Human-in-the-loop workflows with Airflow
Human-in-the-loop (HITL) workflows are processes that require human intervention, for example, to approve or reject an AI generated output, or choose a branch in a dag depending on the result of an upstream task. The Airflow standard provider contains a set of operators to create tasks that will wait for human input, either in the Airflow UI or through the Airflow REST API. Note that you need to be on Airflow 3.1+ to use the human-in-the-loop operators.
This guide covers the available HITL operators, as well as how to interact with them in the UI and via the API.
Assumed knowledge
To get the most out of this guide, you should have an existing knowledge of:
- Airflow basics. See Introduction to Apache Airflow.
- Airflow operators. See Operators 101.
- Deferrable operators. See Deferrable operators.
When to use human-in-the-loop workflows
Human-in-the-loop workflows are useful whenever you need the input from a human (or another entitiy outside of Airflow) within a dag. For example:
- Your dag uses AI to create responses to a support ticket, and you want to ask a human to review the response and approve it or request changes.
- Your dag generates a compliance report and you need a human to verify and acknowledge the results.
- You’d like to use AI to route product feature requests to the appropritate team and need a human to decide where to send edge cases.
- You have a dag that requires input from a domain expert, for example to input feedback gathered in user research interviews.
Human-in-the-loop workflows are very common, especially with increased usage of AI to generate assets that are in need of human review. The Airflow HITL features allows you to build these workflows and have non-technical team members provide their input either in the Airflow UI or via an implementation built around the relevant Airflow REST API endpoints.
Required Actions
Each task instance created by a human-in-the-loop operator creates a Required Action object. You can view a list of all required actions, pending and resolved, for your whole Airflow instance under Browse > Required Actions in the Airflow UI.
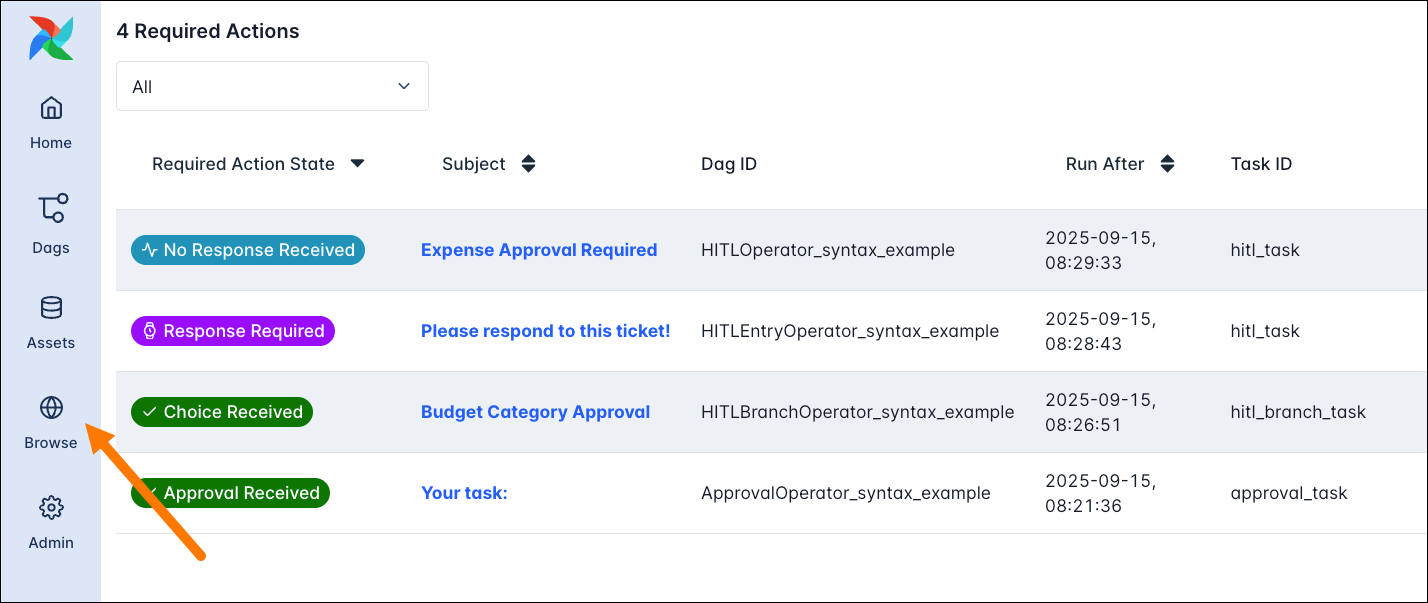
To respond to a required action you can either:
- Navigate to the task instance page’s Required Actions tab and respond directly in the UI.
- Make a call to the Airflow REST API’s update hitl detail endpoint.
Human-in-the-loop operators
There are 4 human-in-the-loop operators available in the Airflow standard provider:
- HITLOperator: The base class for all human-in-the-loop operators.
- ApprovalOperator: An specialised form of the HITLOperator where the two options are “Approve” and “Reject”.
- HITLBranchOperator: An specialised form of the HITLOperator where the user input provides a branching decision, choosing the (set of) task(s) to run next.
- HITLEntryOperator: An specialised form of the HITLOperator where the user provides input to a form.
All human-in-the-loop operators are implemented as deferrable operators, meaning that they will release their worker slot and run an asychronous process in the Triggerer component while waiting for the human input.
When choosing which human-in-the-loop operator to use, consider the following:
- If the human-in-the-loop action centers around a branching decision (choosing the next task(s) to run), use the
HITLBranchOperator. - If you are looking to make a binary decision (approval or rejection of information displayed at runtime), use the
ApprovalOperator. If users need to give additional input add a form field usingparams. - If you are mostly interested in letting users provide input to a form, use the
HITLEntryOperator. - For all other use cases, you can use the
HITLOperatordirectly. It allows you to display custom options for your user to chose from, as well as additional input fields withparams.
In a lot of cases you’ll likely be using a combination of these operators to build your human-in-the-loop workflow, for example using the HITLBranchOperator upstream to choose whether to accept an AI generated ticket response or escalate the ticket to a human. Then, downstream, the human’s answer can be provided in a HITLEntryOperator. Both, the user decision (chosen_options) and any input to parameters (params_input) are available for downstream tasks to use by pulling the information from XComs.
HITLOperator
The HITLOperator is the base class for all human-in-the-loop operators. It is the most versatile operator in this operator family. With it you can display information, let the user choose one or more from a list of options and accept additional input via a form based on Airflow params.
Two parameters are mandatory when instantiating the HITLOperator:
subject(required): The subject of the templated action which is displayed as the title in the Required Actions tab. This field is templatable, which means you can use Jinja templates to render information at runtime, including information computed by an upstream task.options(required): A list of strings that are rendered as response options at the bottom of the required action form. Note that the list cannot be empty. The chosen options can be retrieved in downstream tasks by pulling the information from XComs, which is stored as a list under thechosen_optionskey.
There are also several optional parameters that you can use to further configure the behavior of the HITLOperator:
body: The main text body. This field is templatable as well and supports markdown formatting.defaults: Optionally, you can provide a list of one or more options that are selected by default if the task times out before a human responds. All default options need to be in theoptionslist.multiple: If set toTrue, the user can select multiple options. Default isFalse.params: With this parameters you can create form fields for any user input to the required action using Airflow params. Note that not all param functionality is supported for human-in-the-loop operators. Params can be retrieved in downstream tasks by pulling the information from XComs, which is stored as a nested dictionary under theparams_inputkey.execution_timeout: This is a BaseOperator parameter that times out the task after a specified duration provided as a datetime.timedelta or pendulumduration object. Default isNone. After the timeout has been reached the behavior depends on whether you provided adefaultslist or not:- If you provided a
defaultslist, the default(s) is/are chosen as the response and the task succeeds. - If you did not provide a
defaultslist, the task fails.
- If you provided a
assigned_users: A list of all users who are allowed to respond to the required action. Users are provided asHITLUserobjects (from airflow.sdk.execution_time.hitl import HITLUser) with anidandnamefield.- If you are running Airflow on Astro, the id of each user is their Astro ID in the format
cl1a2b3cd456789ef1gh2ijkl3. You can find each user’s Astro ID under Organization -> Access Management. - If you are using the SimpleAuthManager the id of each user is their username.
- If you are using the FabAuthManager the id of each user is their email.
- If you are running Airflow on Astro, the id of each user is their Astro ID in the format
notifiers: A list of notifiers of which to execute the.notify()method when the task starts running. See Use notifiers with HITL operators for an example.
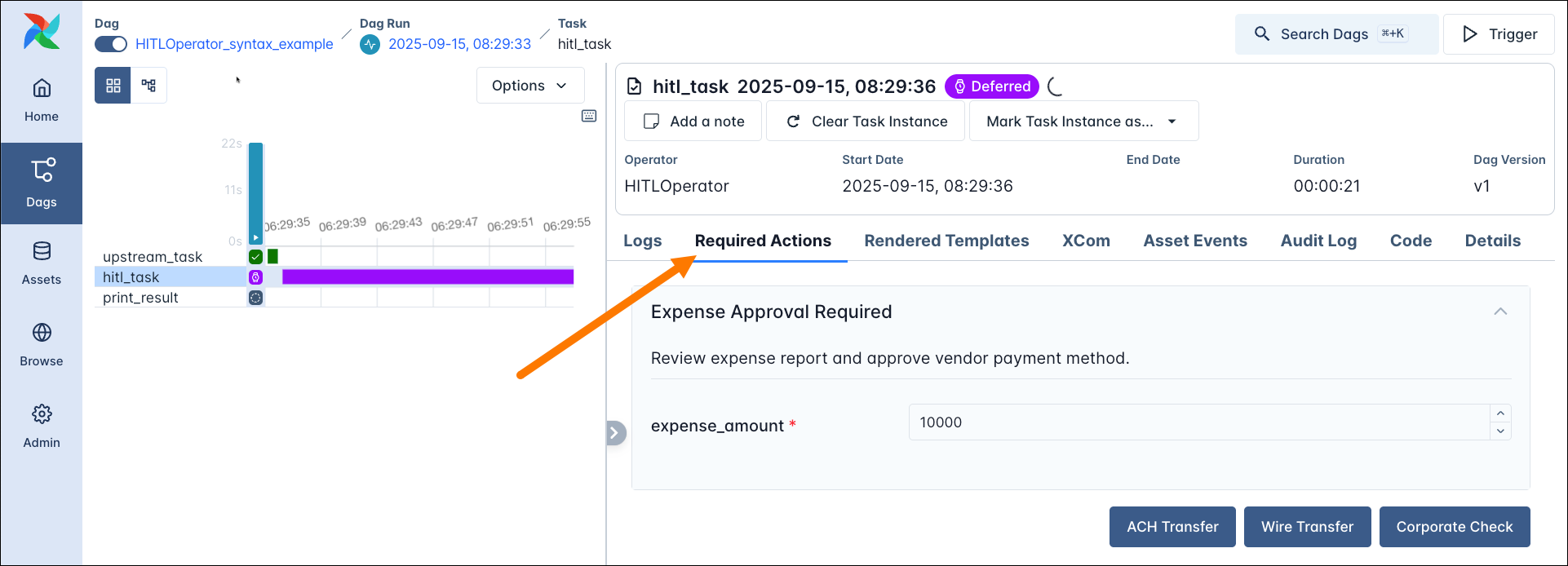
The following example shows a simple use of the HITLOperator where the output of an upstream task is fetched from XComs and the user is given 3 response options to choose from. One additional input field for the expense_amount is rendered in the Airflow UI using an Airflow param. After 5 minutes (execution_timeout) the task times out and chooses the default option: ACH Transfer as the response and 10000 as the expense amount.
The downstream print_result task prints out the information pushed to XComs by the HITLOperator task: the chosen_options and the params_input values.
The open required action form is displayed on the task instance page’s Required Actions tab.
ApprovalOperator
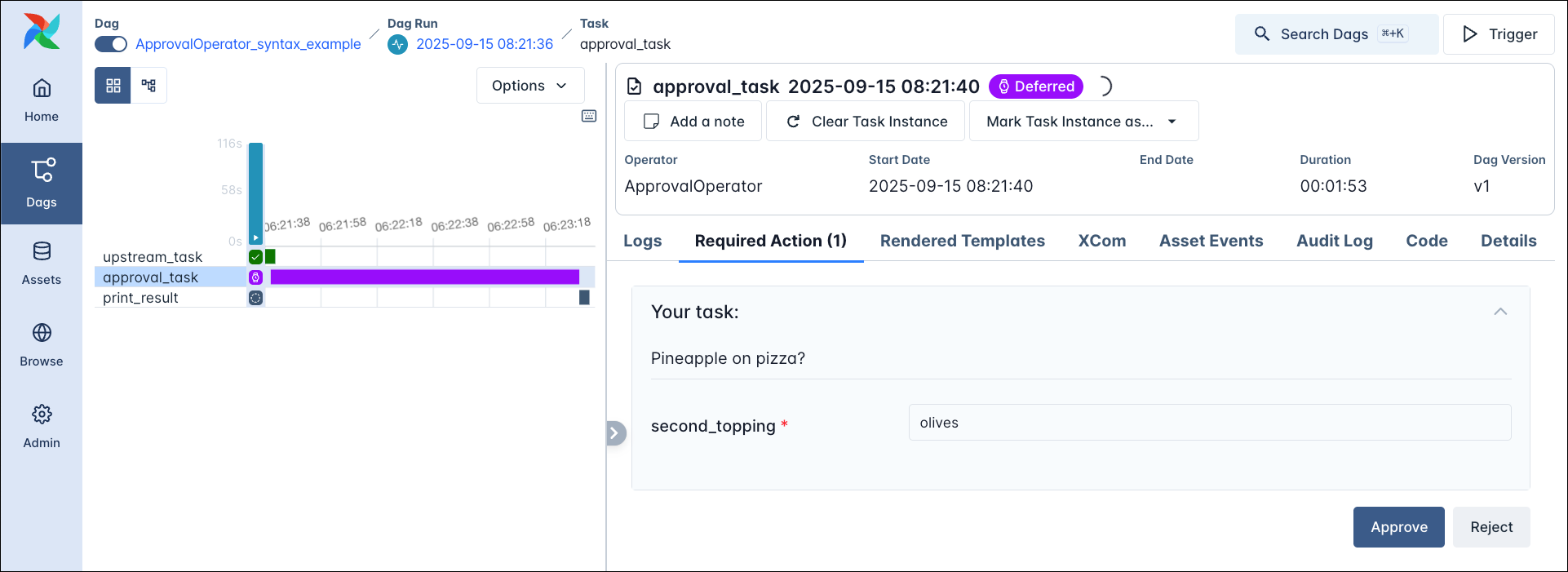
The ApprovalOperator is a specialised form of the HITLOperator where the only two possible response options are Approve and Reject. Additionally, you can provide param form fields for any user input to the required action using Airflow params.
If the human chooses to Approve the task succeeds. If the human chooses to Reject the task succeeds but all downstream tasks are skipped.
The action form shows the two options Approve and Reject alongside any param form fields.
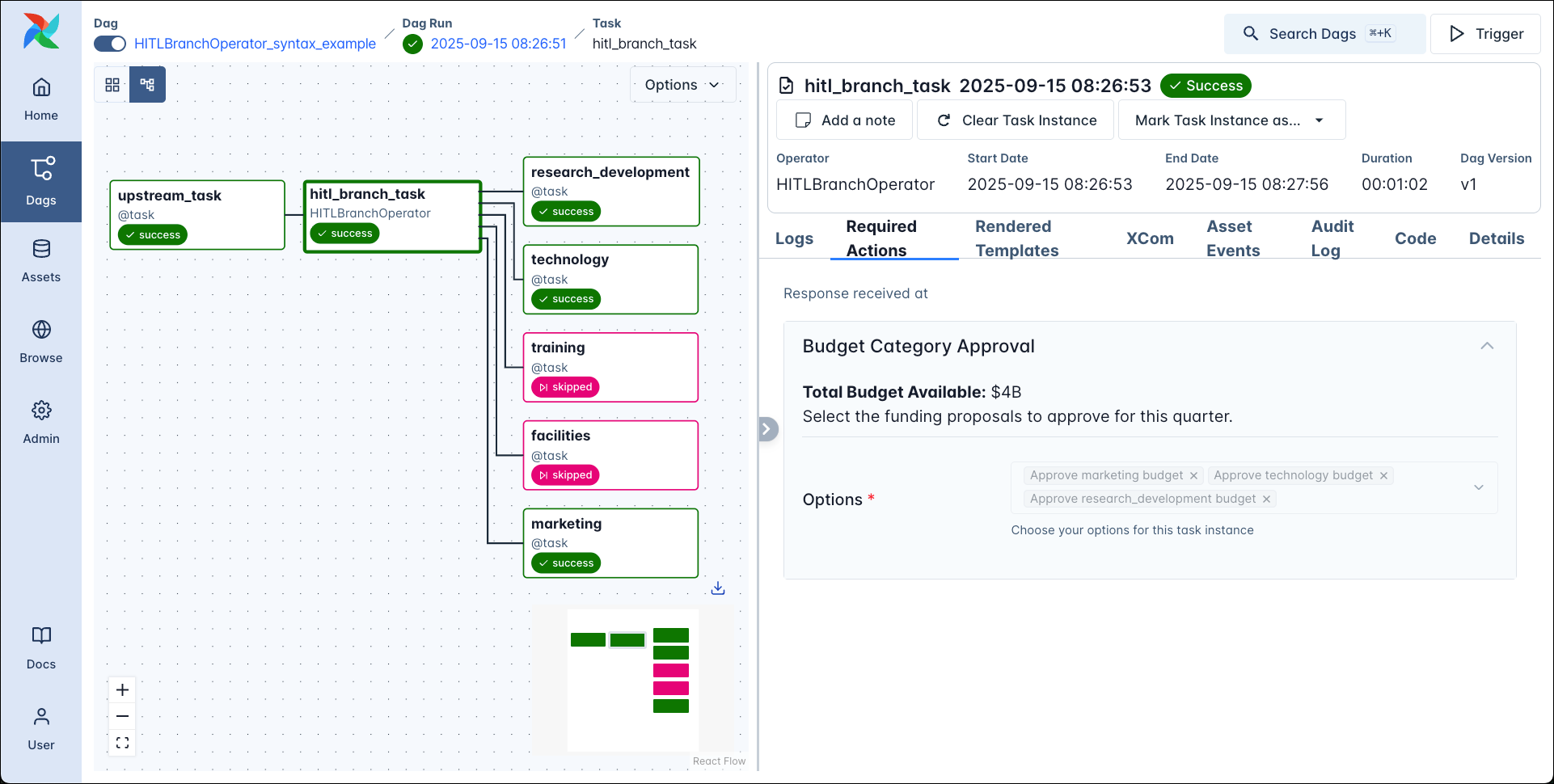
HITLBranchOperator
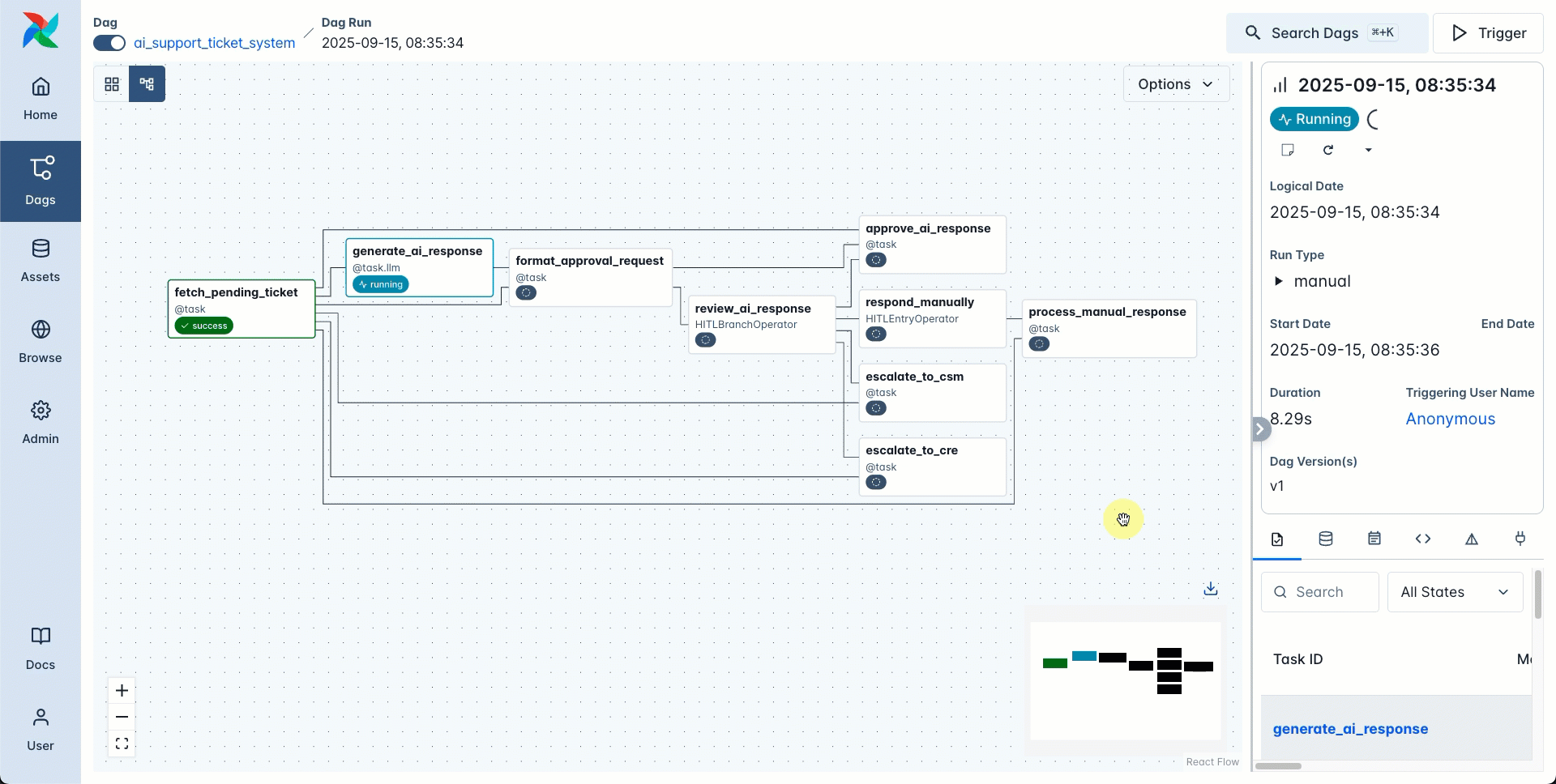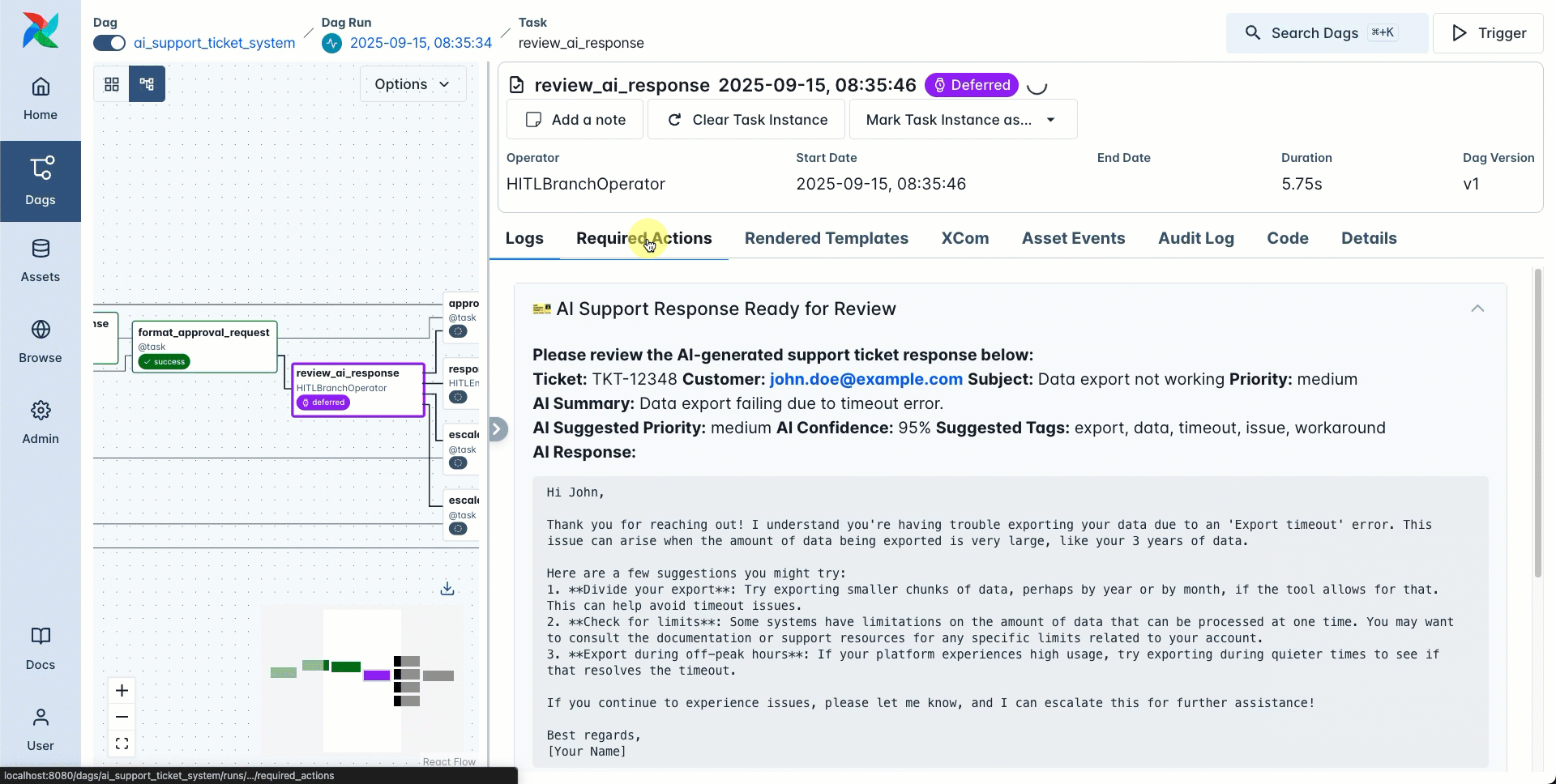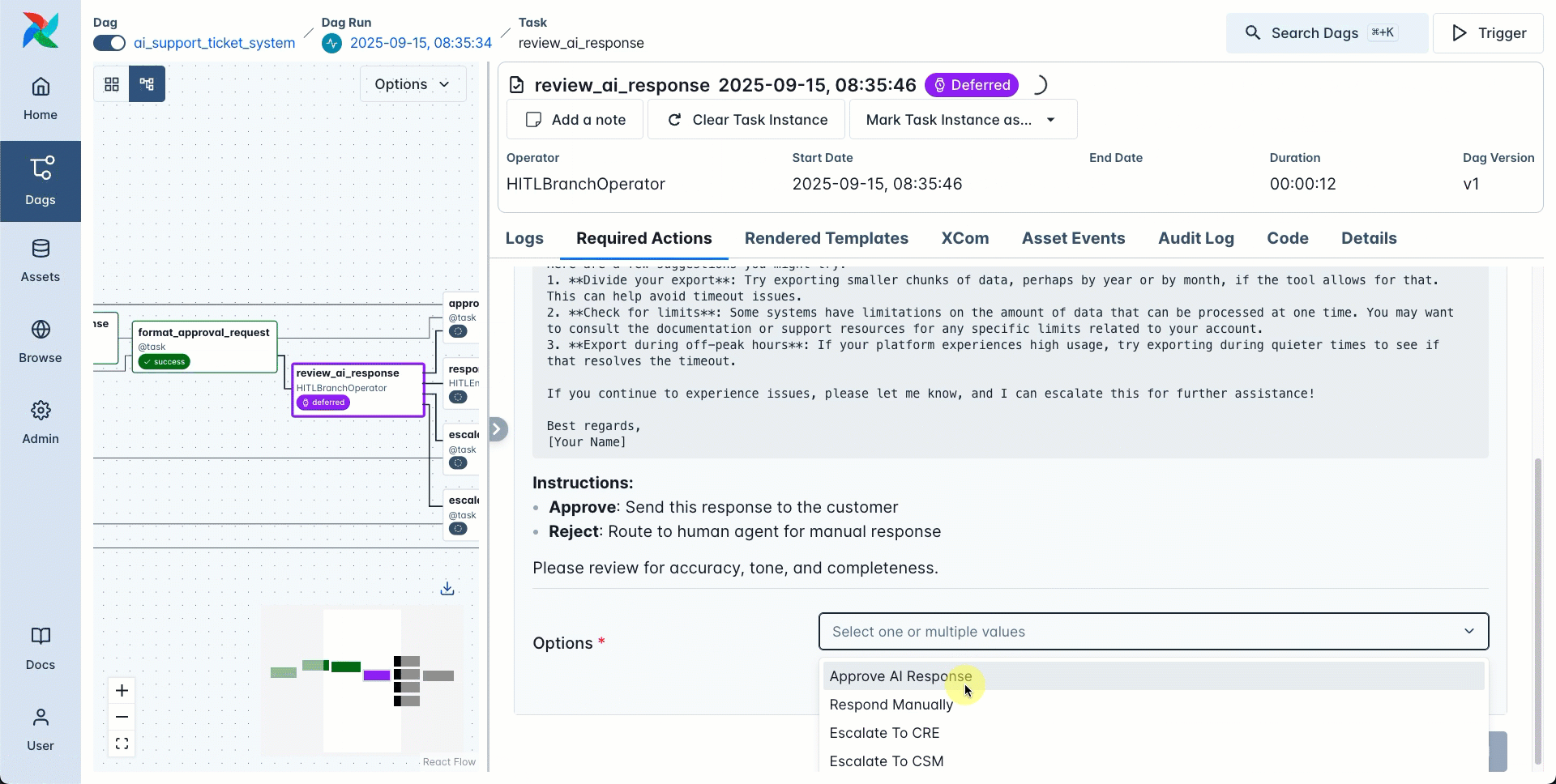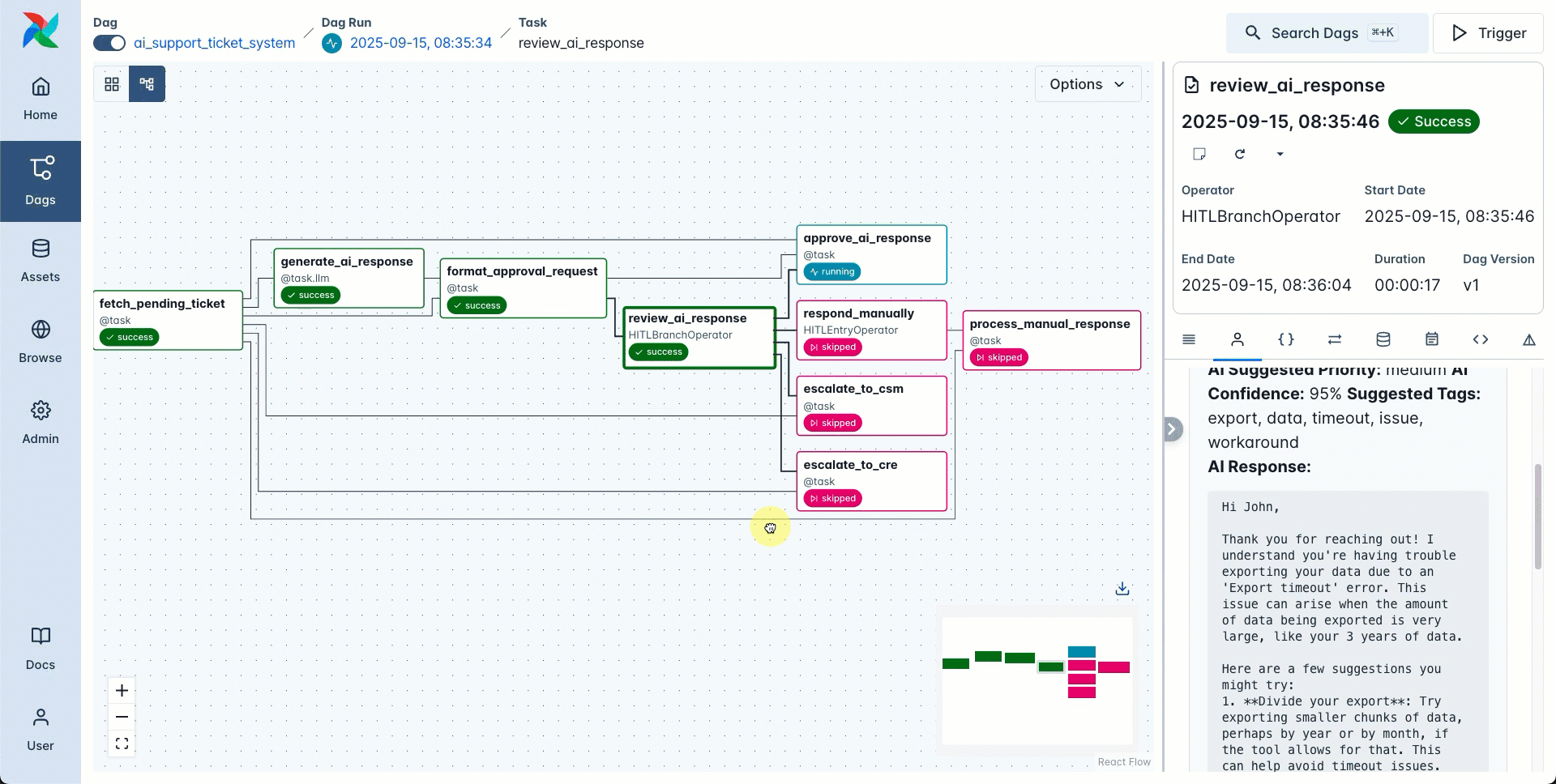
If you want to branch your dag based on the human input, you can use the HITLBranchOperator. This operator allows the user to choose one or more tasks that are directly downstream of the HITLBranchOperator task to run next. All tasks that are not chosen will be skipped.
You can use the options_mapping parameter to map the human facing options to the task IDs of the tasks that are downstream of the HITLBranchOperator task.
The screenshot below shows the graph view created by the code snippet above with 5 tasks downstream of the HITLBranchOperator task and the Required Actions tab showing the form input.
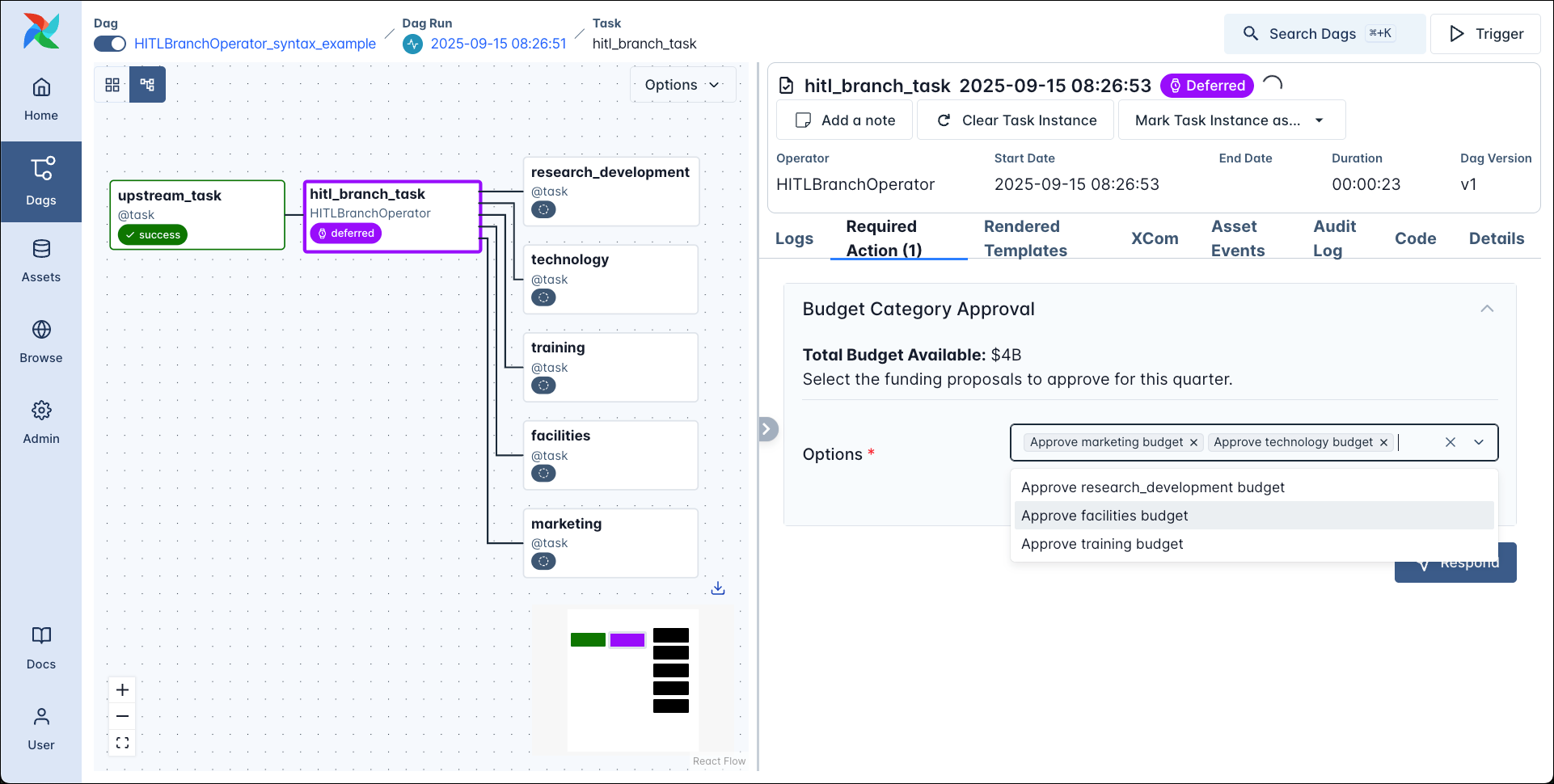
After approving the budget for 3 of the categories the dag completes with 3 downstream tasks being run and 2 being skipped.
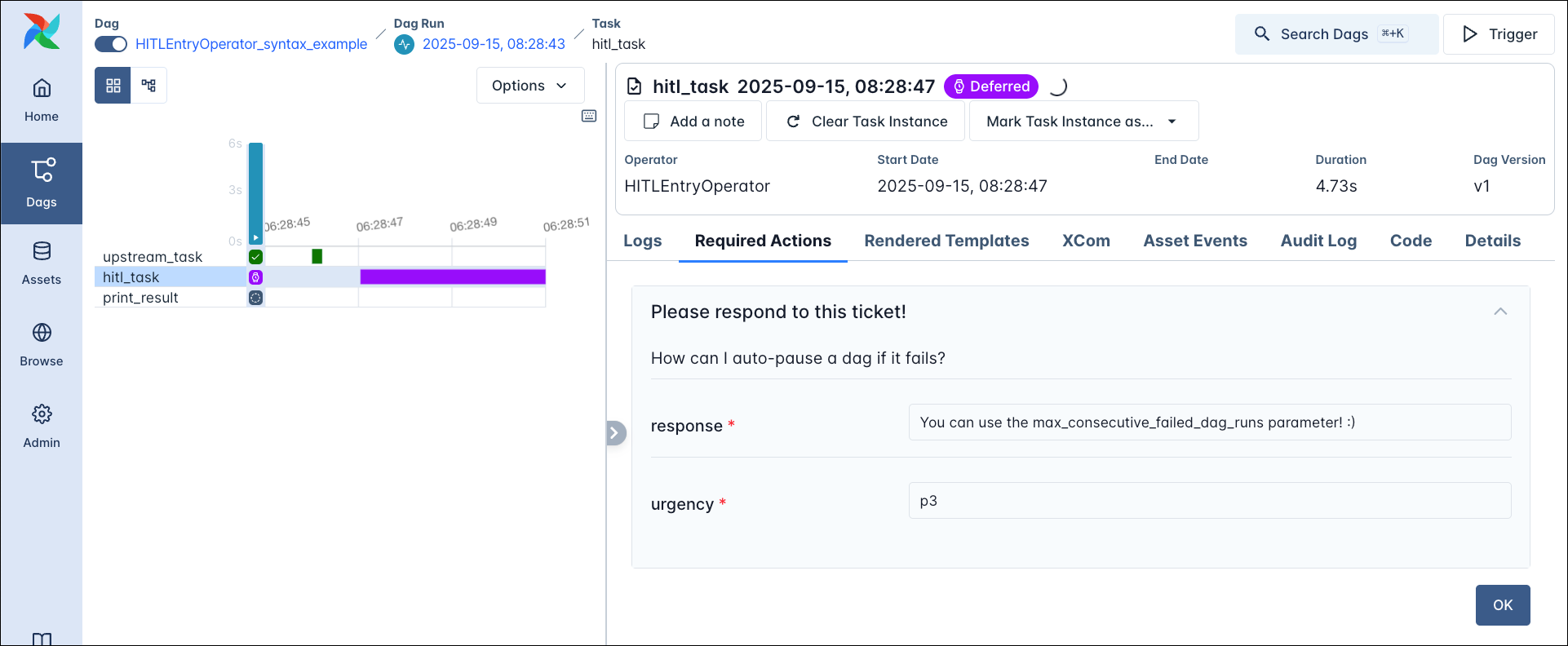
HITLEntryOperator
The HITLEntryOperator is a specialised form of the HITLOperator where the user provides input to a form and then submits the input without choosing from a list of options.
Use notifiers with HITL operators
You can use an Airflow notifier to send information from the human-in-the-loop operator to another system, such as Slack or email. The .notify() method of the notifier is executed when the task starts running. A simple implementation is to use the HITLOperator.generate_link_to_ui_from_context method to return a link to the required action in the Airflow UI for users to click on to respond.
The code snippet below shows a sample notifier MyNotifier that prints the required action information and the link to the required action to the Airflow logs.
Of course you can also add all regular callback functions such as on_failure_callback, on_success_callback, etc. to the human-in-the-loop operators.
Human-in-the-loop API endpoints
If your human (or other entity) does not have access to the Airflow UI, you can use the Airflow REST API to poll for required actions and respond to them.
The relevant endpoints are:
GET api/v2/hitlDetails/to get a list of required actions in an Airflow instance filtered by flags likestate,dag_idand more.GET api/v2/hitlDetails/{dag_id}/{dag_run_id}/{task_id}to get the details of a specific required action.PATCH api/v2/hitlDetails/{dag_id}/{dag_run_id}/{task_id}to respond to a specific required action.
These API calls can be combined with others to create scripts like the one below that allows you to respond to all pending required actions in a specific dag from the command line.