Configure a Kubernetes namespace pool for Astronomer Software
Every Deployment within your Astronomer Software installation requires an individual Kubernetes namespace. You can configure a pool of pre-created namespaces to limit Astronomer Software access to these namespaces.
When you configure a pool of pre-created namespaces, Astronomer users are required to select a namespace from the pool whenever they create a new Deployment. Once the Deployment is created, its corresponding namespace is no longer available. If a Deployment is deleted, its namespace is returned to the pool and is available.
Benefits of pre-created namespaces
A pre-created namespace pool provides the following benefits:
- It limits the cluster-level permissions your organization needs to give to Astronomer Software. Astronomer Software requires permissions only for the individual namespaces you configure. Pre-created namespaces are recommended when your organization does not want to give Astronomer Software cluster-level permissions in a multi-tenant cluster.
- It can reduce costs and resource consumption. By default, Astronomer Software allows users to create Deployments until there is no more unreserved space in your cluster. If you use a pool, you can limit the number of active Deployments running at a time. This is especially important if you run other Elastic workloads on your Software cluster and need to prevent users from accidentally claiming your entire pool of unallocated resources.
When a user creates a new Deployment with the UI or CLI, Astronomer Software creates the necessary Airflow components and isolates them in a dedicated Kubernetes namespace. These Airflow components depend on Kubernetes resources, some of which are stored as secrets.
To protect your Deployment Kubernetes secrets, Astronomer uses dedicated service accounts for parts of your Deployment that need to interact with external components. To enable this ineteraction, Astronomer Software needs extensive cluster-level permissions for all namespaces running in a cluster.
In Kubernetes, you can grant service account permissions for an entire cluster, or you can grant permissions for existing namespaces. Astronomer uses cluster-level permissions because, by default, the amount of Deployments to manage is unknown. This level of permissions is appropriate if Astronomer Software is running in its own dedicated cluster, but can pose security risks when other applications are running in the same cluster.
For example, consider the Astronomer Commander service, which controls creating, updating, and deleting Deployments. By default, Commander has permissions to interact with secrets, roles, and service accounts for all applications in your cluster. The only way to mitigate this risk is by implementing pre-created namespaces.
Setup
To create a namespace pool you have the following options:
- Delegate the creation of each namespace, including roles and rolebindings, to the Astronomer helm chart. This option is suitable for most organizations.
- Create each namespace manually, including roles and rolebindings. This option is suitable if you need to further restrict Astronomer Kubernetes resource permissions. However, using this methodology to limit permissions can prevent Deployments from functioning as expected.
Prerequisites
Option 1: Use the Astronomer Helm chart
- Set the following configuration in your
config.yamlfile:
global:
features:
namespacePools:
# if this is false, everything in this section can be ignored. default should be false
enabled: true
namespaces:
# automatically creates namespace, role and rolebinding for commander if set to true
create: true
# this needs to be populated (something other than null) if global.features.namespacePools.enabled is true
names:
- <your-namespace-1>
- <your-namespace-2>
- Save the changes in your
config.yamlfile and update your Astronomer Software. See Apply a config change.
Based on the namespace names that you specified, Astronomer creates the necessary namespaces and Kubernetes resources. These resources have permissions scoped appropriately for most use-cases.
Once you apply your configuration, you should be able to create new Deployments using a namespace from your pre-created namespace pool. You should also be able to see the namespaces you specified inside your cluster resources.
Option 2: Manually create namespaces, roles, and rolebindings
Complete this setup if you want to further limit the namespace permissions that Astronomer provides by default.
Step 1: Configure namespaces
For every namespace you want to add to a pool, you must create a namespace, role, and rolebinding for Astronomer Software to access the namespace with. The rolebinding must be scoped to the astronomer-commander service account and the namespace you are creating.
-
In a new manifest file, add the following configuration. Replace
<your-namespace-name>with the namespace you want to add to the pool.apiVersion: v1
kind: Namespace
metadata:
name: <your-namespace-name>
---
apiVersion: rbac.authorization.k8s.io/v1
kind: Role
metadata:
name: deployment-commander-role
namespace: <your-namespace-name>
rules:
- apiGroups: ["*"]
resources: ["*"]
verbs: ["list", "watch"]
- apiGroups: [""]
resources: ["configmaps"]
verbs: ["create", "delete", "get", "list", "patch", "update", "watch"]
- apiGroups: ["keda.k8s.io"]
resources: ["scaledobjects"]
verbs: ["get", "create", "delete"]
- apiGroups: [""]
resources: ["secrets"]
verbs: ["create", "delete", "deletecollection", "get", "list", "patch", "update", "watc
- apiGroups: [""]
resources: ["namespaces"]
verbs: ["get", "list", "patch", "update", "watch"]
- apiGroups: [""]
resources: ["serviceaccounts"]
verbs: ["create", "delete", "get", "patch"]
- apiGroups: ["rbac.authorization.k8s.io"]
resources: ["roles"]
verbs: ["*"]
- apiGroups: [""]
resources: ["persistentvolumeclaims"]
verbs: ["create", "delete", "deletecollection", "get", "list", "update", "watch", "patc
- apiGroups: [""]
resources: ["pods"]
verbs: ["get", "list", "watch"]
- apiGroups: [""]
resources: ["endpoints"]
verbs: ["create", "delete", "get", "list", "update", "watch"]
- apiGroups: [""]
resources: ["limitranges"]
verbs: ["create", "delete", "get", "list", "watch", "patch"]
- apiGroups: [""]
resources: ["nodes"]
verbs: ["get", "list", "watch"]
- apiGroups: [""]
resources: ["nodes/proxy"]
verbs: ["get"]
- apiGroups: [""]
resources: ["persistentvolumes"]
verbs: ["create", "delete", "get", "list", "watch", "patch"]
- apiGroups: [""]
resources: ["replicationcontrollers"]
verbs: ["list", "watch"]
- apiGroups: [""]
resources: ["resourcequotas"]
verbs: ["create", "delete", "get", "list", "patch", "watch"]
- apiGroups: [""]
resources: ["services"]
verbs: ["create", "delete", "get", "list", "patch", "update", "watch"]
- apiGroups: ["apps"]
resources: ["statefulsets"]
verbs: ["create", "delete", "get", "list", "patch", "watch"]
- apiGroups: ["apps"]
resources: ["deployments"]
verbs: ["create", "delete", "get", "patch","update"]
- apiGroups: ["autoscaling"]
resources: ["horizontalpodautoscalers"]
verbs: ["list", "watch"]
- apiGroups: ["batch"]
resources: ["jobs"]
verbs: ["list", "watch", "create", "delete"]
- apiGroups: ["batch"]
resources: ["cronjobs"]
verbs: ["create", "delete", "get", "list", "patch", "watch"]
- apiGroups: ["extensions"]
resources: ["daemonsets", "replicasets"]
verbs: ["list", "watch"]
- apiGroups: ["extensions"]
resources: ["deployments"]
verbs: ["create", "delete", "get", "list", "patch", "update", "watch"]
- apiGroups: [""]
resources: ["events"]
verbs: ["create", "delete", "patch"]
- apiGroups: ["extensions"]
resources: ["ingresses"]
verbs: ["create", "delete", "get", "patch"]
- apiGroups: ["extensions"]
resources: ["ingresses/status"]
verbs: ["update"]
- apiGroups: ["networking.k8s.io"]
resources: ["ingresses"]
verbs: ["get", "create", "delete", "patch"]
- apiGroups: ["networking.k8s.io"]
resources: ["ingresses/status"]
verbs: ["update"]
- apiGroups: ["networking.k8s.io"]
resources: ["networkpolicies"]
verbs: ["create", "delete", "get", "patch"]
- apiGroups: ["rbac.authorization.k8s.io"]
resources: ["rolebindings"]
verbs: ["create", "delete", "get", "patch"]
- apiGroups: ["authentication.k8s.io"]
resources: ["tokenreviews"]
verbs: ["create", "delete"]
- apiGroups: ["authorization.k8s.io"]
resources: ["subjectaccessreviews"]
verbs: ["create", "delete"]
- apiGroups: ["kubed.appscode.com"]
resources: ["searchresults"]
verbs: ["get"]
- apiGroups: ["policy"]
resources: ["poddisruptionbudgets"]
verbs: ["create", "delete", "get"]
---
apiVersion: rbac.authorization.k8s.io/v1
kind: RoleBinding
metadata:
name: deployment-commander-rolebinding
namespace: <your-namespace-name> # Should be namespace you are granting access to
roleRef:
apiGroup: rbac.authorization.k8s.io
kind: Role
name: deployment-commander-role # Should match name of Role
subjects:
- namespace: astronomer # Should match namespace where SA lives
kind: ServiceAccount
name: astronomer-commander # Should match service account name, above -
Save this file and name it
commander.yaml. -
In the Kubernetes cluster hosting Astronomer Software, run
kubectl apply -f commander.yaml. -
Optional. Repeat steps 1-3 to add more namespaces to your pool.
Step 2: Configure a namespace pool in Astronomer
-
Set the following values in your
config.yamlfile, making sure to specify all of the namespaces you created in thenamespaces.namesobject:global:
features:
namespacePools:
# if this is false, everything in this section can be ignored. default should be false
enabled: true
namespaces:
# automatically creates namespace, role and rolebinding for commander if set to true
create: false
# this needs to be populated (something other than null) if global.features.namespacePools.enabled is true
# add the namespace names that were created in the previous setp
names:
- <your-namespace-1>
- <your-namespace-2> -
Save the changes in your
config.yamland update Astronomer Software. See Apply a config change.
Creating Deployments in pre-created namespaces
After enabling the pre-created namespace pool, the namespaces you registered now appear as options when you create a new Deployment with the Software UI.
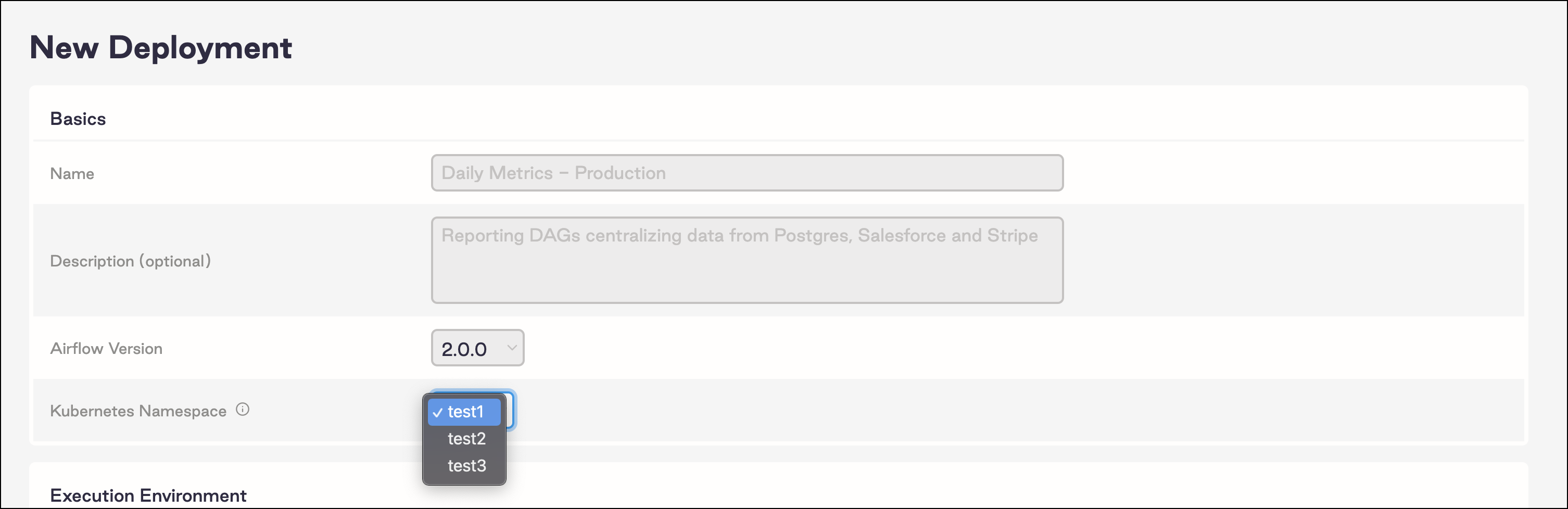
When you create Deployments with the CLI, you are prompted to select one of the available namespaces for your new Deployment.
If no namespaces are available, an error message appears when you create new Deployments in the Software UI and CLI. Delete the Deployment associated with the namespace to return the namespace to the pool.
Advanced settings
If your namespace configurations require more granularity, use the following settings in your config.yaml file.
Mixing global and advanced settings might result in unexpected behavior. If you use the standard settings, Astronomer recommends that you set global.features.namespacePools.enabled to false.
| Setting | Description |
|---|---|
global.manualNamespaceNamesEnabled | Expands the Fluentd rule to look for Deployment component logs in all namespaces |
global.clusterRoles | When set to false, Astronomer does not create a cluster role for Commander |
astronomer.houston.config.deployments.manualNamespaceNames | When set to true, a dropdown field is added to the Software UI’s Deployment settings for namespace selection |
astronomer.houston.config.deployments.preCreatedNamespaces | List of namespaces that were manually created for the namespace pool |
astronomer.commander.env | Inject an environment variable for Commander that prevents namespaces from being created when a new Deployment is triggered. The values specified here must be astronomer.commander.env.name: "COMMANDER_MANUAL_NAMESPACE_NAMES" and astronomer.commander.env.value= true. |
When using these settings, Astronomer recommends enabling hard deletion for Deployments.
In the following example config.yaml file, these settings are configured so that you don't configure namespace pools at a global level:
global:
# Make fluentd gather logs from all available namespaces
manualNamespaceNamesEnabled: true
clusterRoles: false
astronomer:
houston:
config:
deployments:
# Enable manual namespace names
manualNamespaceNames: true
# Pre-created namespace names
preCreatedNamespaces:
- name: <namespace-name-1>
- name: <namespace-name-2>
- name: <namespace-name-x>
# Allows users to immediately reuse a pre-created namespace by hard deleting the associated Deployment
# If set to false, you'll need to wait until a cron job runs before the Deployment record is deleted and the namespace is added back to the pool
hardDeleteDeployment: true
commander:
env:
- name: "COMMANDER_MANUAL_NAMESPACE_NAMES"
value: true
Troubleshooting
My Deployment is in an unknown state
If a Deployment isn't active, check the Commander pods to confirm the Deployment commands have successfully executed. When using a pre-created namespace pool with scoped roles, it’s possible that the astronomer-commander service account doesn't have the permissions necessary to perform a required action. When Commander is successful, the following notification appears:
time="2021-07-21T16:30:23Z" level=info msg="releaseName <release-name>, chart astronomer-ee/airflow, chartVersion 0.20.0, namespace <your-namespace-name>" function=InstallRelease package=helm
time="2021-07-21T16:30:23Z" level=info msg="CHART PATH: /home/commander/.cache/helm/repository/airflow- 0.20.0.tgz\n" function=InstallRelease package=helm
When Commander is unsuccessful, messages similar to the following appear:
time="2022-02-17T22:52:40Z" level=error msg="serviceaccounts is forbidden: User \"system:serviceaccount:astronomer:astronomer-commander\" cannot create resource \"serviceaccounts\" in API group \"\" in the namespace <your-namespace>" function=InstallDeployment package=kubernetes
This error shows that the service accounts couldn't be created in the pre-created namespaces and the roles need to be updated.
My namespace is not returning to the pool
If you're not using hard deletion, it can take several days for pre-created namespaces to become available after the associated Deployment is deleted. To enable hard deletes, see Delete a Deployment.