Data quality
Public Preview
This feature is in Public Preview.Astro Observe data quality helps you monitor tables to ensure data accuracy, completeness, and integrity across your pipelines. It automatically tracks key metrics such as column null percentages, schema changes, and table row counts to detect anomalies or unexpected shifts in your data.
Configure permissions
Before connecting to Astro Observe, configure the necessary permissions for your data platform.
Snowflake
Databricks
For Snowflake connections, the Observe role must have access to both the ACCOUNT_USAGE and INFORMATION_SCHEMA system tables. The service user must have a default warehouse configured to support discovery and ongoing data quality monitoring.
Setup key-pair authentication in Snowflake (recommended)
Astronomer recommends key-pair authentication for Snowflake service users. Generate an RSA key pair, then assign the public key to the Observe service user to enable secure authentication.
All Snowflake integrations require that the Observe role has access to both ACCOUNT_USAGE and INFORMATION_SCHEMA system tables. The service user must have a default warehouse configured for all discovery and monitoring operations.
Set up a connection
After you configure permissions for your data platform, create an Observe connection.
Fill in connection details
Snowflake
Databricks
Complete the following fields:
- Name: A name for the connection.
- Description: Optional description.
- Connection Type: Select Snowflake.
- Polling Schedule: How frequently Observe polls Snowflake for metrics (examples: every 1 hour, 6 hours, 1 day). Polling frequency is the maximum rate at which Observe updates data quality metrics and monitors; more frequent polling may increase Snowflake compute costs.
- Account Identifier: Your Snowflake account identifier (for example,
FY02423-GP2141). Observe maps assets to a connection by account identifier. - Username: The Snowflake service user (
ASTRO_OBSERVE_USER). - Private Key: Paste your private key for key-pair authentication if using key-pair auth.
Only one Observe connection is allowed per Snowflake account identifier. If you have multiple Snowflake accounts, create a separate connection for each account identifier.
Navigating data quality in Astro Observe
Asset Catalog
Navigate to Asset Catalog, filter by your data platform (for example, Snowflake tables or Databricks tables), and select the desired table.
You can sort tables by popularity to quickly identify frequently used tables. Popularity rankings are based on query frequency and the number of unique users accessing each table.
Schema
The Schema tab shows table structure details:
- Column names
- Data types
- Completeness status
- Nullability
- Default values
You can enable monitoring for specific columns to actively track completeness.
Event Timeline
The Event Timeline tab shows data quality events for a selected timeframe. Events are color-coded by severity: Success, Neutral, and Failure. Click an event to view details, historical patterns, and affected metrics.
Data quality
The data quality tab provides visualizations for monitored metrics:
- Table Volume: track changes in row counts and percent change over time to identify unexpected fluctuations.
- Completeness: visualize column null percentages against thresholds to surface completeness problems.
Monitors
The Monitors tab lists all configured data quality monitors (Column Null Percentage, Table Schema Change, Row Volume Change). Each monitor’s schedule and modification history are shown for management. To learn how to create data quality monitors, see Data quality monitors.
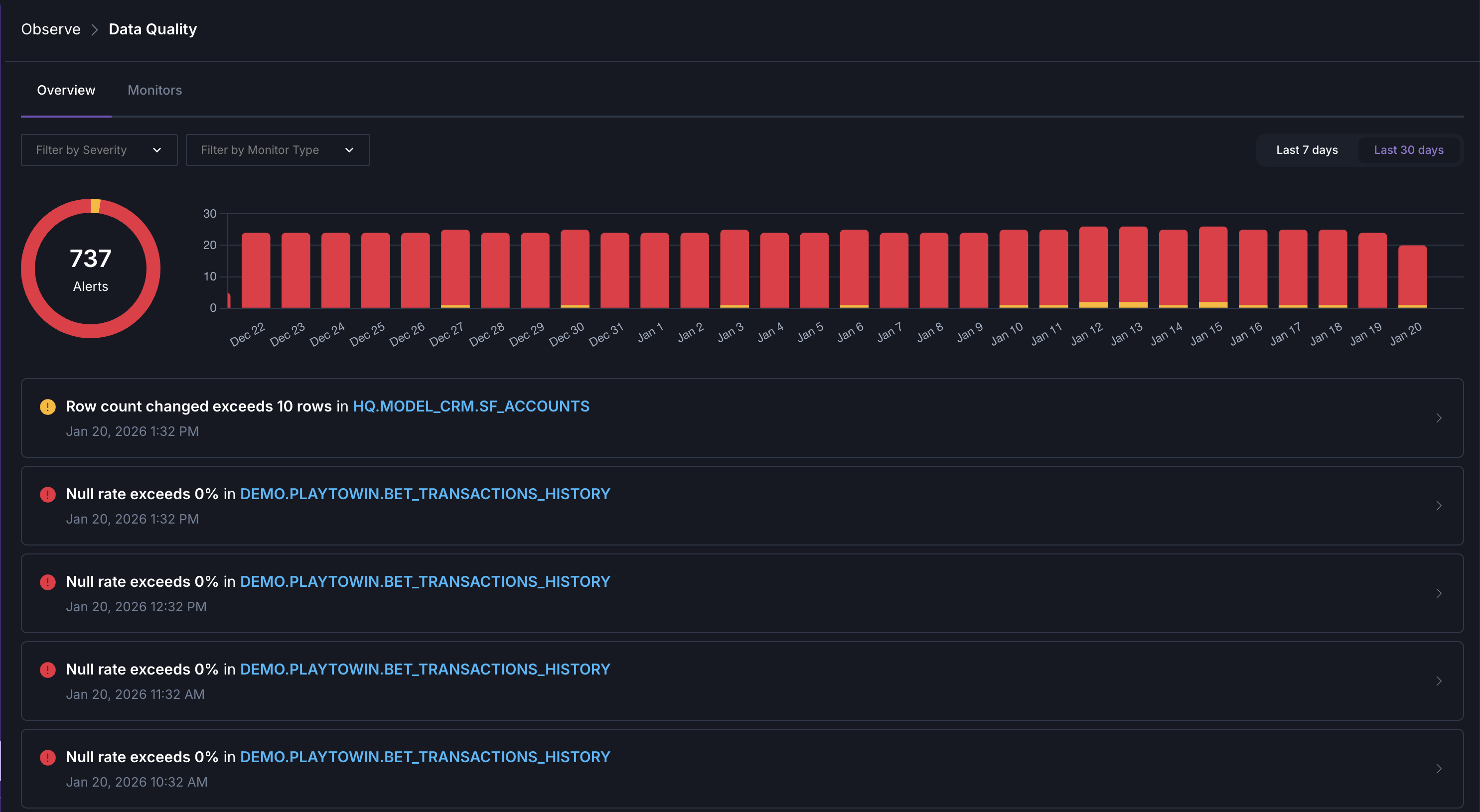
Manage triggered monitors
To see a high-level overview of your organization’s data quality, click Data Quality in the navigation. Here you can see a summary of triggered data quality monitors from the last week or month, grouped by severity and check type.
Click any triggered monitor to investigate it and see the underlying data that triggered the monitor’s conditions.