT NULL, task_id varchar NOT NULL, run_id varchar NOT NULL, multi_index integer NOT NULL, key varchar NOT NULL, value_type varchar NOT NULL, value varchar NOT NULL ); """).collect() snowpark_session.sql(f"""CREATE OR REPLACE STAGE \ {snowflake_objects['demo_database']}.\ {snowflake_objects['demo_schema']}.\ {calls_directory_stage} DIRECTORY = (ENABLE = TRUE) ENCRYPTION = (TYPE = 'SNOWFLAKE_SSE'); """).collect()
-
Task
create_snowflake_objects: The first task creates Snowflake objects (like databases, schemas, and stages) prior to running any tasks, since this demonstrations assumes you started with a fresh trial account. The task creation uses the Airflow setup/teardown task feature, and has a corresponding clean up task at the end of the DAG. This means that no matter what, Airflow deletes temp tables used for this project after usage to prevent unnecessary consumption, mimicking how you might use them in a production setting! -
Task
download_weaviate_backup: To speed up the demonstration process, the data you use has been ingested into Weaviate and vectorized in advance. The data was then backed up and stored in the cloud for easy restore. This task downloads thebackup.zipand makes it available in a Docker mounted filesystem for therestore_weaviatetask. -
Task
restore_weaviate: This task speeds up the demo for subsequent runs. By restoring prefetched embeddings to Weaviate, later tasks skip embeddings and only make calls to OpenAI for data it hasn't yet embedded. -
Task
check_model_registry: This task checks if a Snowpark model registry exists in the specified database and schema. If not, it creates one and returns a dictionary containing the database and schema information.
@task_group() def enter(): @task() def download_weaviate_backup() -> str: """ [Weaviate](http://www.weaviate.io) is a vector database which allows us to store a vectorized representation of unstructured data like twitter tweets or audio calls. In this demo we use the [OpenAI embeddings](https://platform.openai.com/docs/guides/embeddings/embeddings) model to build the vectors. With the vectors we can do sentiment classification based on cosine similarity with a labeled dataset. This demo uses a version of Weaviate running locally in a Docker container. See the `docker-compose.override.yml` file for details. The Astro CLI will start this container alongside the Airflow webserver, trigger, scheduler and database. In order to speed up the demo process the data has already been ingested into weaviate and vectorized. The data was then backed up and stored in the cloud for easy restore. This task will download the backup.zip and make it available in a docker mounted filesystem for the weaviate restore task. Normally this would be in an cloud storage. """ import urllib import zipfile weaviate_restore_uri = f'{restore_data_uri}/weaviate-backup/backup.zip' zip_path, _ = urllib.request.urlretrieve(weaviate_restore_uri) with zipfile.ZipFile(zip_path, "r") as f: f.extractall('/usr/local/airflow/include/weaviate/data/backups') @task.snowpark_python() def check_model_registry(snowflake_objects:dict) -> dict: """ Snowpark ML provides a model registry leveraging tables, views and stages to track model state as well as model artefacts. If the model registry objects have not yet been created in Snowflake this task will create them and return a dictionary with the database and schema where they exist. """ from snowflake.ml.registry import model_registry assert model_registry.create_model_registry(session=snowpark_session, database_name=snowflake_objects['demo_database'], schema_name=snowflake_objects['demo_schema']) snowpark_model_registry = {'database': snowflake_objects['demo_database'], 'schema': snowflake_objects['demo_schema']} return snowpark_model_registry _snowpark_model_registry = check_model_registry(snowflake_objects) _restore_weaviate = WeaviateRestoreOperator(task_id='restore_weaviate', backend='filesystem', id='backup', include=list(weaviate_class_objects.keys()), replace_existing=True) _restore_weaviate.doc_md = dedent( """ ### Restoring Demo Data In order to speed up the demo process the data has already been ingested into weaviate and vectorized. The data was then backed up and stored in the cloud for easy restore. This task restores the pre-vectorized demo data using the backup.zip file downloaded in the `download_weaviate_backup` task. Upstream tasks will try to import to weaviate will but will be `skipped` since they already exist. For any new data Weaviate will use OpenAI embeddings to vectorize and import data. """ ) download_weaviate_backup() >> _restore_weaviate return _snowpark_model_registry, _restore_weaviate
Structured data ingestion and transformation
The structured data contains various data points about customers, such as their purchasing histories and lifetime value, all of which are transformed using Snowpark so you can easily join it with the unstructured data.
-
Task Group
load_structured_data: This task group uses aforloop to dynamically create tasks to upload structured datasets containing customer information from various data sources into a Snowflake database. For each source indata_sources, this task loads a CSV file, namedsource.csv, from a specified URI,restore_data_uri. -
Task Group
transform_structured: This task group encompasses three different tasks that transform the structured data into reporting-ready format. The tasks are as follows:-
Task
jaffle_shop: This task begins by aggregating orders to calculate each customer's first and most recent order dates, as well as their total number of orders. Next, it joins the payments data with the orders, grouping by customer ID to sum up the total payment amounts. This results in a comprehensive view of each customer's transaction history. -
Task
mrr_playbook: This task computes the Monthly Recurring Revenue (MRR), a crucial metric for subscription-based businesses. It starts by constructing a timeline of months since a specific start date and then matches this timeline with subscription data to determine the active subscription periods for each customer. The task then performs detailed calculations to determine the MRR for each customer in each month. -
Task
attribution_playbook: This task tackles the complex challenge of marketing attribution, aiming to understand how different marketing efforts contribute to customer conversions. It does this by linking customer conversion data with their session data. The task then applies various attribution models, such as first touch, last touch, and linear, to assign credit to different marketing touchpoints. It calculates the revenue attributed to each touchpoint based on the chosen model, providing insights into which marketing channels are most effective in driving customer conversions.
-
@task_group() def structured_data(): @task_group() def load_structured_data(): for source in data_sources: aql.load_file(task_id=f'load_{source}', input_file = File(f"{restore_data_uri}/{source}.csv"), output_table = Table(name=f'STG_{source.upper()}', conn_id=_SNOWFLAKE_CONN_ID) ) @task_group() def transform_structured(): @task.snowpark_python() def jaffle_shop(customers_df:SnowparkTable, orders_df:SnowparkTable, payments_df:SnowparkTable): customer_orders_df = orders_df.group_by('customer_id').agg(F.min('order_date').alias('first_order'), F.max('order_date').alias('most_recent_order'), F.count('order_id').alias('number_of_orders')) customer_payments_df = payments_df.join(orders_df, how='left', on='order_id')\ .group_by('customer_id')\ .agg((F.sum('amount') / 100).alias('total_amount')) customers = customers_df.join(customer_orders_df, how='left', on='customer_id')\ .join(customer_payments_df, how='left', on='customer_id')\ .rename('total_amount', 'customer_lifetime_value') payment_types = ['credit_card', 'coupon', 'bank_transfer', 'gift_card'] orders = payments_df.drop('payment_id')\ .pivot('payment_method', payment_types )\ .agg(F.sum('amount'))\ .group_by('order_id')\ .agg({f"'{x}'": "sum" for x in payment_types})\ .rename({f"SUM('{x.upper()}')": x+'_amount' for x in payment_types})\ .join(payments_df.group_by('order_id')\ .agg(F.sum('amount').alias('total_amount')), on='order_id')\ .join(orders_df, on='order_id') return customers @task.snowpark_virtualenv(python_version='3.8', requirements=['snowflake-snowpark-python>=1.8']) def mrr_playbook(subscription_df:SnowparkTable): from snowflake.snowpark import Window from datetime import date day_count = date.today() - date(2018,1,1) months = snowpark_session.generator(F.seq4(), rowcount=day_count.days)\ .with_column('date_month', F.date_trunc('month', F.date_add(F.to_date(F.lit('2018-01-01')), F.row_number().over(Window.order_by('SEQ4(0)')))))\ .select('date_month').distinct().sort('date_month', ascending=True) subscription_periods = subscription_df.with_column('start_date', F.to_date('start_date'))\ .with_column('end_date', F.to_date('end_date')) customers = subscription_periods.group_by('customer_id').agg(F.date_trunc('month', F.min('start_date')).alias('date_month_start'), F.date_trunc('month', F.max('end_date')).alias('date_month_end')) customer_months = customers.join(months, how='inner', on=(months['date_month'] >= customers['date_month_start']) & ( months['date_month'] < customers['date_month_end']))\ .select(['customer_id', 'date_month']) customer_revenue_by_month = customer_months.join(subscription_periods, how='left', rsuffix='_', on=(customer_months.customer_id == subscription_periods.customer_id) & (customer_months.date_month >= subscription_periods.start_date) & ((customer_months.date_month < subscription_periods.end_date) | (subscription_periods.end_date.is_null())))\ .fillna(subset=['monthly_amount'], value=0)\ .select(F.col('date_month'), F.col('customer_id'), F.col('monthly_amount').alias('mrr'))\ .with_column('is_active', F.col('mrr')>0)\ .with_column('first_active_month', F.when(F.col('is_active'), F.min(F.col('date_month')).over(Window.partition_by('customer_id'))))\ .with_column('last_active_month', F.when(F.col('is_active'), F.max(F.col('date_month')).over(Window.partition_by('customer_id'))))\ .with_column('is_first_month', F.col('first_active_month') == F.col('date_month'))\ .with_column('is_last_month', F.col('last_active_month') == F.col('date_month')) customer_churn_month = customer_revenue_by_month.where('is_last_month')\ .select(F.add_months(F.col('date_month'), 1), 'customer_id', F.to_decimal('mrr', 38, 2), F.lit(False).alias('is_active'), 'first_active_month', 'last_active_month', F.lit(False).alias('is_first_month'), F.lit(False).alias('is_last_month')) customer_date_window = Window.partition_by('customer_id').order_by('date_month') mrr = customer_revenue_by_month.union_all(customer_churn_month)\ .with_column('id', F.md5(F.col('customer_id')))\ .with_column('previous_month_is_active', F.lag('is_active', default_value=False).over(customer_date_window))\ .with_column('previous_month_mrr', F.lag('mrr', default_value=0).over(customer_date_window))\ .with_column('mrr_change', F.col('mrr') - F.col('previous_month_mrr'))\ .with_column('change_category', F.when(F.col('is_first_month'), 'new')\ .when(F.not_(F.col('is_active') & F.col('previous_month_is_active')), 'churn')\ .when(F.col('is_active') & F.not_(F.col('previous_month_is_active')), 'reactivation')\ .when(F.col('mrr_change') > 0, 'upgrade')\ .when(F.col('mrr_change') < 0, 'downgrade') )\ .with_column('renewal_amount', F.least(F.col('mrr'), F.col('previous_month_mrr'))) return mrr @task.snowpark_ext_python(python='/home/astro/.venv/snowpark/bin/python') def attribution_playbook(customer_conversions_df:SnowparkTable, sessions_df:SnowparkTable): from snowflake.snowpark import Window customer_window = Window.partition_by('customer_id') attribution_touches = sessions_df.join(customer_conversions_df, on='customer_id')\ .filter((F.col('started_at') <= F.col('converted_at')) & (F.col('started_at') >= F.date_add(F.col('converted_at'), -30)))\ .with_column('total_sessions', F.count('customer_id')\ .over(customer_window))\ .with_column('session_index', F.row_number()\ .over(customer_window\ .order_by('started_at')))\ .with_column('first_touch_points', F.when(F.col('session_index') == 1, 1)\ .otherwise(0))\ .with_column('last_touch_points', F.when(F.col('session_index') == F.col('total_sessions'), 1)\ .otherwise(0))\ .with_column('forty_twenty_forty_points', F.when(F.col('total_sessions') == 1, 1)\ .when(F.col('total_sessions') == 2, .5)\ .when(F.col('session_index') == 1, .4)\ .when(F.col('session_index') == F.col('total_sessions'), .4)\ .otherwise(F.lit(0.2) / (F.col('total_sessions') - 2)))\ .with_column('linear_points', F.lit(1) / F.col('total_sessions'))\ .with_column('first_touch_revenue', F.col('revenue') * F.col('first_touch_points'))\ .with_column('last_touch_revenue', F.col('revenue') * F.col('last_touch_points'))\ .with_column('forty_twenty_forty_revenue', F.col('revenue') * F.col('forty_twenty_forty_points'))\ .with_column('linear_revenue', F.col('revenue') * (1 / F.col('total_sessions'))) return attribution_touches _customers = jaffle_shop(customers_df=SnowparkTable('stg_customers'), orders_df=SnowparkTable('stg_orders'), payments_df=SnowparkTable('stg_payments')) _mrr = mrr_playbook(subscription_df=SnowparkTable('stg_subscription_periods')) _attribution_touches = attribution_playbook(customer_conversions_df=SnowparkTable('stg_customer_conversions'), sessions_df=SnowparkTable('stg_sessions')) return _attribution_touches, _mrr, _customers _structured_data = load_structured_data() _attribution_touches, _mrr, _customers = transform_structured() _structured_data >> [_attribution_touches, _mrr, _customers] return _attribution_touches, _mrr, _customers
Unstructured data ingestion and transformation
The unstructured data task group extracts twitter comments, reviews, and customer support calls, before transcribing the calls and converting all the unstructured data into Weaviate vector embeddings.
-
Task Group
unstructured_data: Theunstructured_datatask group processes various forms of unstructured data, including customer call recordings, Twitter comments, and training data for sentiment analysis. This task group is divided into three main task subgroups:load_unstructured_data,transcribe_calls, andgenerate_embeddings.- Task Group
load_unstructured_data: This subgroup focuses on loading unstructured data from different sources.
- Task Group
-
Task
load_support_calls_to_stage: This task downloads and extracts a ZIP file containing customer call recordings from a specified URI. The task then uploads the extracted files to a specified Snowflake stage for additional processing.-
Task
load_twitter_comments: Loads Twitter comments from a given URI in Parquet format and stores them in a Snowflake table namedSTG_TWITTER_COMMENTS. -
Task
load_comment_training: Similar to theload_twitter_commentstask, this one loads training data for comment analysis from a Parquet file located at a specified URI. The data is stored in a Snowflake table namedSTG_COMMENT_TRAINING. -
Task
transcribe_calls: After loading the call recordings, this task transcribes them using the Whisper model. It extracts audio files from the specified Snowflake stage, processes each file through the OpenAI Whisper model to generate transcripts, and then returns a dataframe containing customer IDs, relative paths of the recordings, and their transcriptions.
-
-
Task Group
generate_embeddings: The final subgroup focuses on generating embeddings for different data types using OpenAI's models before importing them into the Weaviate vector database.-
Task
generate_training_embeddings: Processes the training data loaded earlier in theload_comment_trainingtask to create embeddings using an OpenAI model. The embeddings are then used for sentiment analysis. -
Task
generate_twitter_embeddings: Similar to thegenerate_training_embeddingstask, but focuses on Twitter comments. It transforms the loaded Twitter data and generates embeddings for analyzing customer sentiment. -
Task
generate_call_embeddings: Processes the transcribed call data to generate embeddings. These embeddings provide insights into overall sentiment expressed during the calls.
-
@task_group() def unstructured_data(): @task_group() def load_unstructured_data(): @task.snowpark_python() def load_support_calls_to_stage(restore_data_uri:str, calls_directory_stage:str) -> str: import zipfile import io import tempfile import requests with tempfile.TemporaryDirectory() as td: calls_zipfile = requests.get(f'{restore_data_uri}/customer_calls.zip').content buffer = io.BytesIO(calls_zipfile) z = zipfile.ZipFile(buffer) z.extractall(td) snowpark_session.file.put(local_file_name=f"file://{td}/customer_calls/*", stage_location=f"@{calls_directory_stage}", source_compression=None, auto_compress=False, overwrite=True) snowpark_session.sql(f"ALTER STAGE {calls_directory_stage} REFRESH;").collect() return calls_directory_stage _calls_directory_stage = load_support_calls_to_stage(restore_data_uri=restore_data_uri, calls_directory_stage=calls_directory_stage) _stg_comment_table = aql.load_file(task_id='load_twitter_comments', input_file = File(f'{restore_data_uri}/twitter_comments.parquet'), output_table = Table(name='STG_TWITTER_COMMENTS', conn_id=_SNOWFLAKE_CONN_ID), use_native_support=False) _stg_training_table = aql.load_file(task_id='load_comment_training', input_file = File(f'{restore_data_uri}/comment_training.parquet'), output_table = Table(name='STG_COMMENT_TRAINING', conn_id=_SNOWFLAKE_CONN_ID), use_native_support=False) return _calls_directory_stage, _stg_comment_table, _stg_training_table _calls_directory_stage, _stg_comment_table, _stg_training_table = load_unstructured_data() whisper_requirements = [ 'numpy', 'torch==2.0.0', 'tqdm', 'more-itertools==9.1.0', 'transformers==4.27.4', 'ffmpeg-python==0.2.0', 'openai-whisper==v20230314'] @task.snowpark_virtualenv(requirements=whisper_requirements) def transcribe_calls(calls_directory_stage:str): import requests import tempfile from pathlib import Path import os import whisper model = whisper.load_model('tiny.en', download_root=os.getcwd()) calls_df = snowpark_session.sql(f"""SELECT *, get_presigned_url(@{calls_directory_stage}, LIST_DIR_TABLE.RELATIVE_PATH) as presigned_url FROM DIRECTORY( @{calls_directory_stage})""") calls_df = calls_df.to_pandas() #Extract customer_id from file name calls_df['CUSTOMER_ID']= calls_df['RELATIVE_PATH'].apply(lambda x: x.split('-')[0]) with tempfile.TemporaryDirectory() as tmpdirname: calls_df.apply(lambda x: Path(tmpdirname)\ .joinpath(x.RELATIVE_PATH)\ .write_bytes(requests.get(x.PRESIGNED_URL).content), axis=1) calls_df['TRANSCRIPT'] = calls_df.apply(lambda x: model.transcribe(Path(tmpdirname) .joinpath(x.RELATIVE_PATH).as_posix())['text'], axis=1) return snowpark_session.create_dataframe(calls_df[['CUSTOMER_ID', 'RELATIVE_PATH', 'TRANSCRIPT']]) _stg_calls_table = transcribe_calls(calls_directory_stage=_calls_directory_stage) @task_group() def generate_embeddings(): @task.snowpark_python() def get_training_pandas(stg_training_table:SnowparkTable): return stg_training_table.to_pandas() @task.snowpark_python() def get_comment_pandas(stg_comment_table:SnowparkTable): return stg_comment_table.to_pandas() @task.snowpark_python() def get_calls_pandas(stg_calls_table:SnowparkTable): return stg_calls_table.to_pandas() @task.weaviate_import() def generate_training_embeddings(stg_training_table:pd.DataFrame): df = stg_training_table df.rename({'REVIEW_TEXT': 'rEVIEW_TEXT', 'LABEL': 'lABEL'}, axis=1, inplace=True) df['lABEL'] = df['lABEL'].apply(str) #openai works best without empty lines or new lines df = df.replace(r'^\s*$', np.nan, regex=True).dropna() df['rEVIEW_TEXT'] = df['rEVIEW_TEXT'].apply(lambda x: x.replace("\n","")) df['UUID'] = df.apply(lambda x: generate_uuid5(x.to_dict(), 'CommentTraining'), axis=1) return {"data": df, "class_name": 'CommentTraining', "uuid_column": "UUID", "batch_size": 1000, "error_threshold": 0} @task.weaviate_import() def generate_twitter_embeddings(stg_comment_table:pd.DataFrame): df = stg_comment_table df.rename({'CUSTOMER_ID': 'cUSTOMER_ID', 'REVIEW_TEXT': 'rEVIEW_TEXT', 'DATE': 'dATE'}, axis=1, inplace=True) df['cUSTOMER_ID'] = df['cUSTOMER_ID'].apply(str) df['dATE'] = pd.to_datetime(df['dATE']).dt.strftime("%Y-%m-%dT%H:%M:%S-00:00") #openai works best without empty lines or new lines df = df.replace(r'^\s*$', np.nan, regex=True).dropna() df['rEVIEW_TEXT'] = df['rEVIEW_TEXT'].apply(lambda x: x.replace("\n","")) df['UUID'] = df.apply(lambda x: generate_uuid5(x.to_dict(), 'CustomerComment'), axis=1) return {"data": df, "class_name": 'CustomerComment', "uuid_column": "UUID", "batch_size": 1000, "error_threshold": 0} @task.weaviate_import() def generate_call_embeddings(stg_calls_table:pd.DataFrame): df = stg_calls_table df.rename({'CUSTOMER_ID': 'cUSTOMER_ID', 'TRANSCRIPT': 'tRANSCRIPT', 'RELATIVE_PATH': 'rELATIVE_PATH'}, axis=1, inplace=True) df['cUSTOMER_ID'] = df['cUSTOMER_ID'].apply(str) #openai works best without empty lines or new lines df = df.replace(r'^\s*$', np.nan, regex=True).dropna() df['tRANSCRIPT'] = df['tRANSCRIPT'].apply(lambda x: x.replace("\n","")) df['UUID'] = df.apply(lambda x: generate_uuid5(x.to_dict(), 'CustomerCall'), axis=1) return {"data": df, "class_name": 'CustomerCall', "uuid_column": "UUID", "batch_size": 1000, "error_threshold": 0} _training_table = get_training_pandas(stg_training_table=_stg_training_table) _training_table = generate_training_embeddings(stg_training_table=_training_table) _comment_table = get_comment_pandas(stg_comment_table=_stg_comment_table) _comment_table = generate_twitter_embeddings(stg_comment_table=_comment_table) _calls_table = get_calls_pandas(stg_calls_table=_stg_calls_table) _calls_table = generate_call_embeddings(stg_calls_table=_calls_table) return _training_table, _comment_table, _calls_table _training_table, _comment_table, _calls_table = generate_embeddings() return _training_table, _comment_table, _calls_table
Model training
After you prepared the structured and unstructured data, split it into testing and training datasets, before using it to train a sentiment-classifier model that predicts customer life time value based on their sentiment. Finally, you can use the trained model to generate predictions for customers life time value based on their sentiment.
- Task
train_sentiment_classifier: After the structured and unstructured data has been extracted, transformed/transcribed, and loaded in the previousunstructured_dataandstructured_datatask groups, it is used in this task to train a sentiment classifier model within Snowpark. The embedding vectors in Weaviate combined with a sentiment-labeled dataset allow the DAG to train a very simple classifier model. After training the model, the DAG registers it into the Snowflake model registry so that it can be used to generate sentiment predictions later in the DAG. One of the biggest advantages of this approach is that you can run your model on the data within Snowpark, without needing to extract data to cloud object storage for inference.
@task.snowpark_virtualenv(requirements=['lightgbm==3.3.5', 'scikit-learn==1.2.2', 'astro_provider_snowflake']) def train_sentiment_classifier(class_name:str, snowpark_model_registry:dict): from snowflake.ml.registry import model_registry import numpy as np import pandas as pd from sklearn.model_selection import train_test_split from lightgbm import LGBMClassifier from uuid import uuid1 from weaviate_provider.hooks.weaviate import WeaviateHook registry = model_registry.ModelRegistry(session=snowpark_session, database_name=snowpark_model_registry['database'], schema_name=snowpark_model_registry['schema']) weaviate_client = WeaviateHook('weaviate_default').get_conn() df = pd.DataFrame(weaviate_client.data_object.get(with_vector=True, class_name=class_name)['objects']) df = pd.concat([pd.json_normalize(df['properties']), df['vector']], axis=1) model_version = uuid1().urn model_name='sentiment_classifier' X_train, X_test, y_train, y_test = train_test_split(df['vector'], df['lABEL'], test_size=.3, random_state=1883) X_train = np.array(X_train.values.tolist()) y_train = np.array(y_train.values.tolist()) X_test = np.array(X_test.values.tolist()) y_test = np.array(y_test.values.tolist()) model = LGBMClassifier(random_state=42) model.fit(X=X_train, y=y_train, eval_set=(X_test, y_test)) model_id = registry.log_model( model=model, model_name=model_name, model_version=model_version, sample_input_data=X_test[0].reshape(1,-1), tags={'stage': 'dev', 'model_type': 'lightgbm.LGBMClassifier'}) return {'name': model_id.get_name(), 'version':model_id.get_version()}
-
Task
call_sentiment: This task retrieves vectors and properties of data objects from Weaviate, a vector search engine, for the classCustomerCall. The task then normalizes the properties and uses the vectors as features for a sentiment analysis model loaded from Snowflake's Model Registry. The sentiment scores are predicted using thepredict_probamethod of the model, focusing on the probability associated with one of the classes. It outputs a Snowpark dataframe containing the original data enhanced with sentiment scores. -
Task
twitter_sentiment: Similar in structure to thecall_sentimenttask, this task also retrieves vectors and properties from Weaviate for the classCustomerComment. The task processes the data in the same way, using a model from Snowflake's Model Registry to predict sentiment scores. It outputs a Snowpark dataframe that includes Twitter comment data augmented with their respective sentiment scores.
@task_group() def score_sentiment(): @task.snowpark_virtualenv(requirements=['lightgbm==3.3.5', 'astro_provider_snowflake'], retries=2, retry_delay=datetime.timedelta(seconds=5)) def call_sentiment(class_name:str, snowpark_model_registry:dict, model:dict) -> SnowparkTable: from snowflake.ml.registry import model_registry import numpy as np import pandas as pd from weaviate_provider.hooks.weaviate import WeaviateHook weaviate_client = WeaviateHook('weaviate_default').get_conn() df = pd.DataFrame(weaviate_client.data_object.get(with_vector=True, class_name=class_name)['objects']) df = pd.concat([pd.json_normalize(df['properties']), df['vector']], axis=1) registry = model_registry.ModelRegistry(session=snowpark_session, database_name=snowpark_model_registry['database'], schema_name=snowpark_model_registry['schema']) metrics = registry.get_metrics(model_name=model['name'], model_version=model['version']) model = registry.load_model(model_name=model['name'], model_version=model['version']) df['sentiment'] = model.predict_proba(np.stack(df['vector'].values))[:,1] return snowpark_session.create_dataframe(df.rename(columns=str.upper)) @task.snowpark_virtualenv(requirements=['lightgbm==3.3.5', 'astro_provider_snowflake'], retries=2, retry_delay=datetime.timedelta(seconds=5)) def twitter_sentiment(class_name:str, snowpark_model_registry:dict, model:dict) -> SnowparkTable: from snowflake.ml.registry import model_registry import numpy as np import pandas as pd from weaviate_provider.hooks.weaviate import WeaviateHook weaviate_client = WeaviateHook('weaviate_default').get_conn() df = pd.DataFrame(weaviate_client.data_object.get(with_vector=True, class_name=class_name)['objects']) df = pd.concat([pd.json_normalize(df['properties']), df['vector']], axis=1) registry = model_registry.ModelRegistry(session=snowpark_session, database_name=snowpark_model_registry['database'], schema_name=snowpark_model_registry['schema']) metrics = registry.get_metrics(model_name=model['name'], model_version=model['version']) model = registry.load_model(model_name=model['name'], model_version=model['version']) df['sentiment'] = model.predict_proba(np.stack(df['vector'].values))[:,1] return snowpark_session.create_dataframe(df.rename(columns=str.upper)) _pred_calls_table = call_sentiment(class_name='CustomerCall', snowpark_model_registry=_snowpark_model_registry, model=_model) _pred_comment_table = twitter_sentiment(class_name='CustomerComment', snowpark_model_registry=_snowpark_model_registry, model=_model) return _pred_calls_table, _pred_comment_table
Create reporting tables
After the model has generated its predictions, the next tasks cleans and organizes the results into presentation tables for viewing using a Streamlit application.
-
Task
Create_Presentation_Tables: Thecreate_presentation_tablestask consolidates and processes various data sources to create tables specifically for presentation in a Streamlit app. This function takes five Snowpark tables as input:attribution_df,mrr_df,customers_df,pred_calls_table, andpred_comment_table. The task processes each of these tables to generate new tables suited for visual presentation and analysis. The following shares a summary of each step:- Customer Data Processing: Enhances the
customers_dftable by adding a rounded 'Customer Lifetime Value' (CLV) column. - Sentiment Analysis: Combines sentiment data from
pred_calls_tableandpred_comment_tabletables. It calculates the average sentiment score for each customer based on call and comment data. The final sentiment score is the average of these two scores, and customers are bucketed into sentiment categories. This processed data is saved as thePRES_SENTIMENTtable. - Advertising Spend Analysis: Processes the
attribution_dftable to understand the revenue generated from different advertising mediums. The data is grouped by the medium, and the revenue is summed up for each group. The task saves the table asPRES_AD_SPEND. - Customer Lifetime Value (CLV) Analysis: Creates a comprehensive view of customer lifetime value by joining
customers_dfwith sentiment data. It sorts the data by CLV and includes various customer details. This table, namedPRES_CLV, is valuable for understanding the high-value customers and their sentiment scores. - Churn Analysis: Analyzes churn by joining customer data with MRR data and sentiment scores. It filters for customers who have churned and sorts them by their last active month. This table,
PRES_CHURN, is critical for identifying recently churned customers and understanding their value and sentiment. - Saving Raw Sentiment Data: The raw sentiment data for customer calls (
pred_calls_table) and Twitter comments (pred_comment_table) are saved asPRED_CUSTOMER_CALLSandPRED_TWITTER_COMMENTS, respectively. - Saving Attribution Touches: The
attribution_dftable is saved asATTRIBUTION_TOUCHES, which holds detailed data on customer interactions and their revenue attribution.
- Customer Data Processing: Enhances the
@task.snowpark_python() def create_presentation_tables(attribution_df:SnowparkTable, mrr_df:SnowparkTable, customers_df:SnowparkTable, pred_calls_table:SnowparkTable, pred_comment_table:SnowparkTable): """ This task consolidates all of the structured and unstructured data results to create tables for the presentation layer running in the Streamlit app. Because the app needs to know the name for tables we write them specifically here with `save_as_table` rather than passing through xcom or using the Snowpark return processing. """ customers_df = customers_df.with_column('CLV', F.round(F.col('CUSTOMER_LIFETIME_VALUE'), 2)) sentiment_df = pred_calls_table.group_by(F.col('CUSTOMER_ID'))\ .agg(F.avg('SENTIMENT').alias('CALLS_SENTIMENT'))\ .join(pred_comment_table.group_by(F.col('CUSTOMER_ID'))\ .agg(F.avg('SENTIMENT').alias('COMMENTS_SENTIMENT')), on='cUSTOMER_ID', how='right')\ .fillna(0, subset=['CALLS_SENTIMENT'])\ .with_column('SENTIMENT_SCORE', F.round((F.col('CALLS_SENTIMENT') \ + F.col('COMMENTS_SENTIMENT'))/2, 4))\ .with_column('SENTIMENT_BUCKET', F.call_builtin('WIDTH_BUCKET', F.col('SENTIMENT_SCORE'), 0, 1, 10)) sentiment_df.write.save_as_table('PRES_SENTIMENT', mode='overwrite') ad_spend_df = attribution_df.select(['UTM_MEDIUM', 'REVENUE'])\ .dropna()\ .group_by(F.col('UTM_MEDIUM'))\ .sum(F.col('REVENUE'))\ .rename('SUM(REVENUE)', 'Revenue')\ .rename('UTM_MEDIUM', 'Medium')\ .write.save_as_table('PRES_AD_SPEND', mode='overwrite') clv_df = customers_df.dropna(subset=['CLV'])\ .join(sentiment_df, 'CUSTOMER_ID', how='left')\ .sort(F.col('CLV'), ascending=False)\ .with_column('NAME', F.concat(F.col('FIRST_NAME'), F.lit(' '), F.col('LAST_NAME')))\ .select(['CUSTOMER_ID', 'NAME', 'FIRST_ORDER', 'MOST_RECENT_ORDER', 'NUMBER_OF_ORDERS', 'CLV', 'SENTIMENT_SCORE'])\ .write.save_as_table('PRES_CLV', mode='overwrite') churn_df = customers_df.select(['CUSTOMER_ID', 'FIRST_NAME', 'LAST_NAME', 'CLV'])\ .join(mrr_df.select(['CUSTOMER_ID', 'FIRST_ACTIVE_MONTH', 'LAST_ACTIVE_MONTH', 'CHANGE_CATEGORY']), on='CUSTOMER_ID', how='right')\ .join(sentiment_df, 'CUSTOMER_ID', how='left')\ .dropna(subset=['CLV'])\ .filter(F.col('CHANGE_CATEGORY') == 'churn')\ .sort(F.col('LAST_ACTIVE_MONTH'), ascending=False)\ .with_column('NAME', F.concat(F.col('FIRST_NAME'), F.lit(' '), F.col('LAST_NAME')))\ .select(['CUSTOMER_ID', 'NAME', 'CLV', 'LAST_ACTIVE_MONTH', 'SENTIMENT_SCORE'])\ .write.save_as_table('PRES_CHURN', mode='overwrite') pred_calls_table.write.save_as_table('PRED_CUSTOMER_CALLS', mode='overwrite') pred_comment_table.write.save_as_table('PRED_TWITTER_COMMENTS', mode='overwrite') attribution_df.write.save_as_table('ATTRIBUTION_TOUCHES', mode='overwrite') create_presentation_tables(attribution_df=_attribution_touches, mrr_df=_mrr, customers_df=_customers, pred_calls_table=_pred_calls_table, pred_comment_table=_pred_comment_table)
Task cleanup_temp_tables: The final task is a teardown task. The task deletes the intermediate, temporary data passed between Snowpark tasks for resource optimization.
@task.snowpark_python() def cleanup_temp_tables(snowflake_objects:dict, **context): """ This task will be run as an Airflow 2.7 teardown task. The task deletes the intermediate, temporary data passed between Snowpark tasks. In production it may be best to keep intermediate tables as they provide useful audting data. For dev/test it may be beneficial to reduce objects and noise. The `temp_data_dict` is instantiated by default in the task namespace based on the decorator args or `default_args`. Likewise, all of the variables needed to construct the temporary data URI (e.g. `dag_id`, `ts_nodash`, etc.) are also instantiated. This allows us to cleanup temporary data after the DAG run. In the future this may be added as another operator for the Snowpark provider. Here it shows a good use of teardown tasks. """ snowpark_session.database = temp_data_dict['temp_data_db'] \ or snowflake_objects['demo_database'] snowpark_session.schema = temp_data_dict['temp_data_schema'] \ or snowflake_objects['demo_schema'] if temp_data_dict['temp_data_output'] == 'table': xcom_table_string=f"{temp_data_dict['temp_data_table_prefix']}{dag_id}__%__{ts_nodash}__%".upper() xcom_table_list = snowpark_session.table('information_schema.tables')\ .select('table_name')\ .where(F.col('table_name').like(xcom_table_string))\ .to_pandas()['TABLE_NAME'].to_list() print(f'Removing tables {xcom_table_list}') for table in xcom_table_list: try: snowpark_session.table(table).drop_table() except: pass elif temp_data_dict['temp_data_output'] == 'stage': xcom_stage_string = f"{dag_id.lower()}/.*/{run_id.split('+')[0]}.*/" print(f'Removing files based on {xcom_stage_string}') xcom_file_list = snowpark_session.sql(f"""REMOVE @{temp_data_dict['temp_data_stage']} PATTERN='{xcom_stage_string}'""").collect() _create_snowflake_objects = create_snowflake_objects(snowflake_objects, calls_directory_stage).as_setup() with cleanup_temp_tables(snowflake_objects).as_teardown(setups=_create_snowflake_objects): _snowpark_model_registry, _restore_weaviate = enter() _attribution_touches, _mrr, _customers = structured_data() _training_table, _comment_table, _calls_table = unstructured_data() _model = train_sentiment_classifier(class_name='CommentTraining', snowpark_model_registry=_snowpark_model_registry) _pred_calls_table, _pred_comment_table = score_sentiment() _exit = exit() _restore_weaviate >> [_training_table, _comment_table, _calls_table] >> _model
Additional resources
For additional documentation on the features used in this example, check out the following resources:

