Orchestrate Pinecone operations with Apache Airflow
Pinecone is a proprietary vector database platform designed for handling large-scale vector based AI applications. The Pinecone Airflow provider offers modules to easily integrate Pinecone with Airflow.
In this tutorial you’ll use Airflow to create vector embeddings of series descriptions, create an index in your Pinecone project, ingest the vector embeddings into that index, and query Pinecone to get a suggestion for your next binge-watchable series based on your current mood.
Why use Airflow with Pinecone?
Integrating Pinecone with Airflow provides a robust solution for managing large-scale vector search workflows in your AI applications. Pinecone specializes in efficient vector storage and similarity search, which is essential for leveraging advanced models like language transformers or deep neural networks.
By combining Pinecone with Airflow, you can:
- Use Airflow’s data-driven scheduling to run operations in Pinecone based on upstream events in your data ecosystem, such as when a new model is trained or a new dataset is available.
- Run dynamic queries with dynamic task mapping, for example to parallelize vector ingestion or search operations to improve performance.
- Add Airflow features like retries and alerts to your Pinecone operations. Retries protect your MLOps pipelines from transient failures, and alerts notify you of events like task failures or missed service level agreements (SLAs).
Time to complete
This tutorial takes approximately 30 minutes to complete.
Assumed knowledge
To get the most out of this tutorial, make sure you have an understanding of:
- The basics of Pinecone. See Pinecone Introduction.
- The basics of vector embeddings. See Vector Embeddings for Developers: The Basics.
- Airflow fundamentals, such as writing DAGs and defining tasks. See Get started with Apache Airflow.
- Airflow decorators. See Introduction to the TaskFlow API and Airflow decorators.
- Airflow operators. See Operators 101.
- Airflow hooks. See Hooks 101.
Prerequisites
- The Astro CLI.
- A Pinecone account with an API key. You can use a free tier account for this tutorial.
- An OpenAI API key of at least tier 1 if you want to use OpenAI for vectorization. If you do not want to use OpenAI you can adapt the
create_embeddingsfunction at the start of the DAG to use a different vectorizer. Note that you will likely need to adjust theEMBEDDING_MODEL_DIMENSIONSparameter in the DAG if you use a different vectorizer.
The example code from this tutorial is also available on GitHub.
Step 1: Configure your Astro project
-
Create a new Astro project:
-
Add the following two lines to your
requirements.txtfile to install the Pinecone Airflow Provider and OpenAI Python client in your Astro project: -
Add the following environment variables to your Astro project
.envfile. These variables store the configuration for an Airflow connection to your Pinecone account and allow you to use the OpenAI API. Provide your own values for<your-pinecone-environment>(for examplegcp-starter),<your-pinecone-api-key>and<your-openai-api-key>:
Step 2: Add your data
The DAG in this tutorial runs a query on vectorized series descriptions, which were mostly retrieved from IMDB with added domain expert inputs.
-
In your Astro project
includedirectory, create a file calledseries_data.txt. -
Copy and paste the following text into the file:
Step 3: Create your DAG
-
In your Astro project
dagsfolder, create a file calledquery_series_vectors.py. -
Copy the following code into the file:
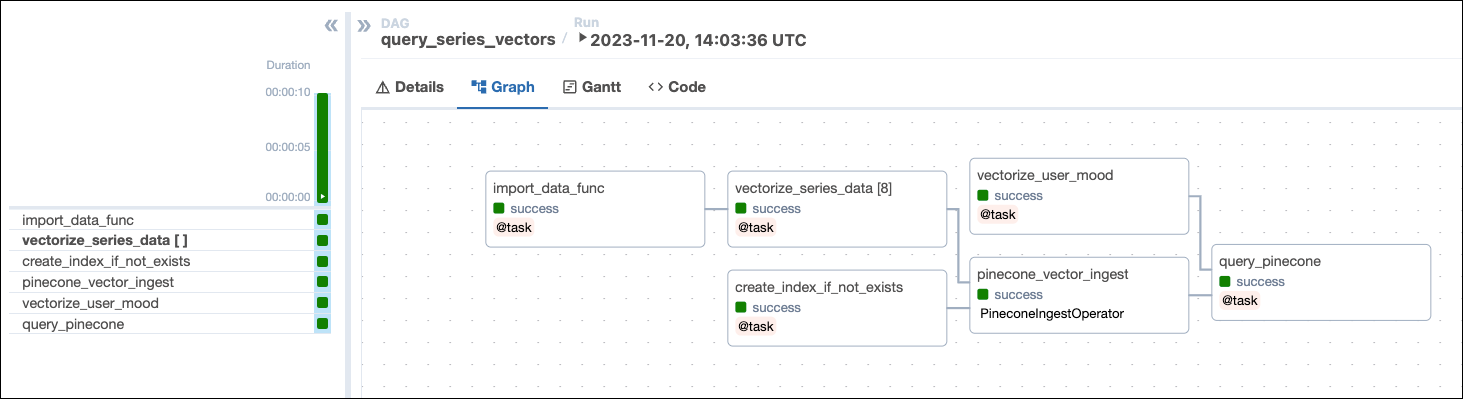
This DAG consists of six tasks to make a simple ML orchestration pipeline.
- The
import_data_functask defined with the@taskdecorator reads the data from theseries_data.txtfile and returns a list of dictionaries containing the series title, year, genre, and description. Note that the task will create a UUID for each series using thecreate_uuidfunction and add it to theidkey. Having a unique ID for each series is required for the Pinecone ingestion task. - The
vectorize_series_datatask is a dynamic task that creates one mapped task instance for each series in the list returned by theimport_data_functask. The task uses thecreate_embeddingsfunction to generate vector embeddings for each series’ description. Note that if you want to use a different vectorizer than OpenAI’stext-embedding-ada-002you can adjust this function to return your preferred vectors and set theEMBEDDING_MODEL_DIMENSIONSparameter in the DAG to the vector size of your model. - The
vectorize_user_moodtask calls thecreate_embeddingsfunction to generate vector embeddings for the mood the user can provide as an Airflow param. - The
create_index_if_not_existstask uses the PineconeHook to connect to your Pinecone instance and retrieve the current list of indexes in your Pinecone environment. If no index of the namePINECONE_INDEX_NAMEexists yet, the task will create it. Note that with a free tier Pinecone account you can only have one index. - The
pinecone_vector_ingesttask uses the PineconeIngestOperator to ingest the vectorized series data into the index created by thecreate_index_if_not_existstask. - The
query_pineconetask performs a vector search in Pinecone to get the series most closely matching the user-provided mood and prints the result to the task logs.
- The
Step 4: Run your DAG
-
Open your Astro project, then run
astro dev startto run Airflow locally. -
Open the Airflow UI at
localhost:8080, then run thequery_series_vectorsDAG by clicking the play button. Provide your input to the Airflow param forseries_mood.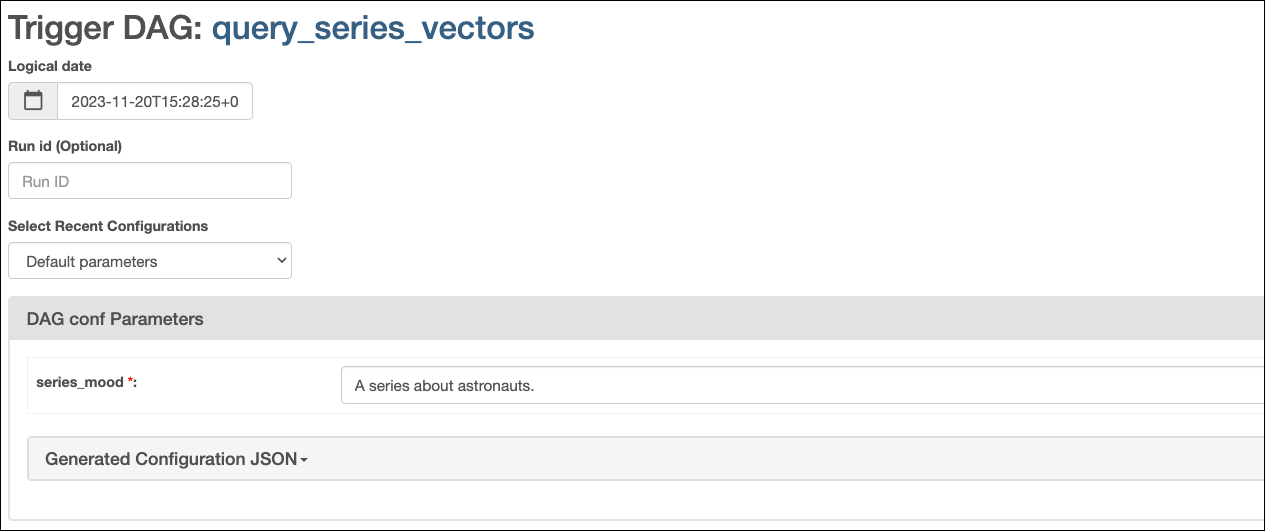
-
View your series suggestion in the task logs of the
query_pineconetask:
When watching For All Mankind, make sure to have a tab with Wikipedia open to compare the alternate timeline with ours and remember, flying spacecraft isn’t like driving a car. It doesn’t just go where you point it.
Conclusion
Congrats! You’ve successfully integrated Airflow and Pinecone! You can now use this tutorial as a starting point to build you own AI applications with Airflow and Pinecone.