Create and use params in Airflow
Params are arguments which you can pass to an Airflow DAG or task at runtime and are stored in the Airflow context dictionary for each DAG run. You can pass DAG and task-level params by using the params parameter.
Params are ideal to store information that is specific to individual DAG runs like changing dates, file paths or ML model configurations. Params are not encrypted and therefore not suitable to pass secrets. See also Best practices for storing information in Airflow.
This guide covers:
- How to pass params to a DAG at runtime.
- How to define DAG-level param defaults which are rendered in the Trigger DAG UI.
- How to access params in an Airflow task.
- The hierarchy of params in Airflow.
Assumed knowledge
To get the most out of this guide, you should have an understanding of:
- Airflow DAGs. See Introduction to Airflow DAGs.
- Airflow operators. See Operators 101.
- Airflow context. See Access the Apache Airflow context.
Pass params to a DAG run at runtime
Params can be passed to a DAG at runtime in four different ways:
- In the Airflow UI by using the Trigger DAG form. This form appears when you click on the Trigger DAG (Play) button in the Airflow UI.
- Running a DAG with the
--confflag using the Airflow CLI (airflow dags trigger). - Using the TriggerDagRunOperator with the
confparameter. - Making a
POSTrequest to the Airflow REST APIs Trigger Dag Run endpoint and using theconfparameter.
Param values passed to a DAG by any of these methods will override existing default values for the same key as long as the Airflow core config dag_run_conf_overrides_params is set to True (which is the default setting).
Info
You can only pass params to a DAG that are JSON-serializeable. Any params that are not JSON-serializeable will cause a DAG Import Error (
ParamValidationError) upon DAG parsing.
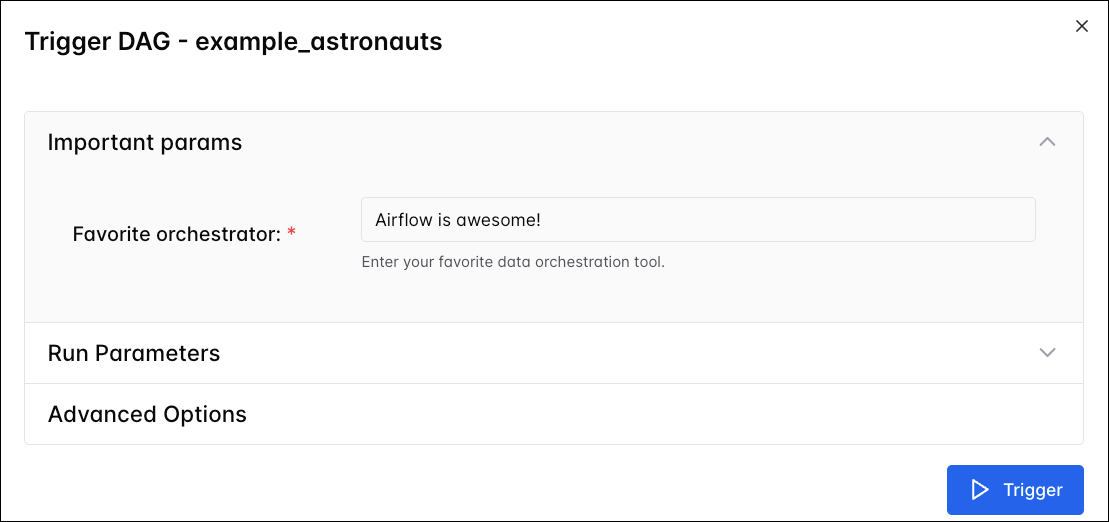
Trigger DAG form
You can pass params to DAGs from the Airflow UI by clicking on the Play button in the DAGs overview or on the blue Trigger button on an individual DAG page.
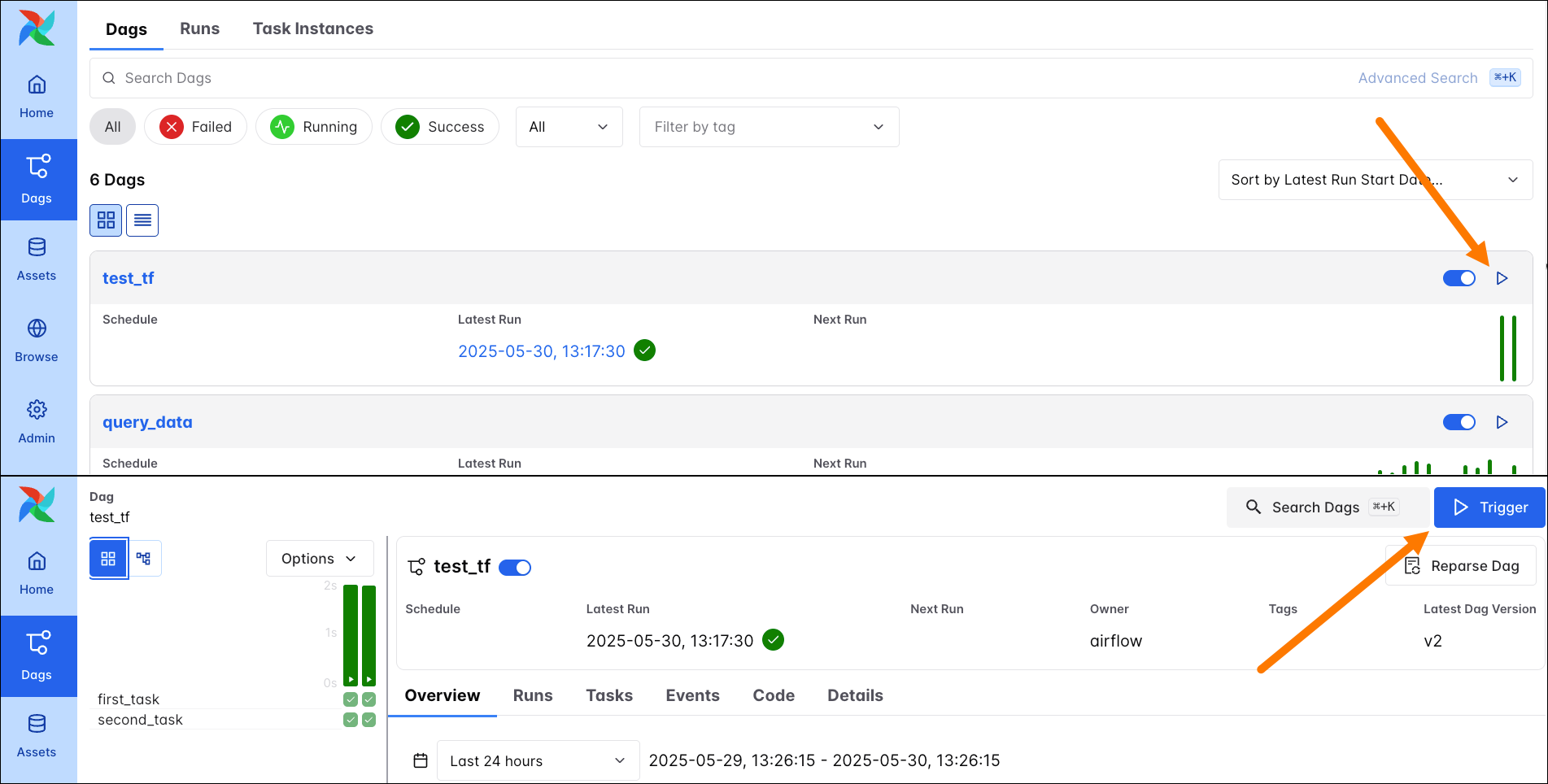
This button opens a form in which you can specify details for the DAG run. If the DAG has any params with defaults values defined, the form will render a field for each those params under Run Parameters. Additional params can be added under Advanced Options -> Configuration JSON.
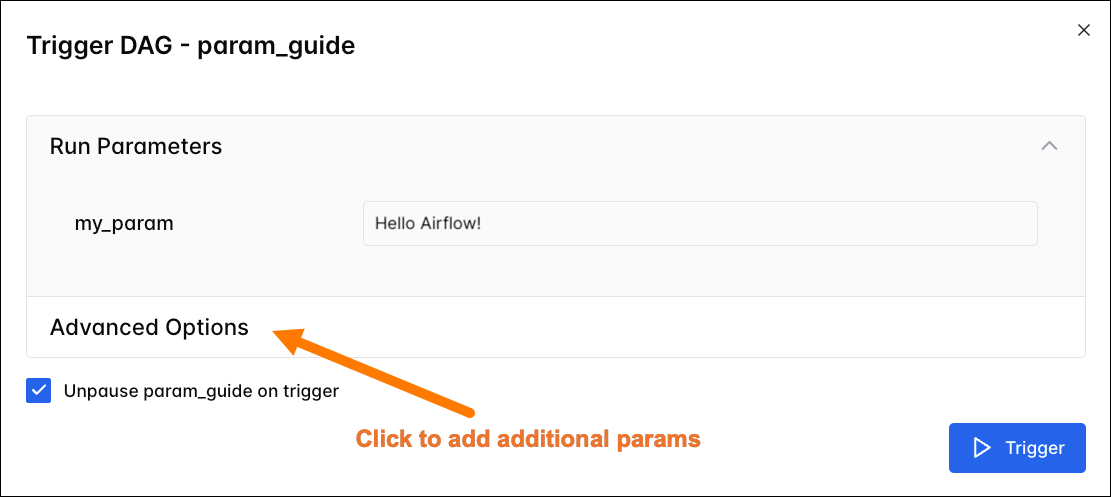
Under Advanced Options, you can also set the Logical Date, define a Run ID, and add a Dag Run Note for the manual DAG run. Note that any params already defined under Run Parameters will be included in the Configuration JSON by default.
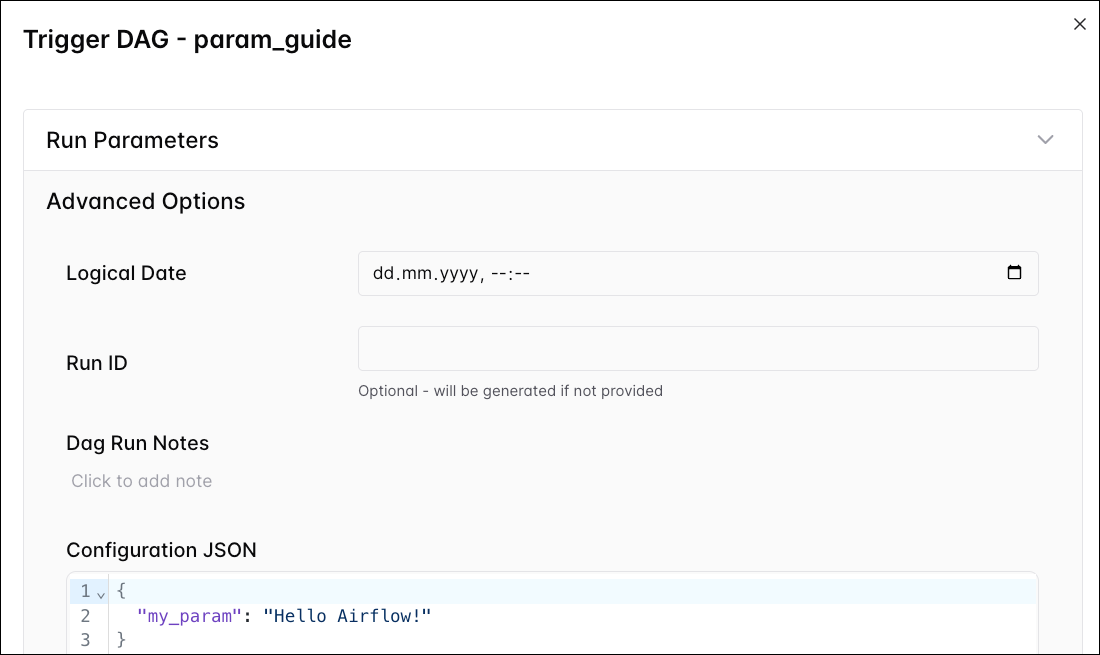
In the Trigger DAG form:
- You can change any default values for params that have been defined in the DAG file under Run Parameters or in the Configuration JSON.
- You can add new params under Advanced Options -> Configuration JSON.
- You can set the Logical Date of the DAG run to any date. Note that you can also provide no logical date, by clearning it in the calendar picker.
- You can set the Run ID to any string. If no Run ID is specified, Airflow generates one based on the run after date.
- You can add a Dag Run Note to the DAG run.
After setting the configuration, you can start the DAG run with the Trigger button.
CLI
When you run an Airflow DAG from the CLI, you can pass params to the DAG run by providing a JSON string to the --conf flag. For example, to trigger the params_default_example DAG with the value of Hello from the CLI for param1, run:
Astro
Run Airflow commands from the Astro CLI using astro dev run:
Airflow
The CLI prints the configuration for the triggered run to the command line:

You can use a --conf flag with the following Airflow CLI sub-commands:
airflow dags backfillairflow dags testairflow dags trigger
TriggerDagRunOperator
The TriggerDagRunOperator is a core Airflow operator that allows you to start a DAG run from within another DAG. You can use the TriggerDAGRunOperator conf param to trigger the dependent DAG with a specific configuration.
The DAG below uses the TriggerDagRunOperator to trigger the tdro_example_downstream DAG while passing a dynamic value for the upstream_color param via the conf parameter. The value for upstream_color is passed via a Jinja template pulling the return value of an upstream task via XCom.
Taskflow
Traditional
Runs of the tdro_example_downstream DAG that are triggered by this upstream DAG will override the default value of the upstream_color param with the value passed via the conf parameter, which leads to the print_color task to print either red, green, blue or yellow.
Taskflow
Traditional
Define DAG-level param defaults
To specify params for all runs of a given DAG, pass default values to the param parameter of the @dag decorator or the DAG class in your DAG file. You can directly specify a default value or use the Param class to define a default value with additional attributes.
The DAG below has two DAG-level params with defaults: param1 and param2, the latter only accepting integers.
Taskflow
Traditional
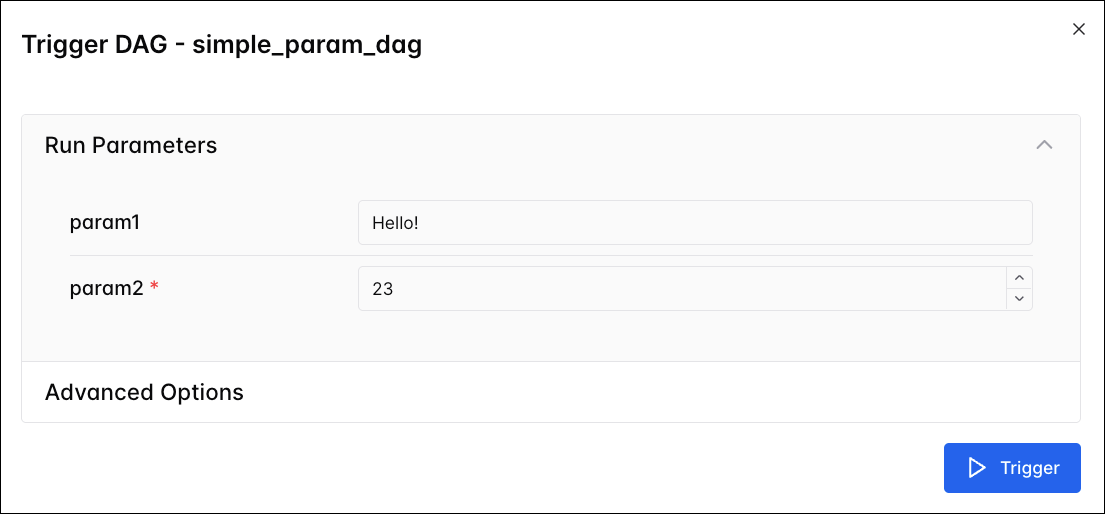
If you define DAG-level param defaults, the Trigger DAG form renders a field for each param. From this UI, you can then override your defaults for individual DAG runs. A param with a red asterisk is a required param.
Info
When you specify a required
typefor a param, the field will be a required input by default because of JSON validation. To make a field optional but still require a specific input type, allow NULL values by setting the type to["null", "<my_type>"].
Info
If you do not specify a type for your param, Airflow will infer it based on the default value you provide.
Param types
The following param types are supported:
string: A string. This is the default type.null: Allows the param to be None by being left empty.integer: An integer.number: A float (or integer).boolean:TrueorFalse.array: An HTML multi line text field, every line edited will be made into a string array as the value.object: A JSON entry field.
Param attributes
Aside from the type attribute, the Param class has several other attributes that you can use to define how users interact with the param:
title: The title of the param that appears in the Trigger DAG UI.description: A description of the param.section: Creates a section under which the param will appear in the Trigger DAG UI. All params with no specified section will appear under the default section DAG conf Parameters.format: A JSON format that Airflow will validate a user’s input against.enum: A list of valid values for a param. Setting this attribute creates a dropdown menu in the UI.const: Defines a permanent default value and hides the param from the Trigger DAG UI. Note that you still need to provide adefaultvalue for the param.
All Param attributes are optional to set. For string type params, you can additionally set minLength and maxLength to define the minimum and maximum length of the input. Similarly, integer and number type params can have a minimum and maximum value.
Param examples in the Airflow UI
This section presents a few examples of params and how they are rendered in the Trigger DAG UI.
The code snippet below defines a mandatory string param with a few UI elements to help users input a value.
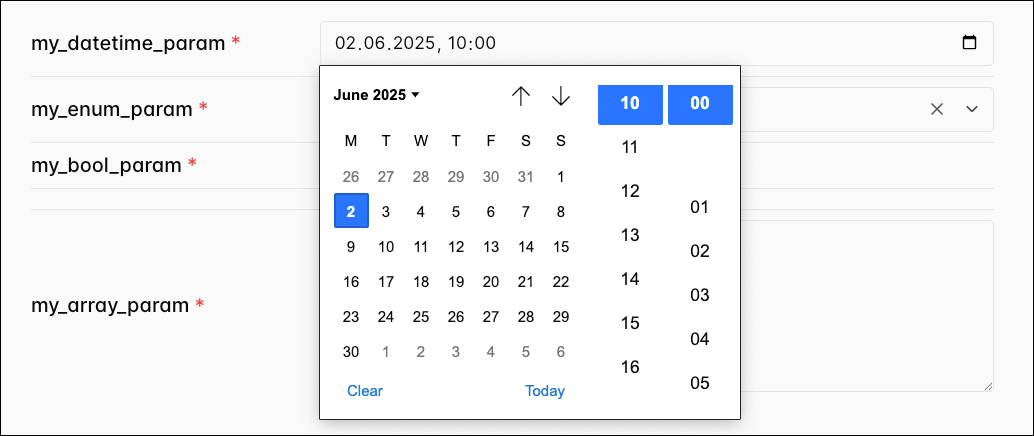
When you define date, datetime, or time param, a calendar picker appears in the Trigger DAG UI.
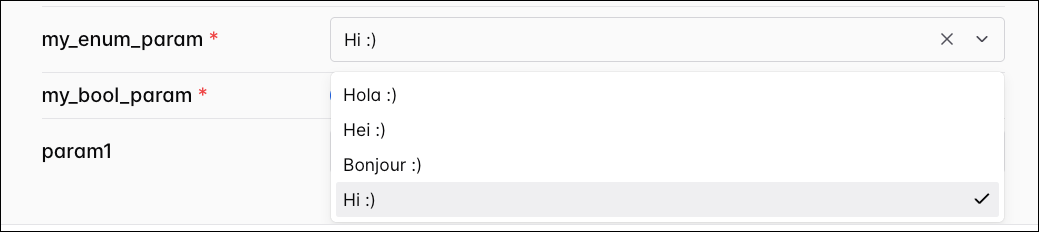
Providing a list of values to the enum attribute will create a dropdown menu in the Trigger DAG UI. Note that the default value must also be in the list of valid values provided to enum. Due to JSON validation rules, a value has to be selected.
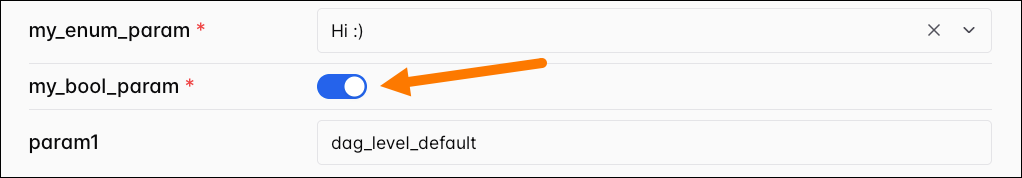
A boolean type param will create a toggle in the Trigger DAG UI.
An array type param will create a multi-line text field in the Trigger DAG UI. Each line will be converted to an item in the array.

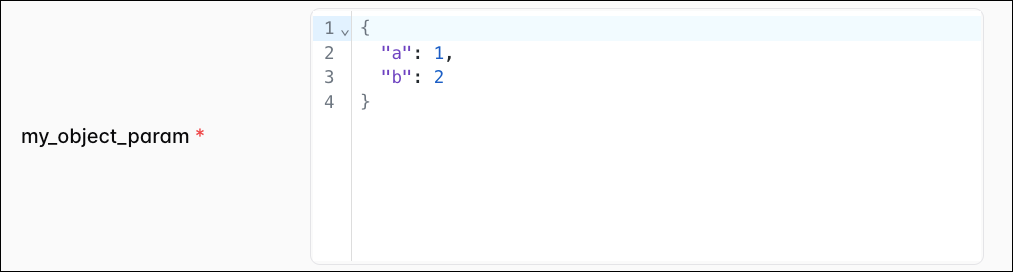
An object type param will create a JSON entry field in the Trigger DAG UI. The value of the param must be a valid JSON object.
Define task-level param defaults
You can set task-level param defaults in the same way as for DAG-level params. If a param of the same key is specified at both the DAG and task level, the DAG-level param will take precedence.
Taskflow
Traditional
Access params in a task
You can access params in an Airflow task like you can with other elements in the Airflow context.
Taskflow
Traditional
Params are also accessible as a Jinja template using the {{ params.my_param }} syntax.
If you try to access a param that has not been specified for a specific DAG run, the task will fail with an exception.
Param precedence
The order of precedence for params, with the first item taking most precedence, is as follows:
- Params that have been provided for a specific DAG run by a method detailed in pass params to a DAG run at runtime as long as the Airflow config core.dag_run_conf_overrides_params is set to
True. - Param defaults that have been defined at the DAG level.
- Param defaults that have been defined at the task level.