Note: This webinar was recorded in April 2021 and many exciting features have been added to Airflow and Astro since then. We recommend you also check out our in-depth guide on how to Use the KubernetesPodOperator. Astronomer customers can learn more about the KubernetesExecutor and the KubernetesPodOperator on Astro in our documentation.
Topics that will be discussed:
- Kubernetes Executor
- Kubernetes Pod Operator
- KEDA Autoscaler
Kubernetes Executor
- Each Airflow task is launched as a pod
- Workers scale to zero
- Expose Kubernetes API to the data engineer so they can have more control over the resources of each task
Old Architecture
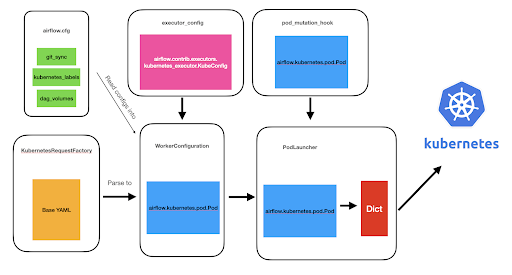
- Attempted to abstract Kubernetes API for “simplicity”
- Result: Lots of PRs to expose Kubernetes, lots of code to maintain, lost of steps before a pod is launched
- Goal: Offer flexibility of the Kubernetes API and reduce Airflow’s code footprint
New Architecture
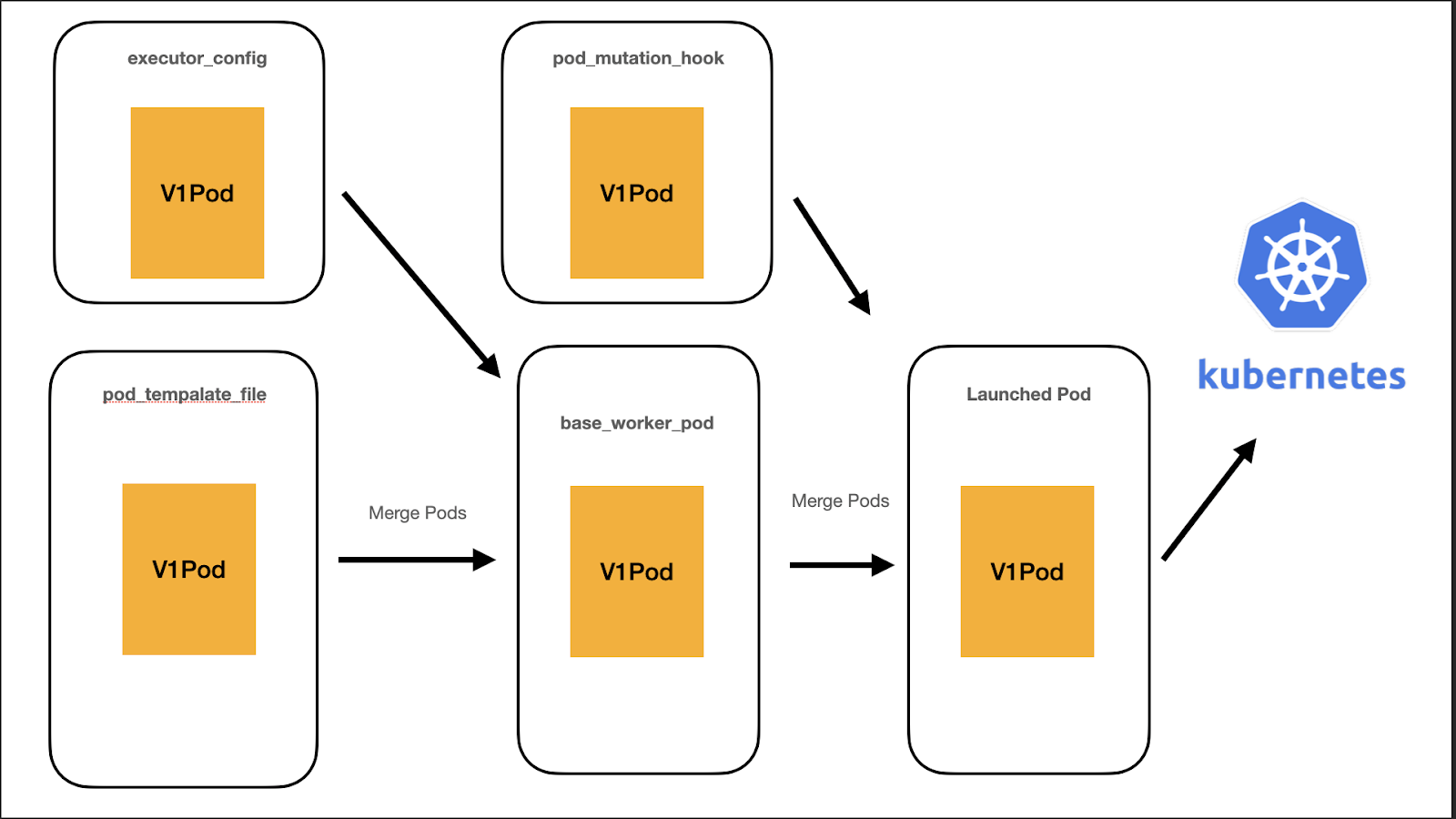
- Every step along the way, users have access to the Kubernetes models.V1Pod API
- Merging steps is much easier, faster, and stable.
- Removed 4k lines of code(!)
pod_template_file
- Infrastructure engineers can now define default pod layouts in yaml or json files
- Can define default
pod_template_filein theairflow.cfg
apiVersion: v1
kind: Pod
metadata:
name: dummy-name
spec:
containers:
- env:
- name: AIRFLOW__CORE__EXECUTOR
value: LocalExecutor
# Hard Coded Airflow Envs
- name: AIRFLOW__CORE__FERNET_KEY
valueFrom:
secretKeyRef:
name: RELEASE-NAME-fernet-key
key: fernet-key
- name: AIRFLOW__CORE__SQL_ALCHEMY_CONN
….
# Extra env
image: apache/airflow:2.0.0
imagePullPolicy: IfNotPresent
name: base
ports: []
volumeMounts:
- mountPath: "/opt/airflow/logs"
name: airflow-logs
- name: config
mountPath: "/opt/airflow/airflow.cfg"
subPath: airflow.cfg
readOnly: true
hostNetwork: false
restartPolicy: Never
securityContext:
runAsUser: 50000
fsGroup: 0
serviceAccountName: 'RELEASE-NAME-worker'
volumes:executor_config
- New “pod_override” object accepts a k8s.V1Pod instead of a dictionary.
- Can now use official Kubernetes API reference for building spec
- Add side-cars, secrets, affinities, etc.
volume_task = PythonOperator(
task_id="task_with_volume",
python_callable=test_volume_mount,
executor_config={
"pod_override": k8s.V1Pod(
spec=k8s.V1PodSpec(
containers=[
k8s.V1Container(
name="base",
volume_mounts=[
k8s.V1VolumeMount(
mount_path="/foo/",
name="test-volume"
)
],
)
],
volumes=[
k8s.V1Volume(
name="test-volume",
host_path=k8s.V1HostPathVolumeSource(path="/tmp/"),
)
],
)
),
},
)You can even point to a custom pod_template_file and then add overrides on top of it!
task_with_template = PythonOperator(
task_id="task_with_template",
python_callable=print_stuff,
executor_config={
"pod_template_file": os.path.join(
AIRFLOW_HOME, "pod_templates/basic_template.yaml"
),
"pod_override": k8s.V1Pod(
metadata=k8s.V1ObjectMeta(labels={"release": "stable"})
),
},
)KubernetesPodOperator
KubernetesPodOperator (KPO) is now in the cncf.kubernetes Provider. Visit the KubernetesPodOperator page of the Astronomer Registry to learn more.
- KPO is no longer bound to an Airflow version
- You can get upgrades and bug fixes more often without requiring an Airflow upgrade
- Backport providers for upgrading to 2.0
KPO Now Directly uses Kubernetes API
volume = k8s.V1Volume(
name='test-volume',
persistent_volume_claim=k8s.V1PersistentVolumeClaimVolumeSource(claim_name='test-volume'),
)
volume_mounts = [
k8s.V1VolumeMount(mount_path='/etc/foo', name='test-volume', sub_path=None, read_only=True)
]
env_vars = [k8s.V1EnvVar(name='key1', value='value1'), k8s.V1EnvVar(name='key2', value='value2')]
k = KubernetesPodOperator(
task_id="task" + self.get_current_task_name(),
in_cluster=False,
volume_mounts = volume_mounts,
volumes=[volume],
env=env_vars,
do_xcom_push=True,
)KPO now also allows templates
template_path = '/airflow/dags/basic_pod.yaml'
pod_spec = k8s.V1Pod(
metadata=k8s.V1ObjectMeta(
labels={"foo": "bar", "fizz": "buzz"},
),
spec=k8s.V1PodSpec(
containers=[
k8s.V1Container(
name="base",
env=[k8s.V1EnvVar(name="env_name", value="value")],
)
]
),
)
env_vars = [k8s.V1EnvVar(name='key1', value='value1'), k8s.V1EnvVar(name='key2', value='value2')]
k = KubernetesPodOperator(
task_id="task" + self.get_current_task_name(),
in_cluster=False,
pod_template_file=template_path,
full_pod_spec=pod_spec,
env=env_vars,
do_xcom_push=True,
)KEDA Autoscaler
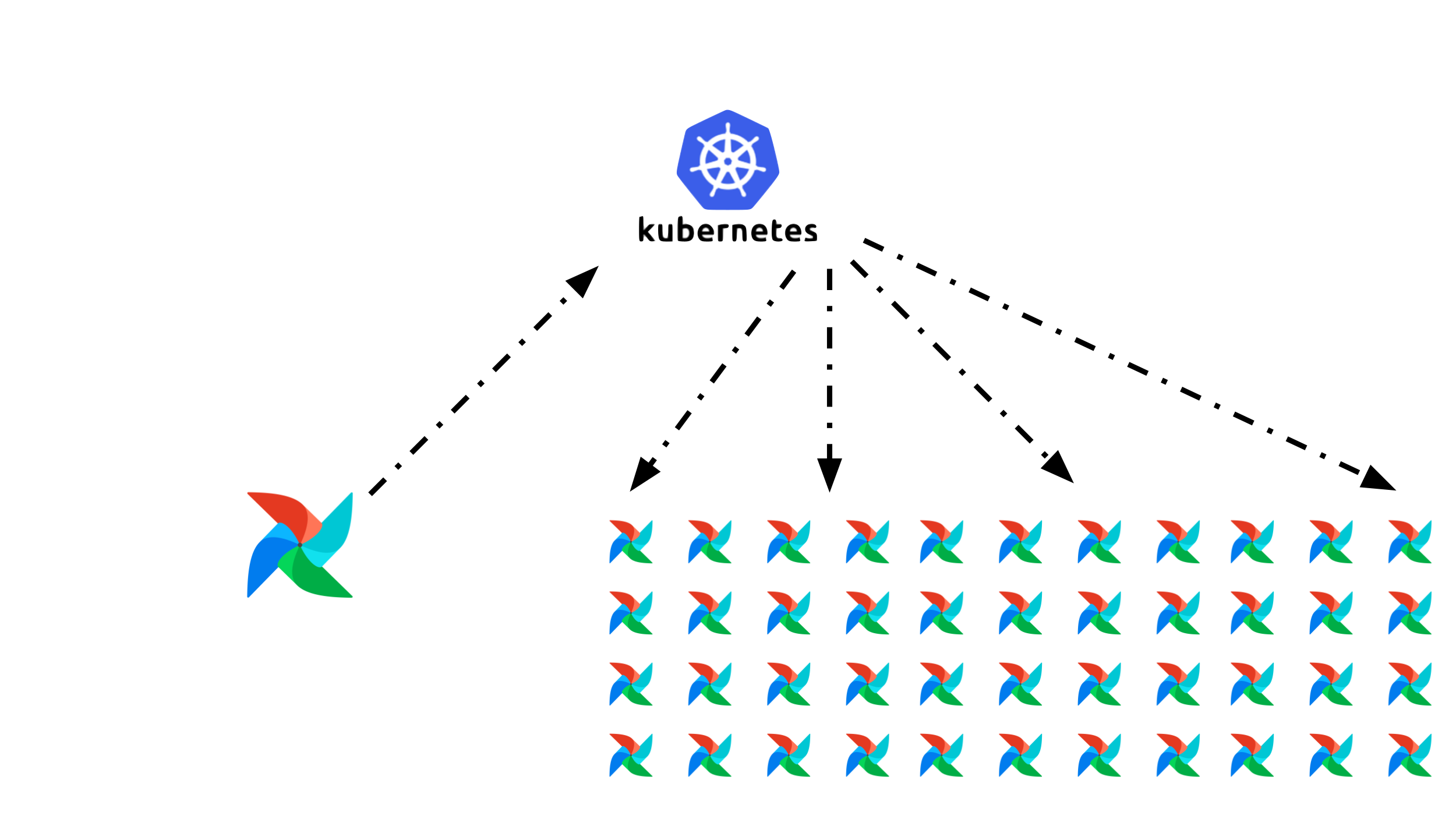
With KubernetesExecutor for every single task you launch, Airflow speaks to the Kubernetes API and launches a pod for that task and runs that pod to completion. This works fantastic for small to medium scale use cases. For really large scale cases, with thousands of tasks at a time, the Kubernetes Executor can become unwieldy.
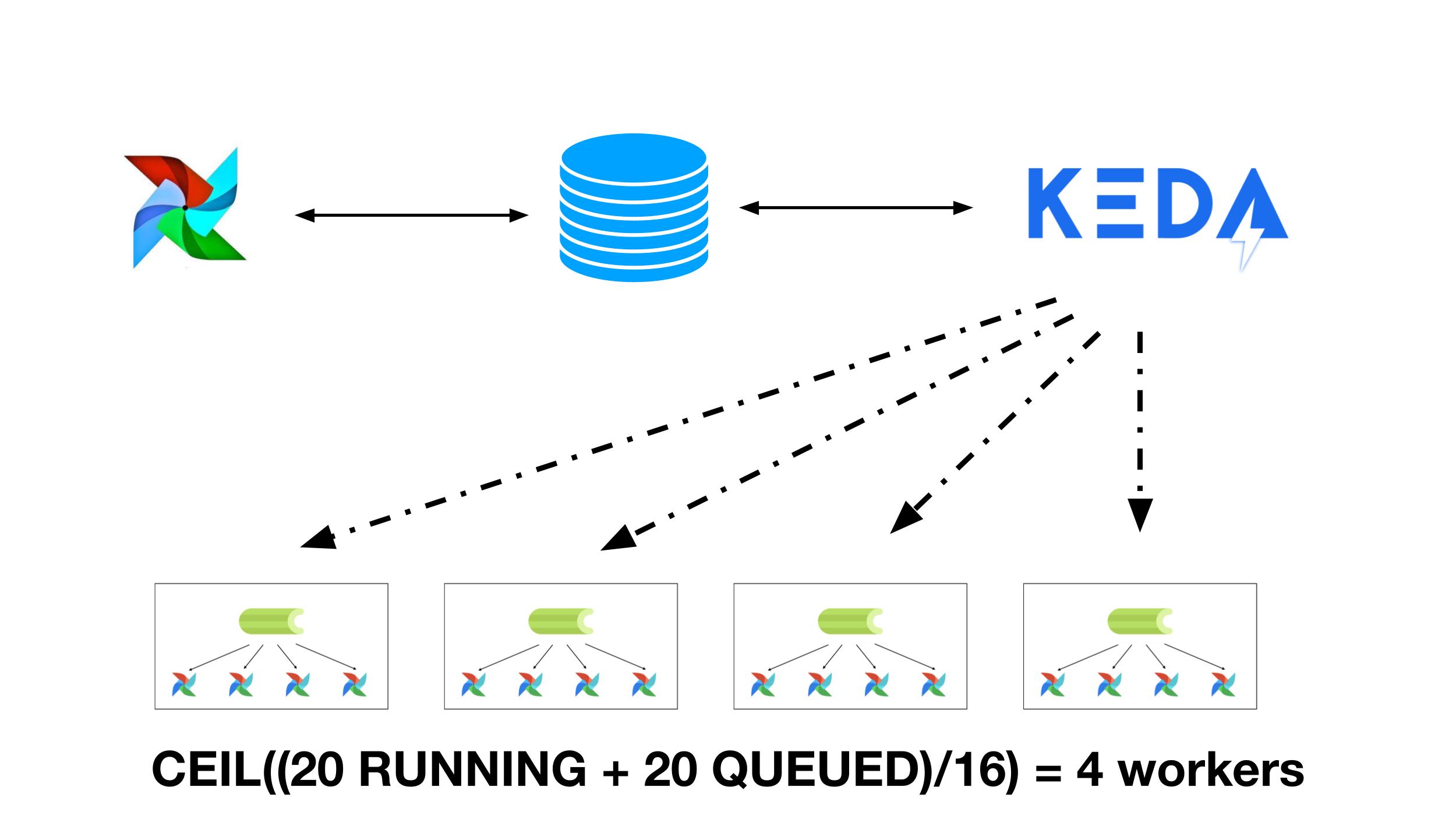
The KEDA Autoscaler allows you to create custom autoscalers. At Astronomer we created a PostgreSQL autoscaler and donated it back to the KEDA project.
The easiest way to get started with Apache Airflow® 2.0 is by using the Astronomer CLI. To make it easy you can get up and running with Airflow by following our Quickstart Guide.