Note: This webinar was recorded in April 2021 and many exciting features have been added to Airflow and Astro since then. We recommend you also check out our in-depth guide on how to Use the KubernetesPodOperator. Astronomer customers can learn more about the KubernetesExecutor and the KubernetesPodOperator on Astro in our documentation.
Topics that will be discussed:
- Kubernetes Executor
- Kubernetes Pod Operator
- KEDA Autoscaler
Kubernetes Executor
- Each Airflow task is launched as a pod
- Workers scale to zero
- Expose Kubernetes API to the data engineer so they can have more control over the resources of each task
Old Architecture
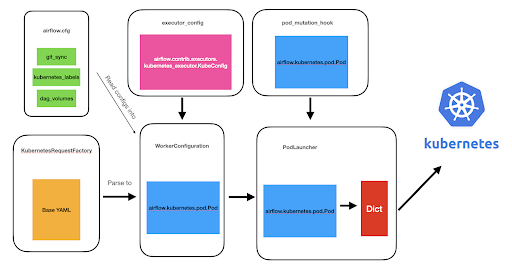
- Attempted to abstract Kubernetes API for “simplicity”
- Result: Lots of PRs to expose Kubernetes, lots of code to maintain, lost of steps before a pod is launched
- Goal: Offer flexibility of the Kubernetes API and reduce Airflow’s code footprint
New Architecture
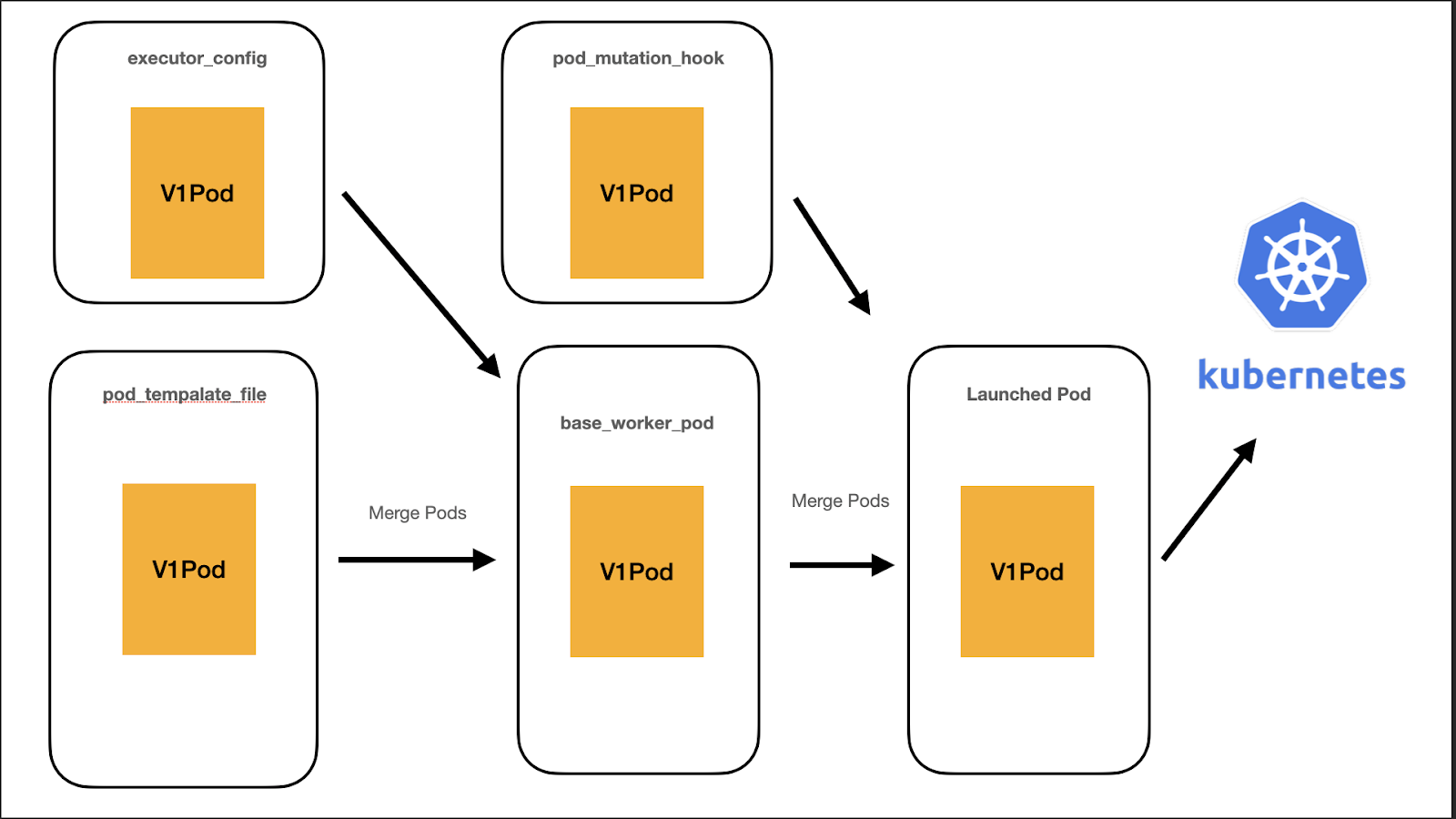
- Every step along the way, users have access to the Kubernetes models.V1Pod API
- Merging steps is much easier, faster, and stable.
- Removed 4k lines of code(!)
pod_template_file
- Infrastructure engineers can now define default pod layouts in yaml or json files
- Can define default
pod_template_filein theairflow.cfg
apiVersion: v1
kind: Pod
metadata:
name: dummy-name
spec:
containers:
- env:
- name: AIRFLOW__CORE__EXECUTOR
value: LocalExecutor
# Hard Coded Airflow Envs
- name: AIRFLOW__CORE__FERNET_KEY
valueFrom:
secretKeyRef:
name: RELEASE-NAME-fernet-key
key: fernet-key
- name: AIRFLOW__CORE__SQL_ALCHEMY_CONN
….
# Extra env
image: apache/airflow:2.0.0
imagePullPolicy: IfNotPresent
name: base
ports: []
volumeMounts:
- mountPath: "/opt/airflow/logs"
name: airflow-logs
- name: config
mountPath: "/opt/airflow/airflow.cfg"
subPath: airflow.cfg
readOnly: true
hostNetwork: false
restartPolicy: Never
securityContext:
runAsUser: 50000
fsGroup: 0
serviceAccountName: 'RELEASE-NAME-worker'
volumes:executor_config
- New “pod_override” object accepts a k8s.V1Pod instead of a dictionary.
- Can now use official Kubernetes API reference for building spec
- Add side-cars, secrets, affinities, etc.
volume_task = PythonOperator(
task_id="task_with_volume",
python_callable=test_volume_mount,
executor_config={
"pod_override": k8s.V1Pod(
spec=k8s.V1PodSpec(
containers=[
k8s.V1Container(
name="base",
volume_mounts=[
k8s.V1VolumeMount(
mount_path="/foo/",
name="test-volume"
)
],
)
],
volumes=[
k8s.V1Volume(
name="test-volume",
host_path=k8s.V1HostPathVolumeSource(path="/tmp/"),
)
],
)
),
},
)You can even point to a custom pod_template_file and then add overrides on top of it!
task_with_template = PythonOperator(
task_id="task_with_template",
python_callable=print_stuff,
executor_config={
"pod_template_file": os.path.join(
AIRFLOW_HOME, "pod_templates/basic_template.yaml"
),
"pod_override": k8s.V1Pod(
metadata=k8s.V1ObjectMeta(labels={"release": "stable"})
),
},
)KubernetesPodOperator
KubernetesPodOperator (KPO) is now in the cncf.kubernetes Provider. Visit the KubernetesPodOperator page of the Astronomer Registry to learn more.
- KPO is no longer bound to an Airflow version
- You can get upgrades and bug fixes more often without requiring an Airflow upgrade
- Backport providers for upgrading to 2.0
KPO Now Directly uses Kubernetes API
volume = k8s.V1Volume(
name='test-volume',
persistent_volume_claim=k8s.V1PersistentVolumeClaimVolumeSource(claim_name='test-volume'),
)
volume_mounts = [
k8s.V1VolumeMount(mount_path='/etc/foo', name='test-volume', sub_path=None, read_only=True)
]
env_vars = [k8s.V1EnvVar(name='key1', value='value1'), k8s.V1EnvVar(name='key2', value='value2')]
k = KubernetesPodOperator(
task_id="task" + self.get_current_task_name(),
in_cluster=False,
volume_mounts = volume_mounts,
volumes=[volume],
env=env_vars,
do_xcom_push=True,
)KPO now also allows templates
template_path = '/airflow/dags/basic_pod.yaml'
pod_spec = k8s.V1Pod(
metadata=k8s.V1ObjectMeta(
labels={"foo": "bar", "fizz": "buzz"},
),
spec=k8s.V1PodSpec(
containers=[
k8s.V1Container(
name="base",
env=[k8s.V1EnvVar(name="env_name", value="value")],
)
]
),
)
env_vars = [k8s.V1EnvVar(name='key1', value='value1'), k8s.V1EnvVar(name='key2', value='value2')]
k = KubernetesPodOperator(
task_id="task" + self.get_current_task_name(),
in_cluster=False,
pod_template_file=template_path,
full_pod_spec=pod_spec,
env=env_vars,
do_xcom_push=True,
)KEDA Autoscaler
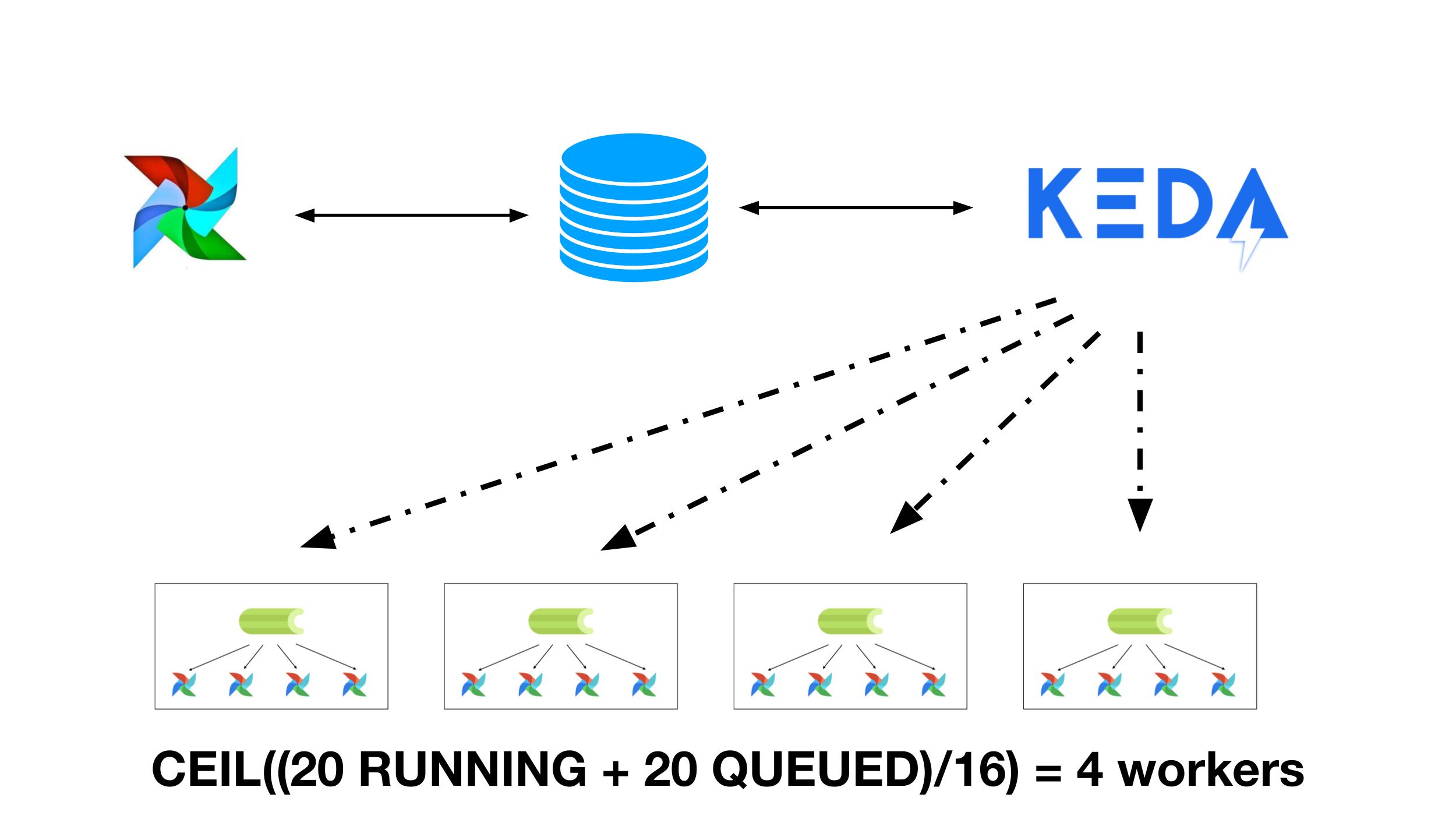
With KubernetesExecutor for every single task you launch, Airflow speaks to the Kubernetes API and launches a pod for that task and runs that pod to completion. This works fantastic for small to medium scale use cases. For really large scale cases, with thousands of tasks at a time, the Kubernetes Executor can become unwieldy.
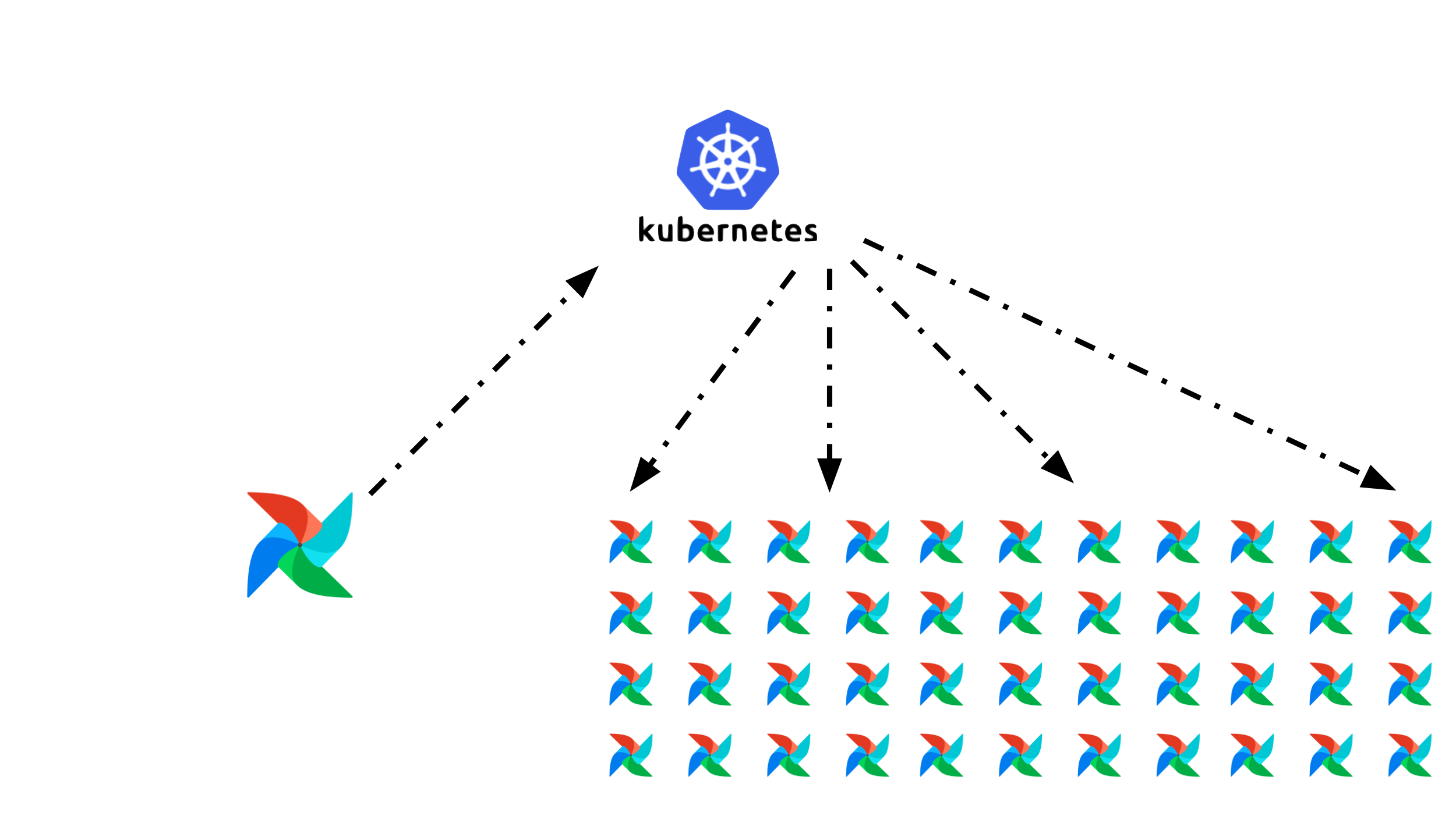
The KEDA Autoscaler allows you to create custom autoscalers. At Astronomer we created a PostgreSQL autoscaler and donated it back to the KEDA project.
The easiest way to get started with Apache Airflow 2.0 is by using the Astronomer CLI. To make it easy you can get up and running with Airflow by following our Quickstart Guide.


