Configure NFS code deploys
Starting in Astronomer Software v0.25, you can use an external Network File System (NFS) Volume to deploy DAGs to an Airflow Deployment on Astronomer.
Unlike deploying DAGs via the Astro CLI, deploying DAGs to an NFS volume, such as Azure File Storage or Google Cloud Filestore, does not require rebuilding a Docker image and restarting your underlying Airflow service. When a DAG is added to an NFS volume, it automatically appears in the Airflow UI without requiring additional action or causing downtime.
Implementation Considerations
Consider the following before completing this setup:
- You can configure NFS volumes only to deploy DAGs. To push dependencies or other requirements to your Airflow Deployment, you'll need to update your
requirements.txtandpackages.txtfiles and deploy using the Astro CLI or CI/CD. For more information on pushing code to your Airflow environment, see Customize images. - If you configure an NFS volume for an Airflow Deployment, you can't use the Astro CLI or an Astronomer service account to deploy DAGs . These options are available only for Deployments configured with an image-based deploy mechanism.
- You can configure NFS volumes only for Airflow Deployments running Airflow 2.0+.
Enable NFS volume storage
NFS volume deploys must be explicitly enabled on Astronomer by a System Admin. To enable it, update your config.yaml file with the following values:
houston:
config:
deployments:
configureDagDeployment: true
nfsMountDagDeployment: true
Once you have saved the file, push the configuration change to your platform as described in Apply a config change. This process needs to be completed only once per Software installation.
Provision an NFS volume
For AWS and GCP, Astronomer recommends using the primary NFS volume solution provided by the cloud provider:
For instructions specific to Azure, see Create and mount an Azure file share.
For each NFS volume you provision for DAG deploys, you need to configure:
- A directory for DAGs.
- Read access for a user with GID
50000and UID50000. For an example setup of this, see Configuring Ip-based access control.
Add an NFS volume to a Deployment
Workspace editors can configure a new or existing Airflow Deployment to use a provisioned NFS volume for DAG deploys. From there, any member of your organization with write permissions to the NFS volume can deploy DAGs to the Deployment.
-
In the Software UI, create a new Airflow Deployment or open an existing one.
-
Go to the DAG Deployment section of the Deployment's Settings page.
-
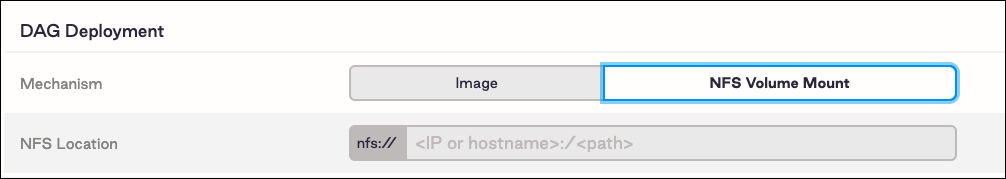
For your Mechanism, select NFS Volume Mount:
-
In the NFS Location field that appears, enter the location of your volume-based DAG directory as
<IP>:/<path>(for example:192.168.0.1:/path/to/your/dags). -
Save your changes.
Note: You can also use the Astro CLI to configure NFS volumes. To do so, specify the
--nfs-locationflag when runningastro deployment createorastro deployment update.
Create and mount an Azure file share
Create and mount an Azure file share to deploy DAGs from an NFS volume to an Astronomer installation on Azure. For additional information about this process, see Premium File Storage.
- Update your
config.yamlfile with the following values:
houston:
config:
deployments:
configureDagDeployment: true
nfsMountDagDeployment: true
-
Save the
config.yamlfile and push the configuration change to your platform. See Apply a config change. This process only needs to be completed once for each Software installation. -
In the Software UI, select a workspace and then the Deployment where you want to add the NFS volume to deploy DAGs.
-
In the DAG Deployment area, select the NFS Volume Mount tab.
-
In the NFS Location field, enter the Azure file share mount address in the following format:
nfs://<storage-account-name>.file.core.windows.net:/<storage-account-name>/<file-share-name>. -
Click Deploy Changes.
-
Add your DAGs to the NFS share.