Rerun Airflow DAGs and tasks
You can set when to run Airflow DAGs using a wide variety of scheduling options. Some uses cases where you might want tasks or DAGs to run outside of their regular schedule include:
- You want one or more tasks to automatically run again if they fail.
- You need to manually rerun a failed task for one or multiple DAG runs.
- You want to deploy a DAG with a start date of one year ago and trigger all DAG runs that would have been scheduled in the past year.
- You have a running DAG and realize you need it to process data for two months prior to the DAG’s start date.
In this guide, you’ll learn how to configure automatic retries, rerun tasks or DAGs, trigger historical DAG runs, and review the Airflow concepts of catchup and backfill.
Assumed knowledge
To get the most out of this guide, you should have an understanding of:
- DAG scheduling. See Schedule DAGs in Airflow
Automatically retry tasks
In Airflow, you can configure individual tasks to retry automatically in case of a failure. The default number of times a task will retry before failing permanently can be defined at the Airflow configuration level using the core config default_task_retries. You can set this configuration either in airflow.cfg or with the environment variable AIRFLOW__CORE__DEFAULT_TASK_RETRIES.
You can overwrite the default_task_retries of an Airflow environment at the task level by using the retries parameter.
The retry_delay parameter (default: timedelta(seconds=300)) defines the time spent between retries. You can set a maximum value for the retry delay in the core Airflow config, max_task_retry_delay (AIRFLOW__CORE__MAX_TASK_RETRY_DELAY), which, by default, is set at 24 hours. Or, for individual tasks, you can set the maximum retry delay with the parameter, max_retry_delay.
To progressively increase the wait time between retries until max_retry_delay is reached, set retry_exponential_backoff to True.
It is common practice to set the number of retries for all tasks in a DAG by using default_args and override it for specific tasks as needed. To override specific tasks, provide a different value to the task level retries parameter.
The DAG below contains 4 tasks that will always fail. Each of the tasks uses a different retry parameter configuration.
Automatically pause a failing DAG
You can configure Airflow to automatically pause a DAG after a certain number of failed DAG runs, preventing a failing DAG from continuing to run and potentially causing more issues.
To set the maximum number of consecutive failed DAG runs at for your all DAGs in your Airflow environment, set the core.max_consecutive_failed_dag_runs_per_dag config. For example, to automatically pause all your DAGs after they had 5 failed DAG runs in a row, set:
You can override this setting for a specific DAG by setting the max_consecutive_failed_dag_runs parameter in the DAG instantiation. For example, to pause a specific DAG after 3 failed DAG runs in a row, set:
Taskflow
Traditional
Caution
The
max_consecutive_failed_dag_runsconfig and DAG-level parameter is currently experimental and and might be subject to breaking changes in future releases.
Manually rerun tasks or DAGs
Rerunning tasks or full DAGs in Airflow is a common workflow.
To rerun a task in Airflow you clear the task status to update the max_tries and current task instance state values in the metastore. After the task reruns, the max_tries value updates to 0, and the current task instance state updates to None.
To clear the task status, go to your DAG in the Airflow UI, select the task instance you want to rerun and click the Clear Task Instance button.
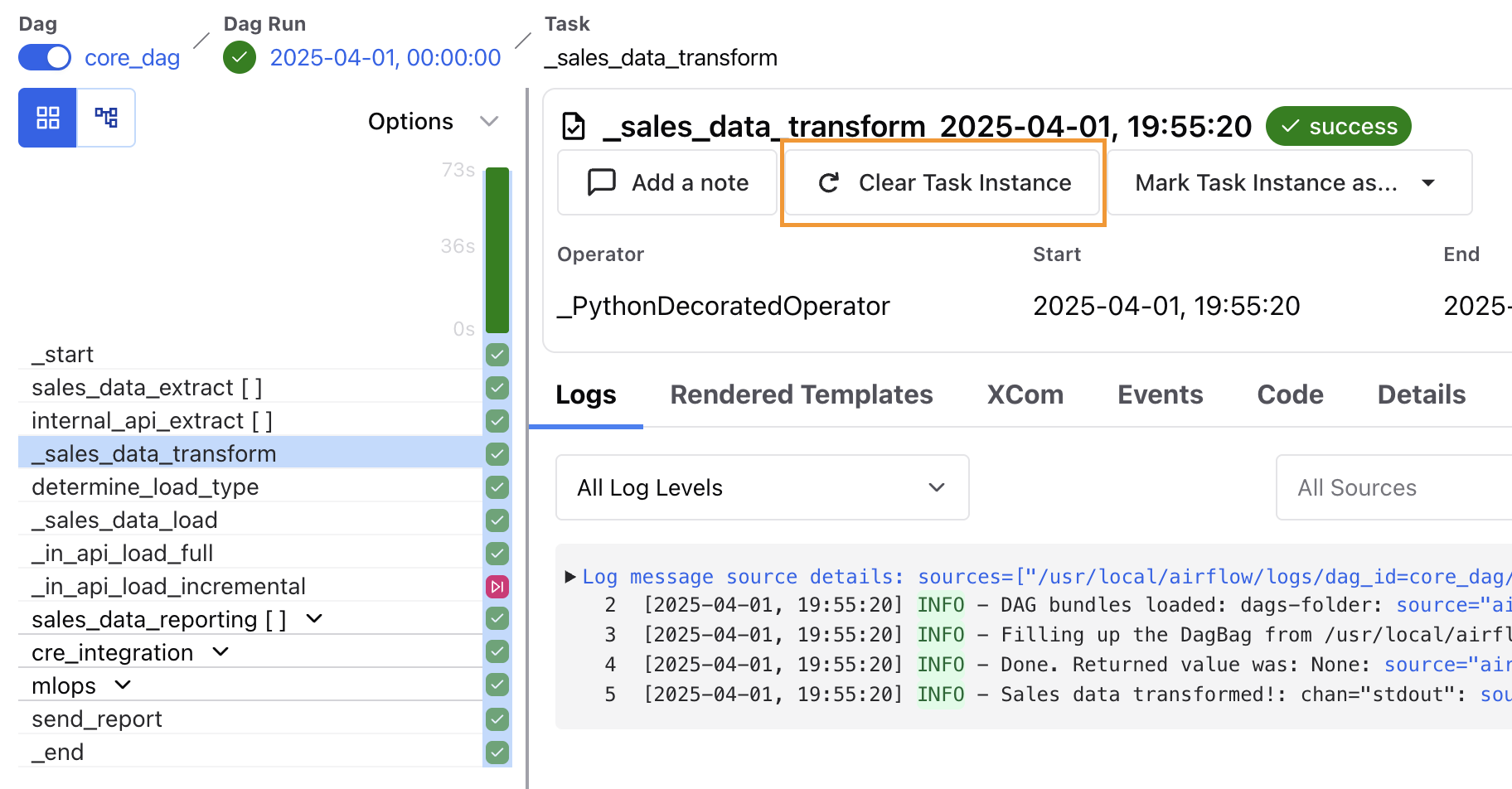
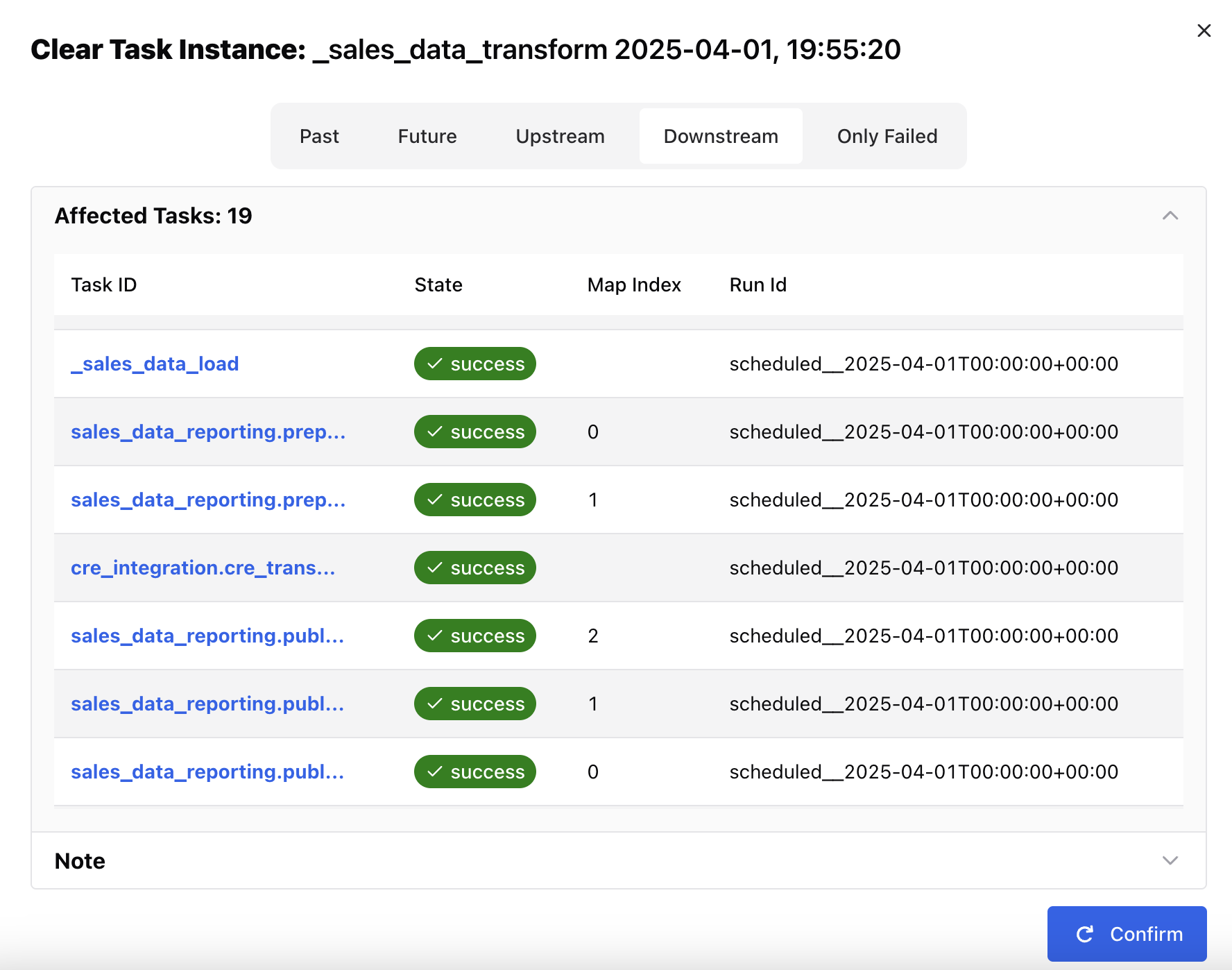
A popup window appears, giving you the following options to clear and rerun additional task instances related to the selected task:
- Past: Clears any instances of the task in DAG runs with a logical date before the selected task instance.
- Future: Clears any instances of the task in DAG runs with a logical date after the selected task instance.
- Upstream: Clears any tasks in the current DAG run which are upstream from the selected task instance.
- Downstream: Clears any tasks in the current DAG run which are downstream from the selected task instance.
- Only Failed: Clears only failed instances of any task instances selected based on the above options.
The window shows which task instances will be cleared with the current settings. Click Confirm and the task(s) will be cleared and rescheduled for another run.
You can also use the Airflow CLI or API to programmatically clear task instances.
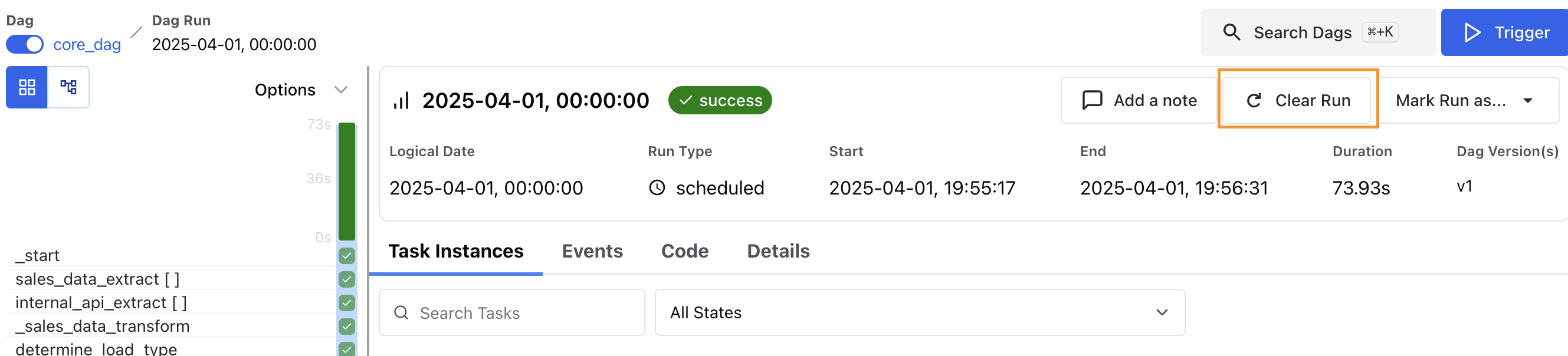
To clear a full DAG run, click on the DAG run, and then click Clear Run as shown in the following image.
Warning
Don’t clear or change task statuses directly in the Airflow metastore. This can cause unexpected behavior in Airflow.
Add notes to cleared tasks and DAGs
You can add notes to task instances and DAG runs in the Airflow UI. This feature is useful for tracking manual changes to task instances, such as reruns or task status changes. Astronomer recommends leaving a note on a task or DAG whenever you manually update a task instance through the Airflow UI.
To add a note to a task instance or DAG run:
- Go to your DAG in the Airflow UI.
- Select a task instance or DAG run.
- Click Add a note.
- Write a note and click Confirm.
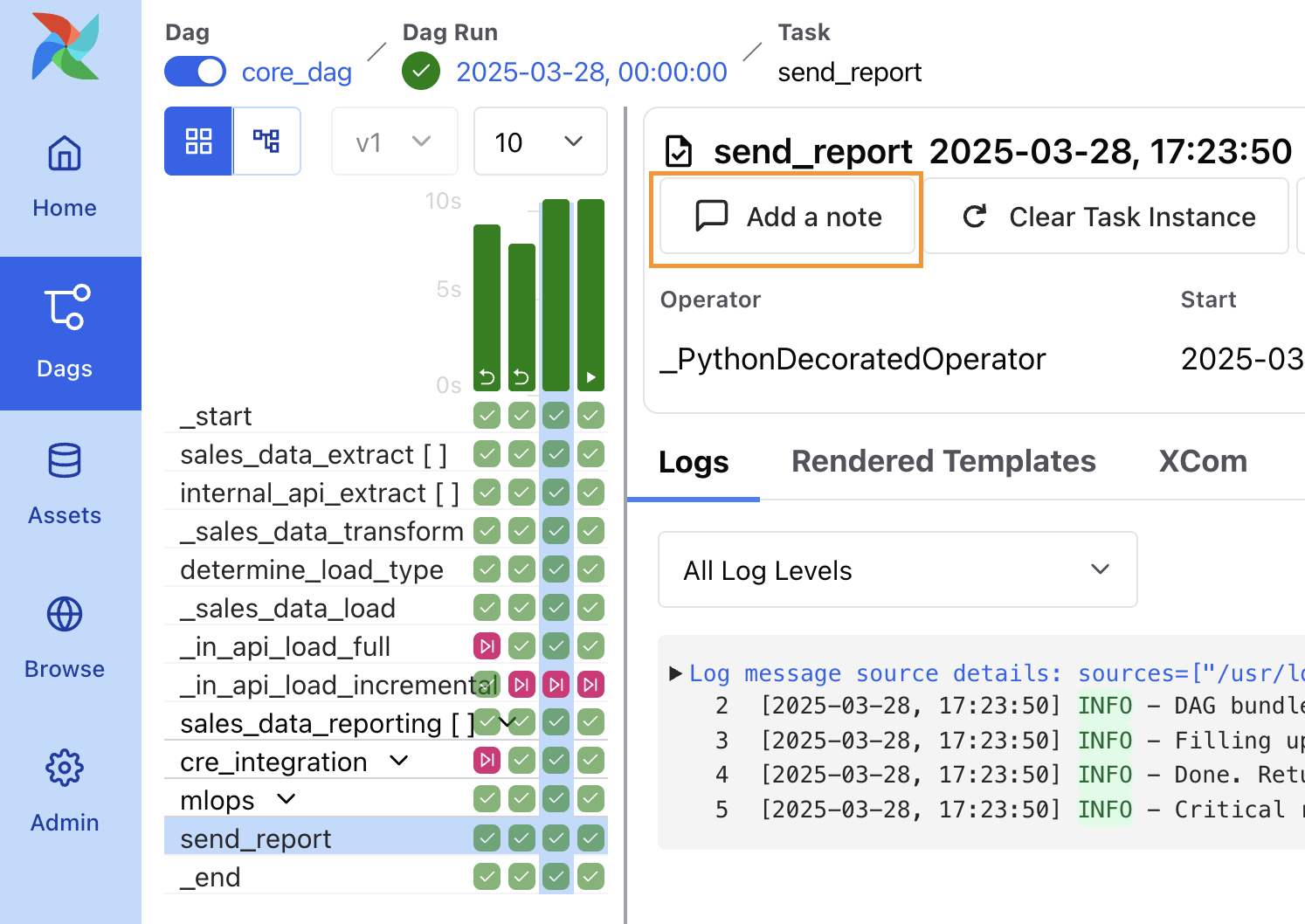
We recommend using this feature for tracking and maintaining visibility of manual changes made to task instances such as rerunning or changing the task status.
Catchup
You can use the built-in catchup DAG argument to process data for logical dates between the set start_date of a DAG and the current date.
When the catchup parameter for a DAG is set to True, at the time the DAG is turned on in Airflow, the scheduler starts a DAG run for every data interval that has not been run between the DAG’s start_date and the current data interval. For example, if your DAG is scheduled to run daily and has a start_date of 1/1/2025, and you deploy that DAG and turn it on 2/1/2025, Airflow will schedule and start all of the daily DAG runs for January. Catchup is also triggered when you turn a DAG off for a period and then turn it on again.
Catchup can be controlled by setting the parameter in your DAG’s arguments. By default, catchup is set to False. This example DAG has catchup turned on:
Catchup is a powerful feature, but it should be used with caution. For example, if you deploy a DAG that runs every 5 minutes with a start date of 1 year ago and set catchup to True, Airflow will schedule numerous DAG runs all at once. When using catchup, keep in mind what resources Airflow has available and how many DAG runs you can support at one time. To avoid overloading your scheduler or external systems, you can use the following parameters in conjunction with catchup:
max_active_runs: Set at the DAG level and limits the number of DAG runs that Airflow will execute for that particular DAG at any given time. For example, if you set this value to 3 and the DAG had 15 catchup runs to complete, they would be executed in 5 chunks of 3 runs.depends_on_past: Set at the task level or as adefault_argfor all tasks at the DAG level. When set toTrue, the task instance must wait for the same task in the most recent DAG run to be successful. This ensures sequential data loads and allows only one DAG run to be executed at a time in most cases.wait_for_downstream: Set at the DAG level and similar to a DAG-level implementation ofdepends_on_past. The entire DAG needs to run successfully for the next DAG run to start.
If you want to set catchup to True by default for all DAGs in your Airflow environment, for example for migration purposes, you can set the Airflow config AIRFLOW__SCHEDULER__CATCHUP_BY_DEFAULT to True.
If you want to deploy your DAG with catchup enabled but there are some tasks you don’t want to run during the catchup, you can use the LatestOnlyOperator in your DAG. This operator only runs during the DAG’s most recent scheduled interval. In every other DAG run it is ignored, along with any tasks downstream of it.
Backfill
Backfilling is the concept of running a DAG for a specified period in the past to re-process historical or missed data. Unlike catchup, which triggers missed DAG runs from the DAG’s start_date through the current data interval, backfill periods can be specified explicitly and can include periods prior to the DAG’s start_date.
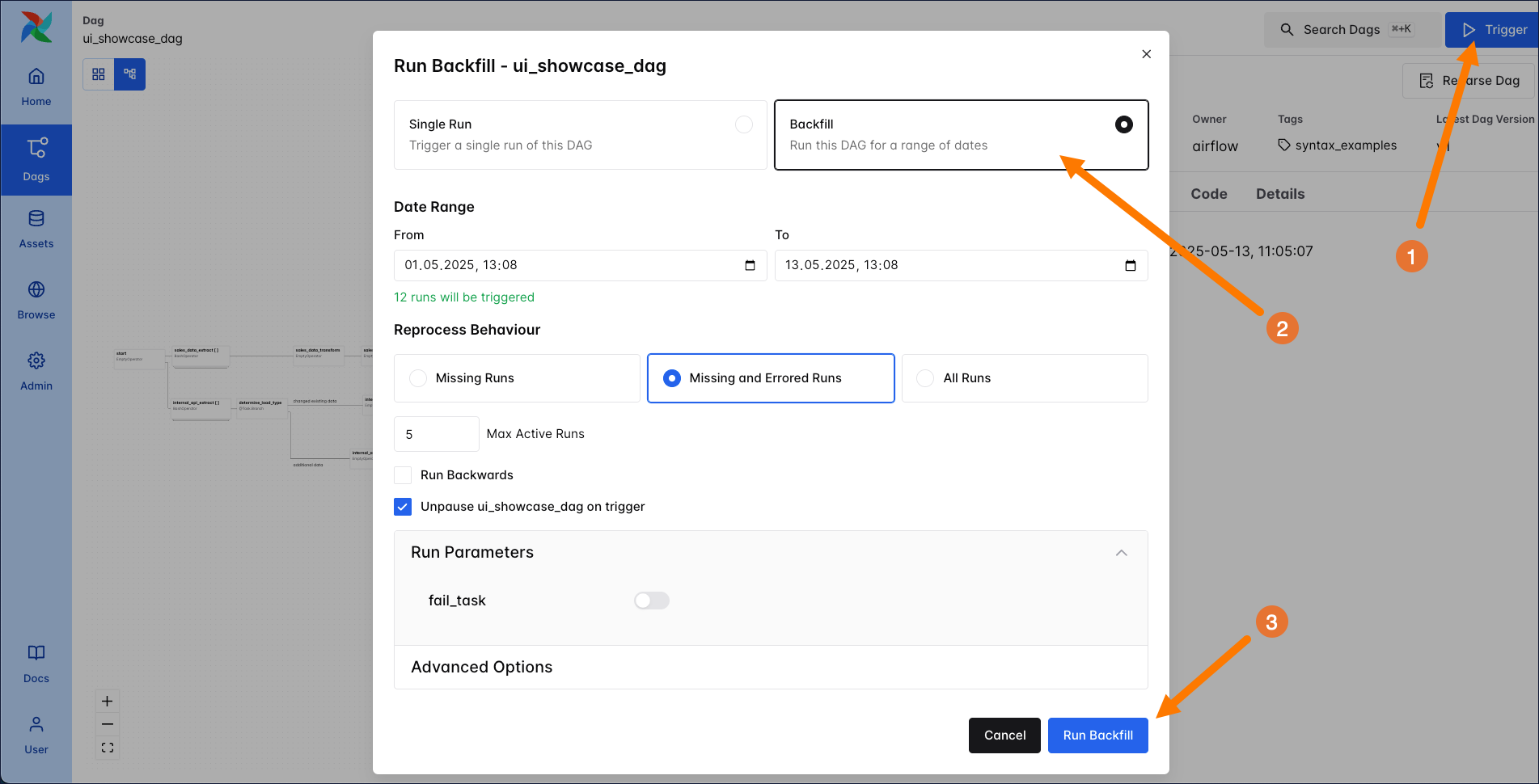
In Airflow 3, backfills are managed by the scheduler and can be triggered through the UI, API, or CLI. To run a backfill from the UI, click the blue Trigger button and select Backfill. Choose the date range you want to backfill for, and which runs you want to reprocess. You also have the option to select the number of max active runs for the backfill, whether you want to run backwards or forwards, specify run parameters and select one of three reprocessing behaviors:
- Missing Runs: Creates and runs only the DAG runs that do not already exist for the selected period.
- Missing and Errored Runs: Creates any missing runs and also re-runs any existing DAG runs that previously failed.
- All Runs: Clears and re-runs all existing DAG runs within the date range, in addition to creating any that are missing.
Execute the backfill by clicking on Run Backfill. The UI will tell you how many runs will be triggered and the backfill will use the latest DAG version that is available for your DAG.
Once the backfill has started, you can pause or cancel it at any time in the UI. Backfilled DAG runs are indicated in your grid by the u-turn arrow.
To see an example of backfilling using the CLI, see the Airflow docs. For information on how to backfill using the Airflow REST API see the Airflow REST API docs.
When using backfill, make sure to consider your available resources. If your backfill will trigger many DAG runs, and/or you have many other DAGs running at the same time, you should set a max active runs that will not overload your scheduler.